A Comprehensive Examination of Standardized Testing in Third Grade: Understanding the Purpose, Benefits, and Challenges
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Examination of Standardized Testing in Third Grade: Understanding the Purpose, Benefits, and Challenges
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Examination of Standardized Testing in Third Grade: Understanding the Purpose, Benefits, and Challenges. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Examination of Standardized Testing in Third Grade: Understanding the Purpose, Benefits, and Challenges

The third grade is a pivotal year in a child’s academic journey. It marks a transition from foundational learning to more complex concepts, laying the groundwork for future academic success. This transition is often accompanied by the introduction of standardized testing, a practice that has become increasingly prevalent in education systems worldwide.
Standardized tests, often referred to as "high-stakes" assessments, aim to provide a snapshot of a student’s academic progress and compare their performance against a national or state-wide benchmark. While these tests have faced criticism for their potential to create undue pressure on students and teachers, they also play a vital role in informing educators about students’ learning needs and guiding educational practices.
Understanding the Purpose and Structure of Standardized Tests in Third Grade
Third-grade standardized tests typically focus on core subjects like reading, writing, and mathematics. These assessments are designed to measure a student’s mastery of essential skills and knowledge acquired in the early grades. The content covered in these tests varies depending on the specific test and the educational standards adopted by the state or district.
These tests are often administered in a controlled environment, with strict time limits and standardized instructions. The format can include multiple-choice questions, short-answer responses, and even essay writing. The goal is to ensure consistency and fairness in the assessment process, allowing for a valid comparison of student performance across different schools and districts.
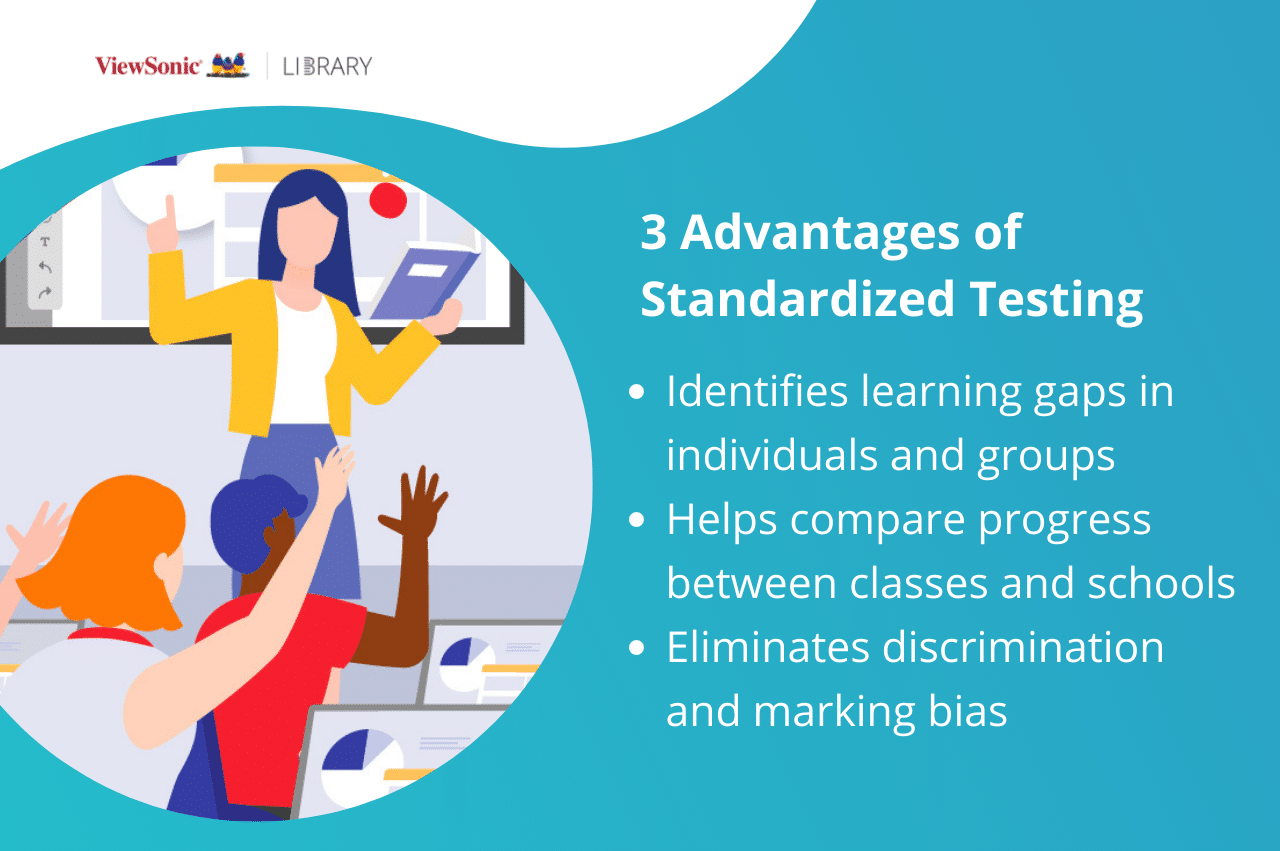
The Benefits of Standardized Testing in Third Grade
While standardized tests have attracted criticism, they also offer several benefits for students, educators, and policymakers:
