A Comprehensive Guide to the Mountain Ranges of Southern California
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to the Mountain Ranges of Southern California
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to the Mountain Ranges of Southern California. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to the Mountain Ranges of Southern California

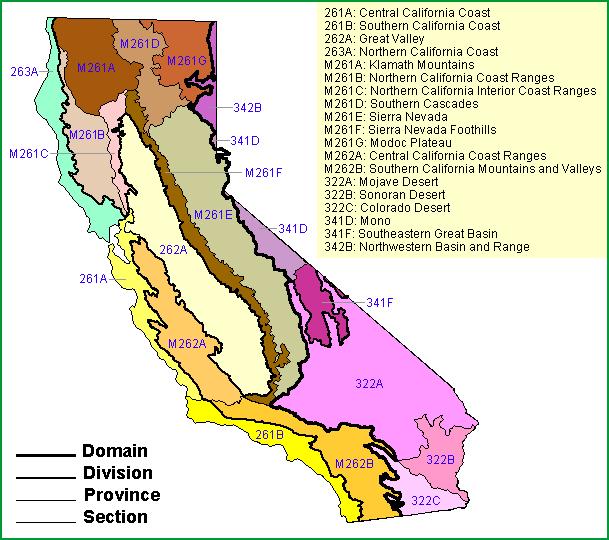
Southern California is renowned for its diverse landscape, encompassing sun-drenched beaches, sprawling deserts, and a dramatic tapestry of mountain ranges. These ranges, sculpted over millennia by tectonic forces and weathering, not only define the region’s physical geography but also play a crucial role in its climate, biodiversity, and human history. Understanding the layout and characteristics of these mountain ranges provides a deeper appreciation for the unique features of Southern California.
A Geological Tapestry: Understanding the Origins
The mountains of Southern California are a product of the ongoing collision between the Pacific and North American tectonic plates. This process, known as subduction, has resulted in the formation of the San Andreas Fault, a major geological feature that traverses the region. The fault zone is characterized by frequent earthquakes, further shaping the landscape and contributing to the rugged terrain.
The mountain ranges themselves are broadly classified into two categories: the Transverse Ranges and the Peninsular Ranges.
The Transverse Ranges: A Barrier to Moisture
The Transverse Ranges, running east-west across Southern California, form a formidable barrier to moisture-laden winds from the Pacific Ocean. This orographic effect leads to a dramatic rainfall gradient, with the windward slopes receiving significant precipitation, while the leeward slopes remain relatively dry.
Key Ranges within the Transverse System:
- Santa Monica Mountains: This range, bordering the Pacific Ocean, is home to iconic landmarks like Malibu and the Hollywood Hills. Its diverse topography supports a rich ecosystem, including chaparral, coastal sage scrub, and oak woodlands.
- Santa Susana Mountains: Situated north of the San Fernando Valley, these mountains offer breathtaking views and are a popular destination for hiking and horseback riding.
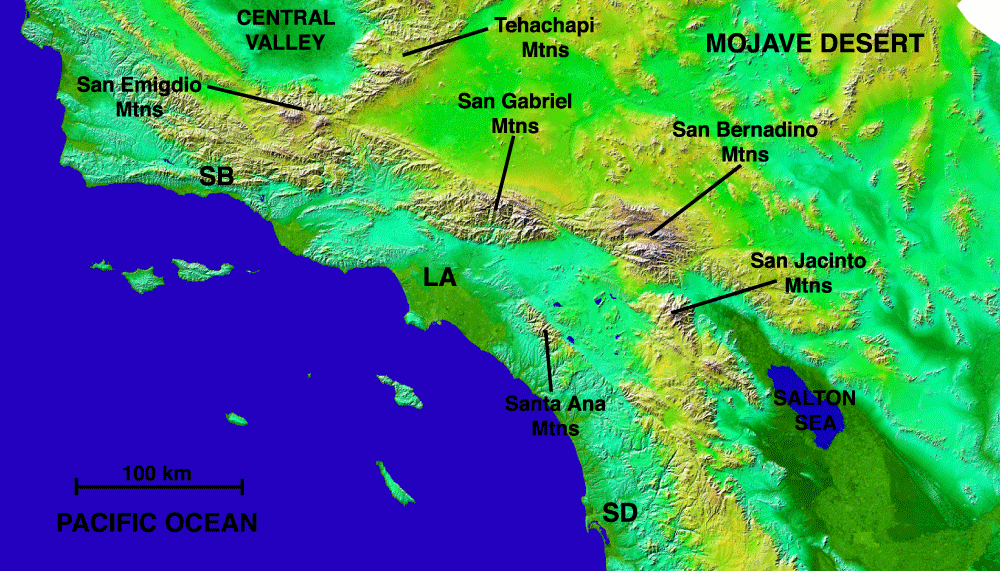
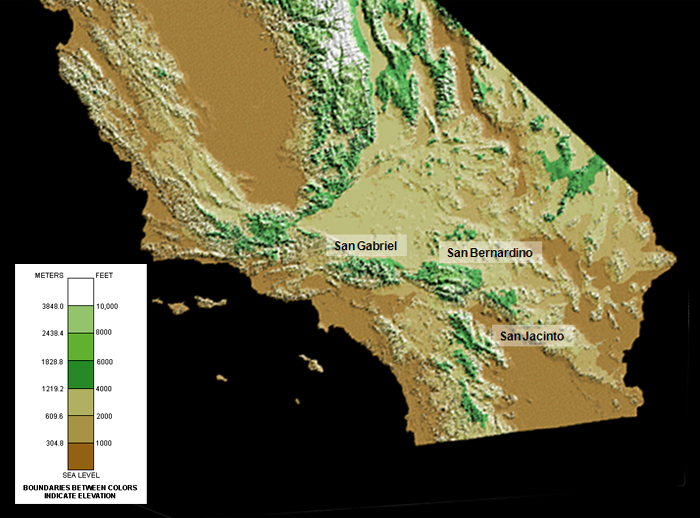
- San Gabriel Mountains: The highest peaks in the Transverse Ranges, the San Gabriels are a haven for outdoor recreation, featuring hiking trails, ski resorts, and scenic drives.
