A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Taiwan: Geography, History, and Significance
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Taiwan: Geography, History, and Significance
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Taiwan: Geography, History, and Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Taiwan: Geography, History, and Significance
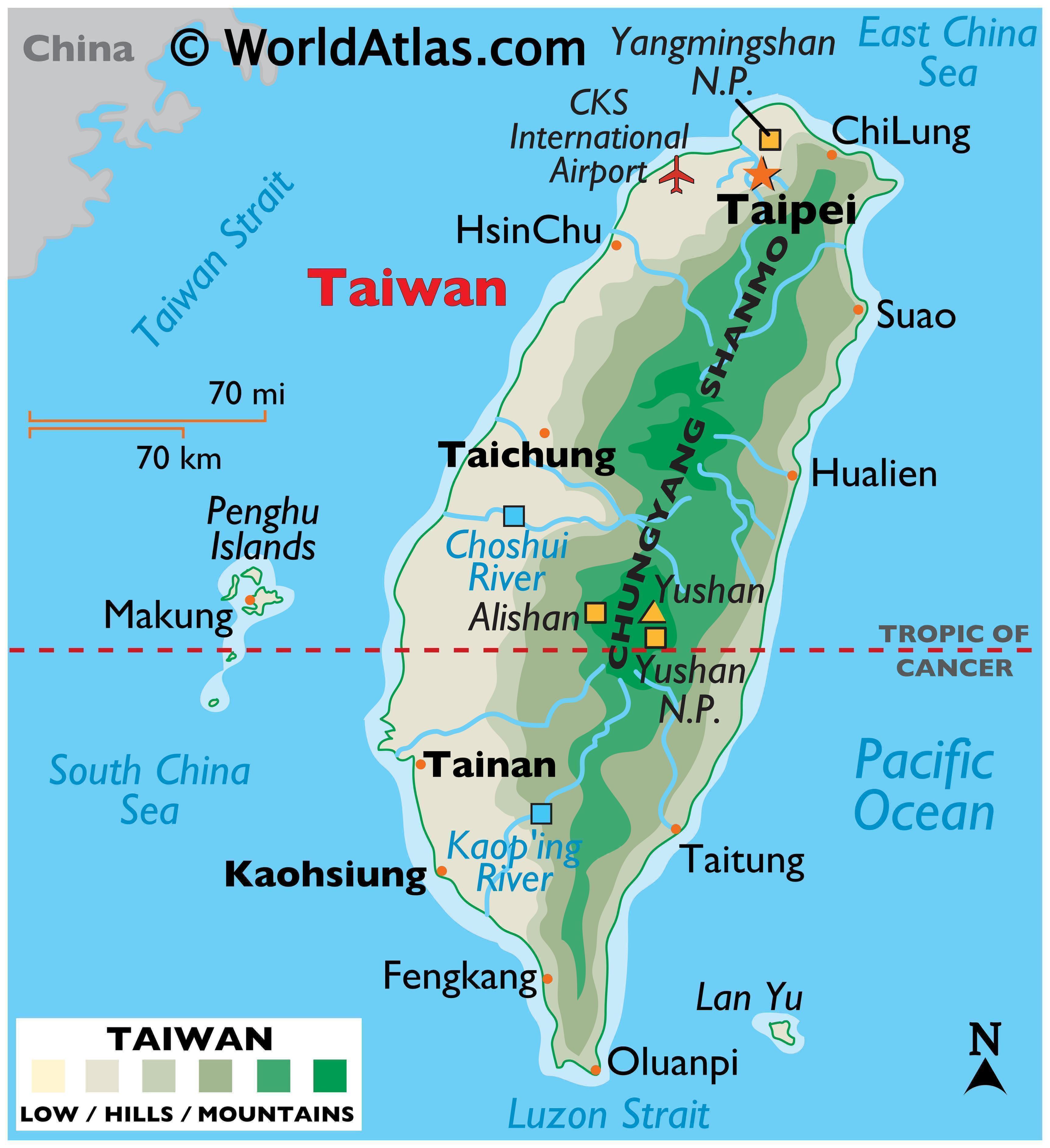
Taiwan, an island nation situated off the southeastern coast of mainland China, holds a unique and multifaceted position in the global landscape. Understanding its geography, history, and political context is essential for comprehending the complexities of the region. This article delves into the intricacies of the map of Taiwan, examining its physical features, historical evolution, and the geopolitical implications that make it a subject of ongoing international attention.