- Monitoring Progress and Identifying Gaps: Standardized tests provide valuable data that allows educators to monitor student progress over time. This data can highlight areas where students are excelling and areas where they may need additional support. By analyzing individual student performance, teachers can tailor their instruction to address specific learning needs.
- Guiding Curriculum Development: Standardized test results can inform curriculum development and resource allocation. By identifying areas where students are struggling, educators can adjust their teaching strategies and focus on strengthening those specific skills. This data-driven approach helps ensure that curriculum aligns with current educational standards and student needs.
- Accountability and Transparency: Standardized testing promotes accountability within the education system. By measuring student performance against established benchmarks, these tests provide a means for evaluating the effectiveness of educational programs and interventions. This transparency allows for informed decision-making regarding resource allocation and program improvement.
- Early Intervention and Support: Standardized tests can identify students who are at risk of falling behind academically at an early stage. This early identification allows for timely intervention and support services, preventing potential learning difficulties from escalating. By providing targeted interventions, educators can help students catch up and reach their full potential.
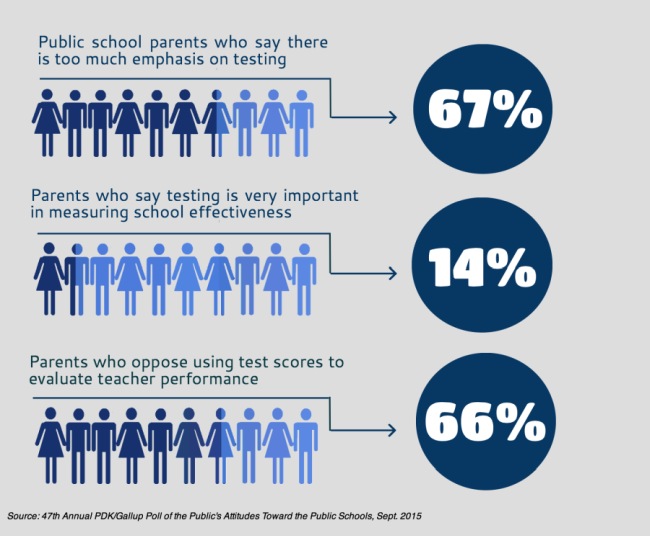
Addressing Concerns and Challenges
Despite the benefits, standardized testing has also generated considerable debate and concern. Common criticisms include:
- Narrow Focus and Limited Scope: Critics argue that standardized tests often focus on a limited range of skills and knowledge, neglecting other important aspects of learning such as creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving. This narrow focus can lead to a "teaching to the test" approach, where educators prioritize rote memorization and test-taking strategies over deeper understanding and genuine learning.
- Increased Pressure and Stress: The high-stakes nature of standardized tests can create undue pressure and stress on students, especially younger children. The fear of failure can negatively impact their motivation and performance, potentially leading to anxiety and test anxiety.
