A Complex Tapestry: Understanding the Geopolitical Landscape of China, Taiwan, and Japan
Related Articles: A Complex Tapestry: Understanding the Geopolitical Landscape of China, Taiwan, and Japan
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Complex Tapestry: Understanding the Geopolitical Landscape of China, Taiwan, and Japan. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Complex Tapestry: Understanding the Geopolitical Landscape of China, Taiwan, and Japan
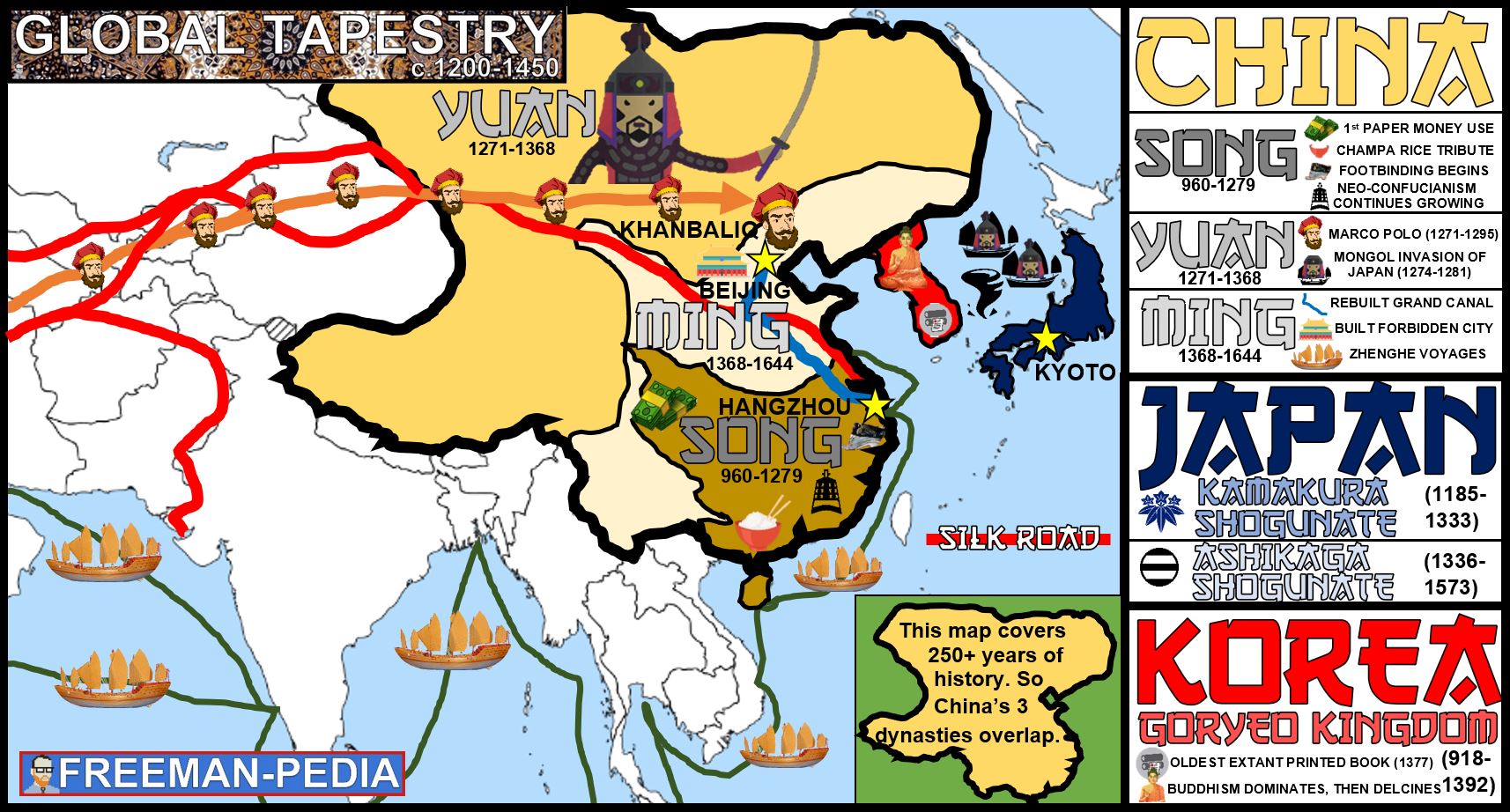
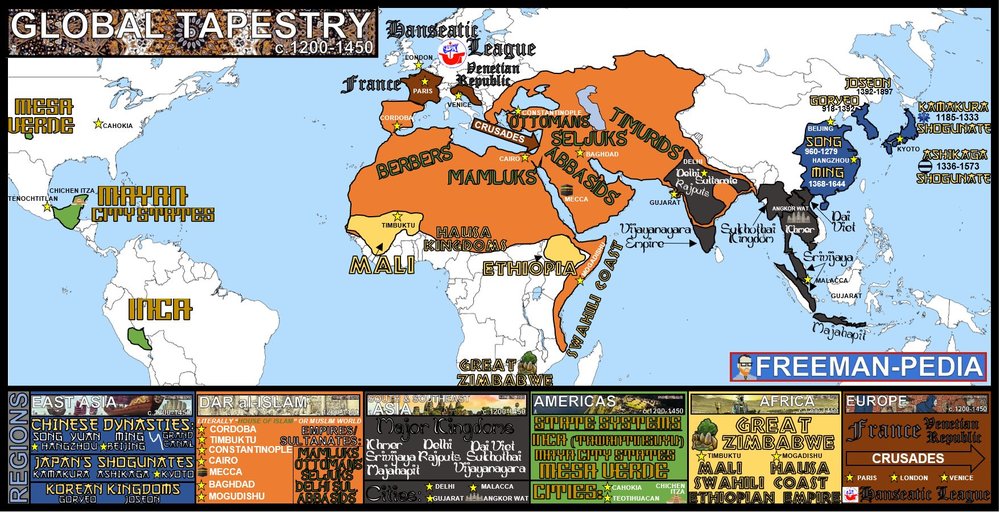
The East Asian region, encompassing China, Taiwan, and Japan, is a dynamic and complex geopolitical landscape. Understanding the intricate relationships between these three nations is crucial for comprehending regional dynamics, global power shifts, and the potential for conflict or cooperation. This article delves into the historical, political, and economic factors that shape the map of this region, highlighting the significance of these interconnected nations within the broader global context.
Historical Roots and Shared Heritage:
The history of China, Taiwan, and Japan is deeply intertwined, shaped by centuries of cultural exchange, political influence, and occasional conflict. China’s influence on the region is undeniable, with its ancient civilization and vast cultural sphere extending across East Asia. Taiwan’s history is intricately linked to mainland China, having been a part of the Chinese empire for centuries. Japan, while geographically distinct, has long been influenced by Chinese culture, adopting elements of its language, philosophy, and art.
Taiwan: A Contested Territory:
The status of Taiwan remains one of the most contentious issues in the region. The island’s political history is marked by a complex interplay of Chinese nationalism, Japanese colonial rule, and the aftermath of the Chinese Civil War. The People’s Republic of China (PRC) claims sovereignty over Taiwan, viewing it as a renegade province, while the Republic of China (ROC), which governs Taiwan, asserts its independence. This unresolved issue has led to ongoing tensions, with the PRC regularly engaging in military exercises and diplomatic pressure to assert its claims.
Japan: A Regional Powerhouse:
Japan, a modern economic powerhouse and technological leader, holds a significant position in the region. Its history is marked by periods of isolation and rapid modernization, culminating in its rise as a major industrial and military force in the 20th century. Following World War II, Japan experienced a remarkable economic recovery, becoming a key player in global trade and a driving force behind technological innovation. However, its past actions, particularly during the war, continue to cast a shadow over its relations with neighboring countries, including China and Korea.
