A Burning Landscape: Mapping the Current Wildfires in Northern California
Related Articles: A Burning Landscape: Mapping the Current Wildfires in Northern California
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Burning Landscape: Mapping the Current Wildfires in Northern California. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Burning Landscape: Mapping the Current Wildfires in Northern California

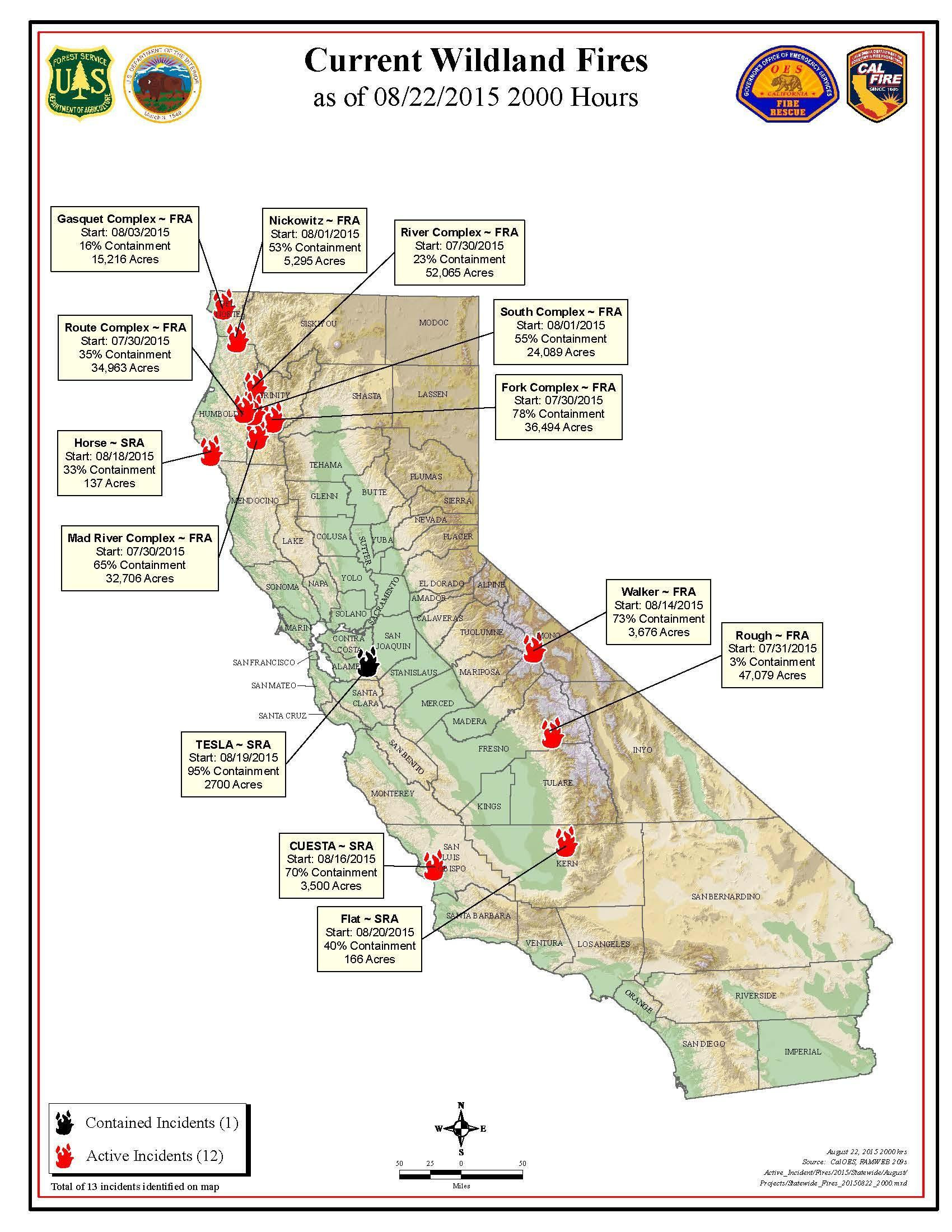
Northern California, a region known for its diverse ecosystems, breathtaking scenery, and vibrant communities, is also grappling with the escalating threat of wildfires. The 2023 fire season has once again underscored the vulnerability of this landscape, with numerous blazes tearing through forests, grasslands, and populated areas, leaving behind a trail of destruction and displacement. Understanding the current wildfire situation requires a comprehensive approach, encompassing mapping tools, real-time data analysis, and a nuanced understanding of the factors driving these events.