- Equity and Access: Critics argue that standardized tests may not be equitable for all students, particularly those from disadvantaged backgrounds. Factors such as socioeconomic status, language proficiency, and access to resources can influence test performance, leading to potential bias and misrepresentation.
- Over-reliance on Test Scores: There is concern that an over-reliance on standardized test scores can lead to a narrow view of student success and may not accurately reflect their overall potential.
Strategies for Effective Standardized Testing in Third Grade
To address the concerns and maximize the benefits of standardized testing, educators and policymakers can implement several strategies:
- Focus on Holistic Learning: Educators should prioritize a holistic approach to learning, emphasizing critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity alongside foundational skills. This broader perspective ensures that students develop a well-rounded education, not just test-taking skills.
- Reduce Test-Taking Pressure: Schools can implement strategies to reduce test-taking pressure and anxiety. This can include providing students with clear explanations of the test format, practicing test-taking strategies, and fostering a supportive and encouraging learning environment.
- Address Equity Concerns: Efforts should be made to ensure equitable access to quality education for all students. This includes providing support services for students from disadvantaged backgrounds, addressing language barriers, and promoting culturally responsive teaching practices.
- Use Test Data Responsively: Test data should be used to inform instruction and identify student needs, not solely for ranking or labeling students. Educators should focus on using test results to guide their teaching strategies and provide targeted support to individual students.
- Promote a Balanced Assessment Approach: Standardized testing should be part of a comprehensive assessment system that includes a variety of methods, such as teacher observations, portfolios, and performance-based assessments. This balanced approach provides a more complete picture of student learning and development.
FAQs About Standardized Testing in Third Grade
Q: What are the main subjects covered in third-grade standardized tests?
A: Third-grade standardized tests typically focus on core subjects like reading, writing, and mathematics. The specific content covered may vary depending on the state or district’s educational standards.
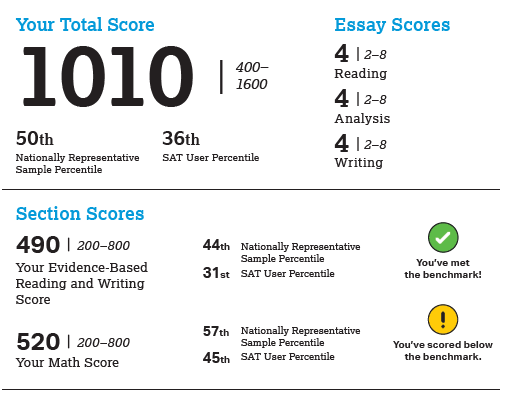
Q: How are standardized test scores used?
A: Test scores are used to monitor student progress, identify areas where students need additional support, inform curriculum development, and evaluate the effectiveness of educational programs.
Q: How can parents help their children prepare for standardized tests?
A: Parents can help by creating a positive learning environment, encouraging regular reading and writing activities, and providing opportunities for their children to practice problem-solving skills. It is important to avoid placing undue pressure on children and emphasize the importance of learning for its own sake.
Q: What are some tips for teachers to help students succeed on standardized tests?
A: Teachers can help students by:
- Providing clear explanations of the test format and expectations.
- Practicing test-taking strategies and familiarizing students with different question types.
- Creating a supportive and encouraging learning environment.
- Focusing on building foundational skills and understanding.
Q: What are some alternative assessment methods that can be used alongside standardized tests?
A: Alternative assessment methods include:
- Teacher observations and anecdotal records.
- Student portfolios showcasing their work and progress.
- Performance-based assessments that require students to apply their knowledge and skills in real-world contexts.
Conclusion
Standardized testing in third grade is a complex and multifaceted issue. While these tests provide valuable information about student progress and can inform educational practices, it is crucial to recognize their limitations and address concerns regarding equity, pressure, and the potential for a narrow focus on test scores. By implementing a balanced approach to assessment, focusing on holistic learning, and using test data responsibly, educators and policymakers can ensure that standardized testing serves as a tool for improving education, not a means of simply measuring and ranking students. The ultimate goal should be to create a supportive and equitable learning environment where all students have the opportunity to reach their full potential.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Examination of Standardized Testing in Third Grade: Understanding the Purpose, Benefits, and Challenges. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