Economic Interdependence and Strategic Competition:
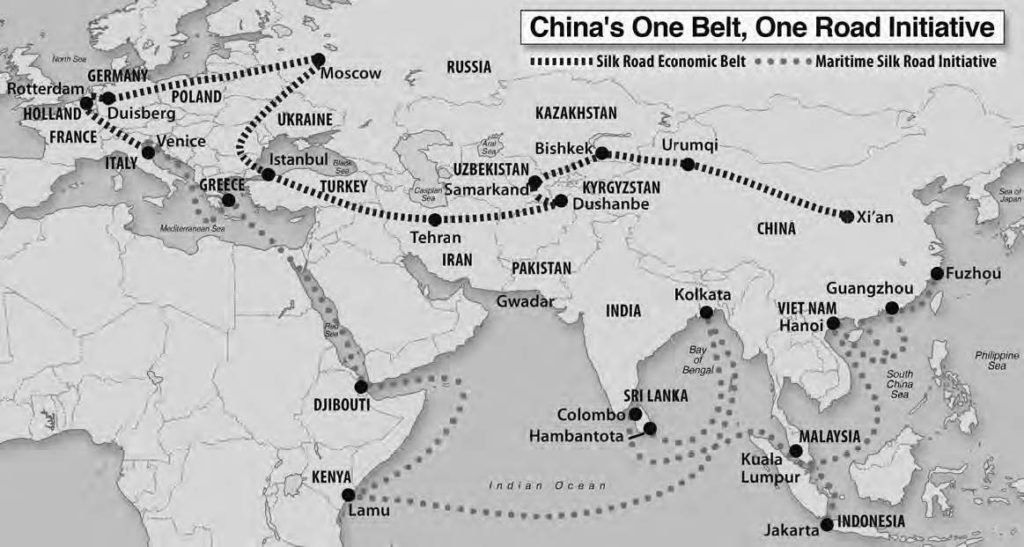
Despite the historical and political complexities, China, Taiwan, and Japan are bound together by strong economic ties. China’s rapidly growing economy has created vast opportunities for trade and investment for both Taiwan and Japan. Taiwan, with its advanced manufacturing sector, is a major supplier of technology and components to China. Japan, while facing economic challenges, remains a key investor in China and a major trading partner for Taiwan.
However, this economic interdependence is also a source of strategic competition. China’s growing military strength and its ambitions to assert its dominance in the region have raised concerns in Japan and Taiwan. Japan, seeking to maintain its security and regional influence, has strengthened its military capabilities and forged closer alliances with the United States. Taiwan, facing the threat of a potential Chinese invasion, has been actively modernizing its defense forces and seeking international support.
The Role of the United States:
The United States plays a crucial role in the East Asian security architecture. Its military presence in the region, through alliances with Japan and South Korea, serves as a deterrent against Chinese aggression. The US also maintains a strategic relationship with Taiwan, providing it with arms sales and diplomatic support. The US’s involvement in the region has been a stabilizing factor, but it has also contributed to tensions with China, which views the US presence as a challenge to its interests.
Navigating the Future:
The future of the China-Taiwan-Japan relationship is uncertain, marked by both opportunities and challenges. The economic interdependence between these nations offers potential for collaboration and shared prosperity. However, the unresolved issue of Taiwan’s status, coupled with China’s growing military power and assertive foreign policy, poses a significant risk of instability.
FAQs:
- What is the current status of Taiwan’s independence? Taiwan is currently self-governed and enjoys de facto independence, but it is not recognized as a sovereign state by the United Nations or most countries.
- What are the main issues in the relationship between China and Japan? The relationship between China and Japan is strained by historical disputes, territorial claims over the Senkaku/Diaoyu Islands, and competition for regional influence.
- How does the US involvement affect the regional dynamics? The US involvement in the region provides a counterbalance to China’s growing power and serves as a security guarantee for Japan and Taiwan. However, it also contributes to tensions with China, which sees the US presence as a threat.
- What are the potential risks of conflict in the region? The potential for conflict in the region is high due to the unresolved issue of Taiwan’s status, China’s assertive foreign policy, and the ongoing territorial disputes between China and Japan.
- What are the potential benefits of cooperation in the region? Cooperation in the region could lead to increased economic growth, improved regional security, and a more stable geopolitical environment.
Tips:
- Stay informed: Keep abreast of developments in the region through reliable news sources and academic research.
- Understand the historical context: Familiarize yourself with the historical events that have shaped the relationship between China, Taiwan, and Japan.
- Recognize the economic interdependence: Appreciate the complex web of economic ties that bind these nations together.
- Consider the role of the US: Analyze the impact of the US’s involvement in the region and its implications for regional stability.
- Be aware of the potential for conflict: Recognize the risks of instability and the need for diplomatic solutions to manage tensions.
Conclusion:
The map of China, Taiwan, and Japan is a dynamic and evolving landscape, shaped by history, politics, and economics. Understanding the intricate relationships between these nations is essential for comprehending the complexities of the East Asian region. The region faces both opportunities and challenges, with the potential for both cooperation and conflict. As global power shifts continue to unfold, the future of this dynamic region will depend on the ability of its key players to navigate complex geopolitical issues and find common ground for stability and prosperity.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Complex Tapestry: Understanding the Geopolitical Landscape of China, Taiwan, and Japan. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!