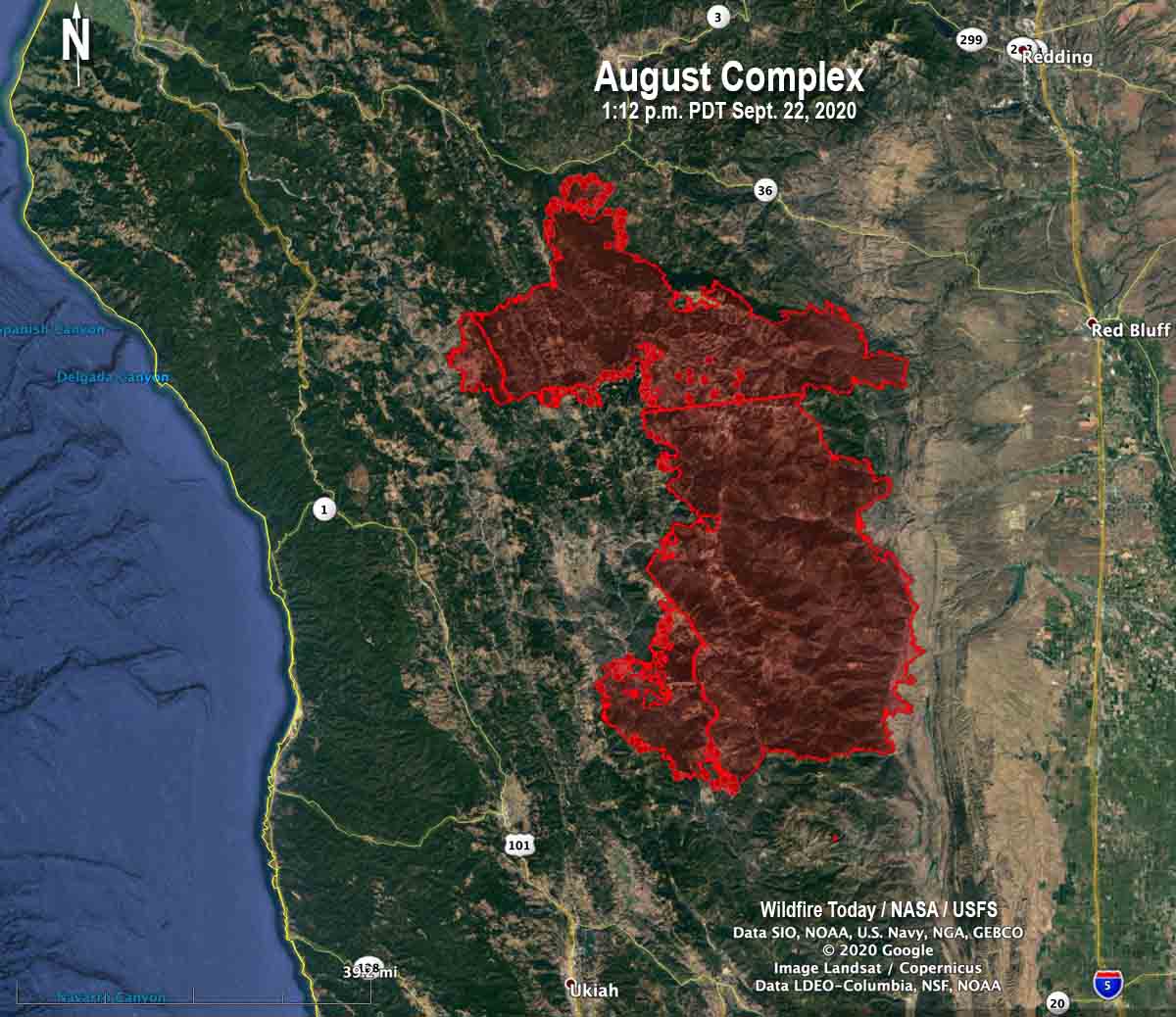
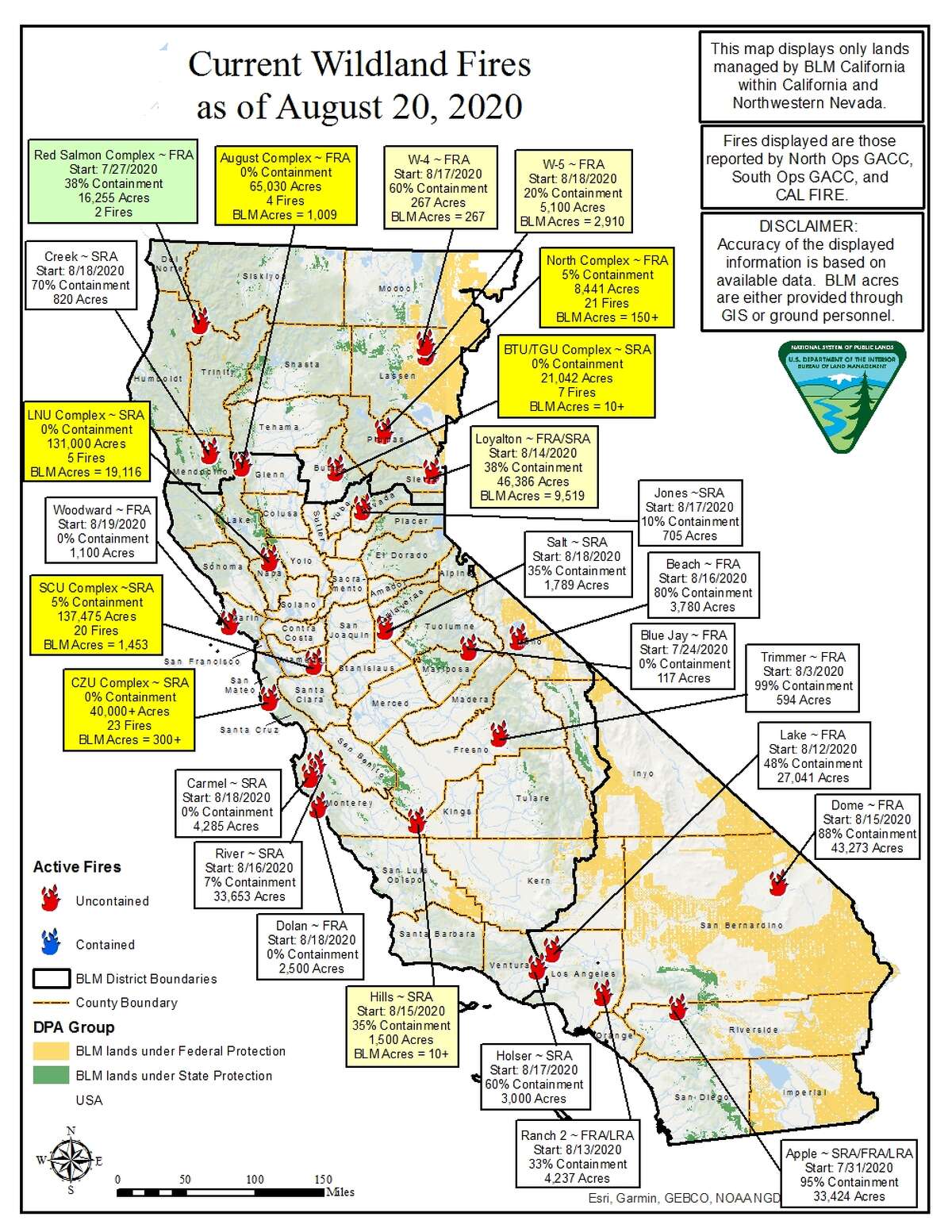
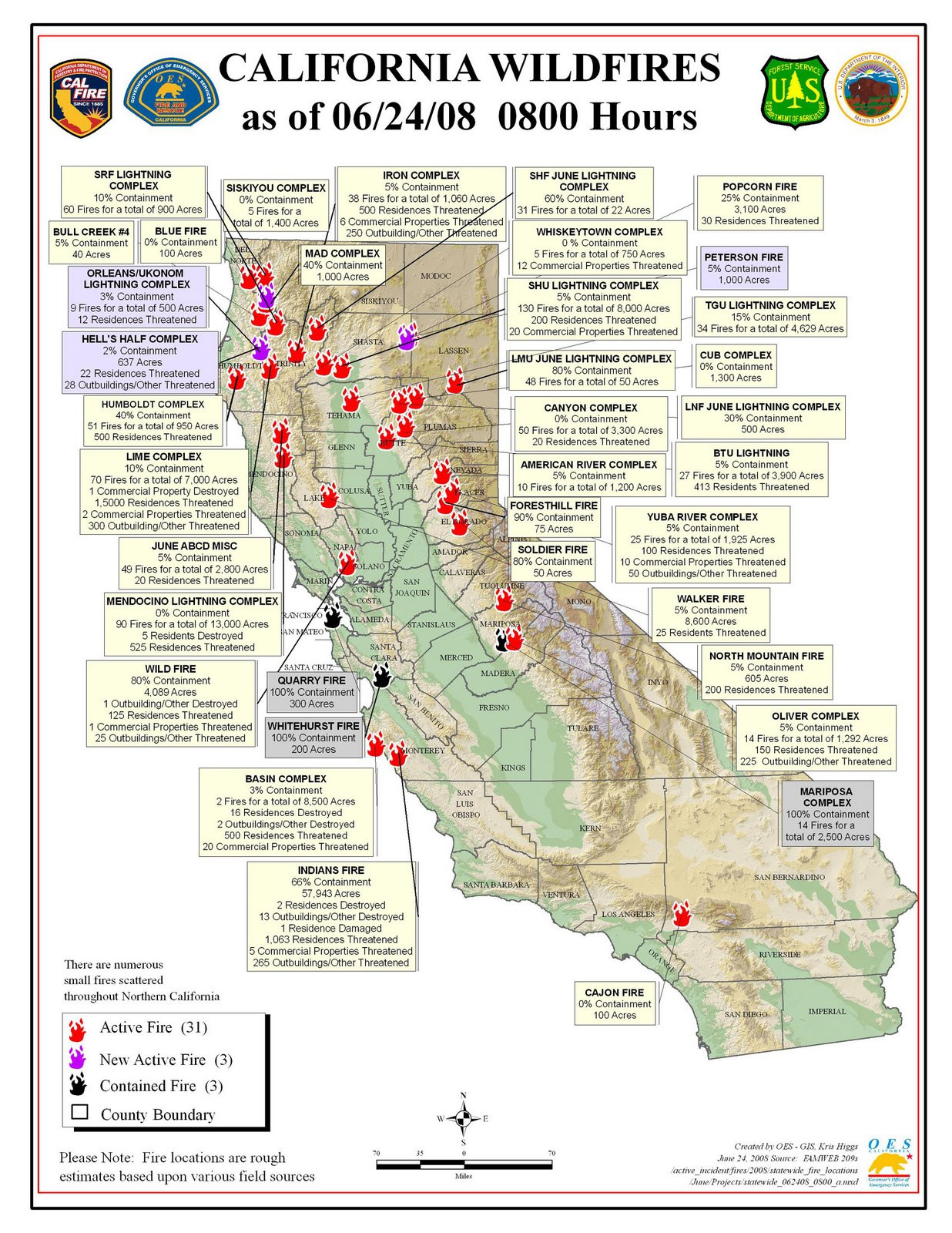
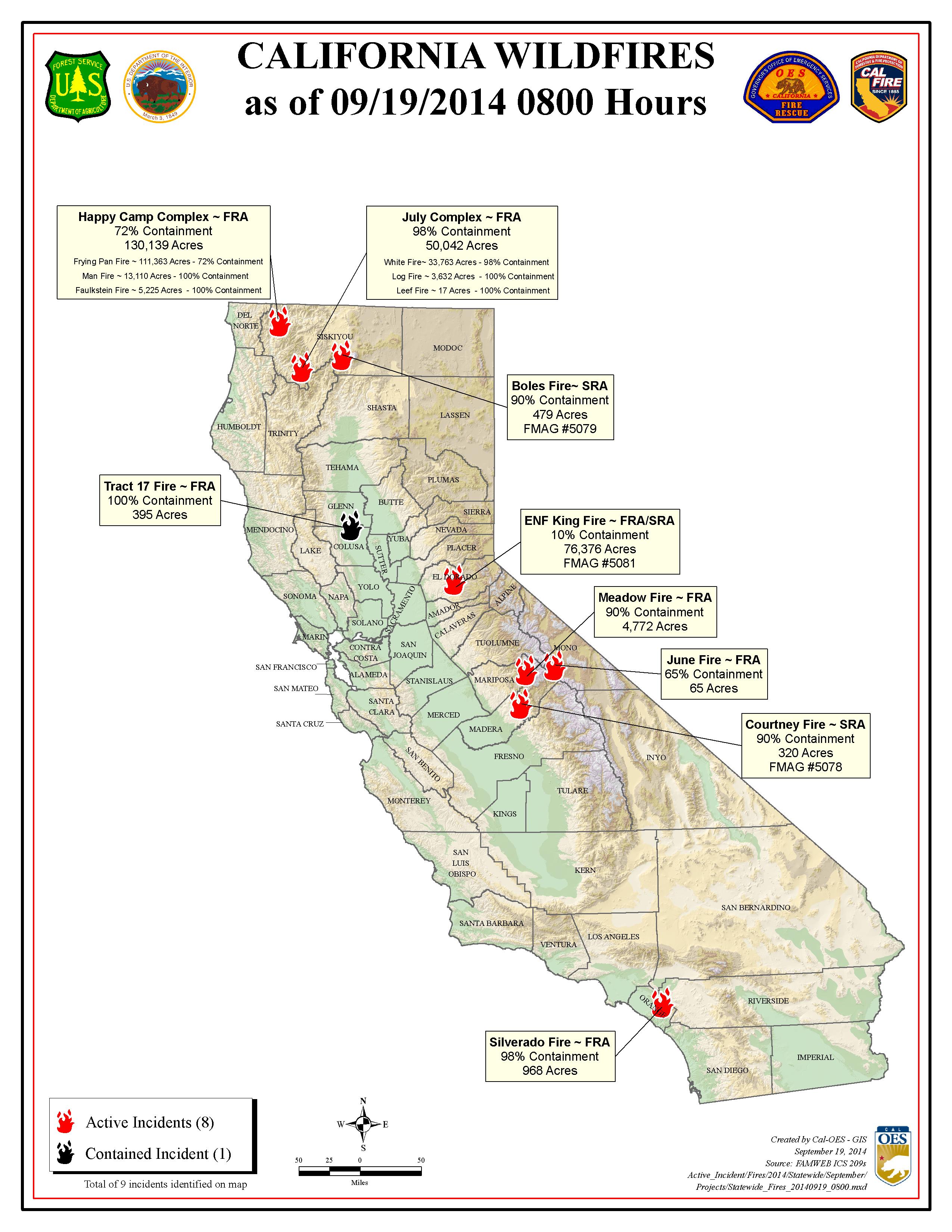
Mapping the Flames: Visualization Tools and Data Analysis
The ability to visualize the spread of wildfires in real-time is crucial for effective response and mitigation efforts. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) play a vital role in this process, providing interactive maps that display active fires, fire perimeters, and areas at risk. These maps are generated using data from various sources, including:
- Satellite Imagery: Sensors on satellites capture high-resolution images of the Earth’s surface, allowing for the detection of active fires and the estimation of fire intensity.
- Ground-Based Sensors: Networks of weather stations and fire lookout towers provide real-time data on wind speed, temperature, and humidity, factors that influence fire behavior.
- Aerial Reconnaissance: Aircraft equipped with infrared cameras and other specialized sensors fly over fire zones to provide detailed information on fire spread, smoke plumes, and potential threats to infrastructure.