- San Bernardino Mountains: Known for their towering peaks, including Mount San Gorgonio, the highest point in Southern California, the San Bernardinos are a popular destination for winter sports.
The Peninsular Ranges: A Spine of Southern California
The Peninsular Ranges, extending south from the Transverse Ranges, form a spine along the California coast. These ranges are characterized by their rugged terrain, deep canyons, and diverse plant and animal life.
Key Ranges within the Peninsular System:
- Santa Ana Mountains: Located east of Los Angeles, these mountains are known for their dramatic canyons and rugged peaks.
- Palomar Mountain: Home to the renowned Palomar Observatory, this range offers stunning views of the surrounding landscape.
- Santa Margarita Mountains: This range, situated in northern San Diego County, is known for its oak woodlands and rolling hills.
- Laguna Mountains: Located east of San Diego, these mountains are popular for their hiking trails, scenic drives, and diverse wildlife.
The Importance of Southern California’s Mountains
The mountain ranges of Southern California are not merely scenic backdrops; they play a vital role in the region’s ecology, economy, and human history.
Ecological Significance:
- Water Source: The mountains act as a vital source of water for Southern California, capturing precipitation and feeding numerous rivers and streams.
- Biodiversity Hotspot: The diverse habitats within the mountain ranges support a rich array of plant and animal life, including endangered species like the California condor and the mountain lion.
- Carbon Sequestration: Forests and woodlands within the mountains play a crucial role in absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, mitigating the effects of climate change.
Economic Importance:
- Recreation and Tourism: The mountains are a major draw for tourism, offering opportunities for hiking, camping, skiing, and other outdoor activities.
- Natural Resources: The mountains provide valuable resources, including timber, minerals, and geothermal energy.
- Water Supply: The mountains are essential for the region’s water supply, providing water for agriculture, industry, and residential use.
Cultural and Historical Significance:
- Indigenous Heritage: The mountains have been home to Native American tribes for thousands of years, who have developed a deep understanding of the land and its resources.
- Early Settlement: The mountains played a role in the early settlement of Southern California, providing resources and access to trade routes.
- Modern Development: The mountains have influenced the development of Southern California, shaping the region’s urban planning, transportation infrastructure, and recreational opportunities.
FAQs about Southern California’s Mountain Ranges
Q: What are the highest peaks in Southern California?
A: Mount San Gorgonio in the San Bernardino Mountains is the highest peak in Southern California, reaching an elevation of 11,502 feet. Other notable peaks include Mount San Jacinto (10,834 feet) and Mount Baldy (10,064 feet).
Q: What is the best time to visit Southern California’s mountains?
A: The best time to visit depends on the activity you are interested in. For hiking and camping, spring and fall offer pleasant weather. For skiing and snowboarding, winter is the ideal time.
Q: Are there any dangers to be aware of when exploring the mountains?
A: Yes, there are several dangers to be aware of, including wildlife encounters, extreme weather conditions, and the risk of wildfires. It is important to be prepared, hike with a partner, and follow safety guidelines.
Q: What are some popular hiking trails in Southern California’s mountains?
A: Some popular hiking trails include the Mount Whitney Trail, the Pacific Crest Trail, the John Muir Trail, and the Tahoe Rim Trail.
Q: What are some tips for planning a trip to Southern California’s mountains?
A: When planning a trip to Southern California’s mountains, consider the following tips:
- Check the weather forecast: Weather conditions can change rapidly in the mountains, so it is important to be aware of the forecast.
- Pack appropriate clothing and gear: Be prepared for a variety of weather conditions, including rain, snow, and wind.
- Bring plenty of water: Staying hydrated is essential, especially during strenuous activities.
- Notify someone of your plans: Let someone know where you are going and when you expect to return.
- Be aware of your surroundings: Pay attention to your surroundings and be aware of potential hazards.
Conclusion
Southern California’s mountain ranges are a testament to the region’s dynamic geological history and a vital component of its ecological, economic, and cultural landscape. From their towering peaks to their rugged canyons, these ranges provide a unique and unforgettable experience for visitors and residents alike. Understanding the layout, characteristics, and significance of these mountain ranges deepens our appreciation for the beauty and complexity of Southern California’s natural world.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to the Mountain Ranges of Southern California. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