These data are then integrated into GIS platforms, creating dynamic maps that allow fire managers, emergency responders, and the public to track the evolution of wildfires. The information gleaned from these maps is vital for:
- Resource Allocation: Fire crews and equipment are strategically deployed based on the location and intensity of fires, ensuring efficient and effective response.
- Evacuation Orders: Real-time data on fire spread helps authorities issue timely evacuation orders, minimizing risk to human life.
- Public Awareness: Interactive maps provide the public with accessible and up-to-date information about fire locations, allowing residents to make informed decisions about their safety.
Understanding the Drivers: Climate Change and Human Influence
The frequency and intensity of wildfires in Northern California are inextricably linked to broader environmental changes, particularly climate change. Rising temperatures, prolonged droughts, and changes in vegetation patterns have created conditions conducive to fire ignition and spread.
- Increased Temperatures: Higher temperatures dry out vegetation, making it more susceptible to ignition and increasing the intensity of fires.
- Drought Conditions: Prolonged periods of drought lead to dry fuels, exacerbating fire risk and making it difficult for firefighters to control blazes.
- Changes in Vegetation: The spread of invasive species and the decline of native tree species can alter forest structure, creating conditions that promote fire spread.
Human activity also plays a significant role in wildfire ignition. Unintentional fires caused by equipment malfunctions, campfires left unattended, and discarded cigarettes are common causes. In addition, the expansion of urban areas into wildland-urban interface zones increases the risk of fire exposure and complicates firefighting efforts.
Addressing the Challenges: Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies
Managing the wildfire threat in Northern California requires a multi-faceted approach that encompasses prevention, preparedness, and adaptation.
- Prevention: This involves proactive measures to reduce the risk of fire ignition, such as controlled burns to remove excess fuel, vegetation management to create defensible spaces around homes, and public education campaigns promoting fire safety practices.
- Preparedness: This includes developing comprehensive plans for fire response, ensuring adequate resources are available, and training firefighters and emergency personnel to respond effectively to wildfires.
- Adaptation: This involves adjusting to the changing wildfire landscape by implementing strategies such as building fire-resistant structures, establishing community evacuation plans, and promoting community resilience in the face of wildfire threats.
FAQs: Addressing Public Concerns
Q: How can I stay informed about current wildfire activity?
A: Reliable information on wildfire activity can be accessed through official sources such as Cal Fire, the National Interagency Fire Center (NIFC), and local news outlets. These sources provide real-time updates on fire locations, containment status, and evacuation orders.
Q: What are the health risks associated with wildfire smoke?
A: Wildfire smoke contains harmful pollutants that can cause respiratory problems, cardiovascular issues, and eye irritation. Individuals with pre-existing health conditions are particularly vulnerable. It is essential to stay indoors when smoke levels are high, use air purifiers, and follow public health recommendations.
Q: What can I do to protect my property from wildfires?
A: Creating a defensible space around your home by clearing vegetation, pruning trees, and removing flammable materials is crucial. You should also ensure that your home has fire-resistant features such as fire-resistant roofing and landscaping.
Tips: Embracing Community Resilience
- Participate in community wildfire preparedness meetings. This allows you to learn about local evacuation plans, fire safety practices, and community resources.
- Develop a family evacuation plan. This should include designated meeting points and communication strategies.
- Check on vulnerable neighbors. Ensure that elderly individuals, people with disabilities, and families with young children have access to support and resources during wildfire events.
Conclusion: A Long-Term Perspective
The current wildfire situation in Northern California underscores the urgent need for proactive measures to address the interconnected challenges of climate change, human influence, and the changing landscape. By embracing a collaborative approach that prioritizes prevention, preparedness, and adaptation, communities can build resilience and navigate the challenges of a fire-prone future. The ongoing efforts to map and understand these fires serve as a vital tool in this endeavor, providing crucial information for effective response, informed decision-making, and ultimately, safeguarding the lives and livelihoods of those living in this beautiful and vulnerable region.

![]()

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Burning Landscape: Mapping the Current Wildfires in Northern California. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