Geographical Features:
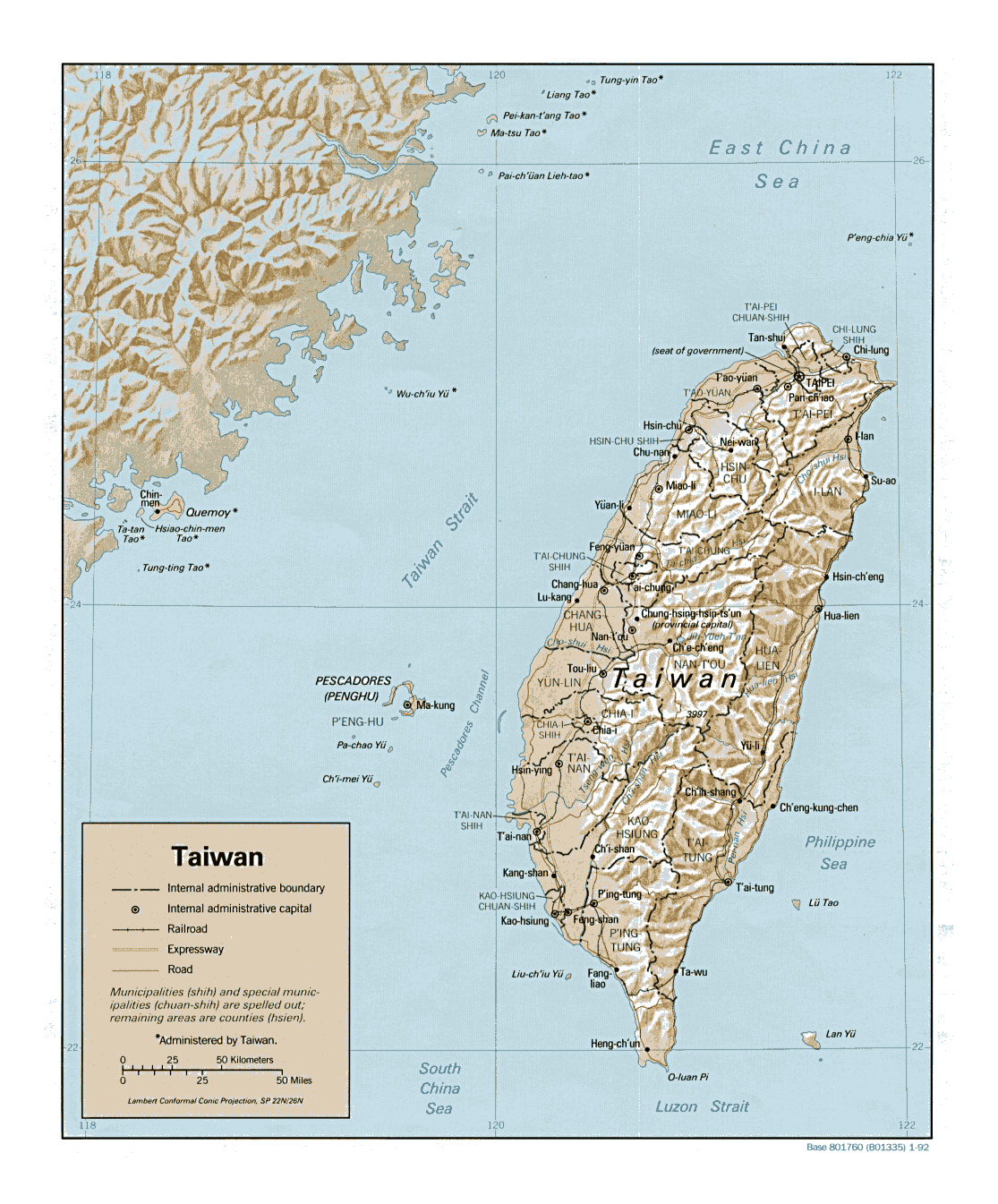
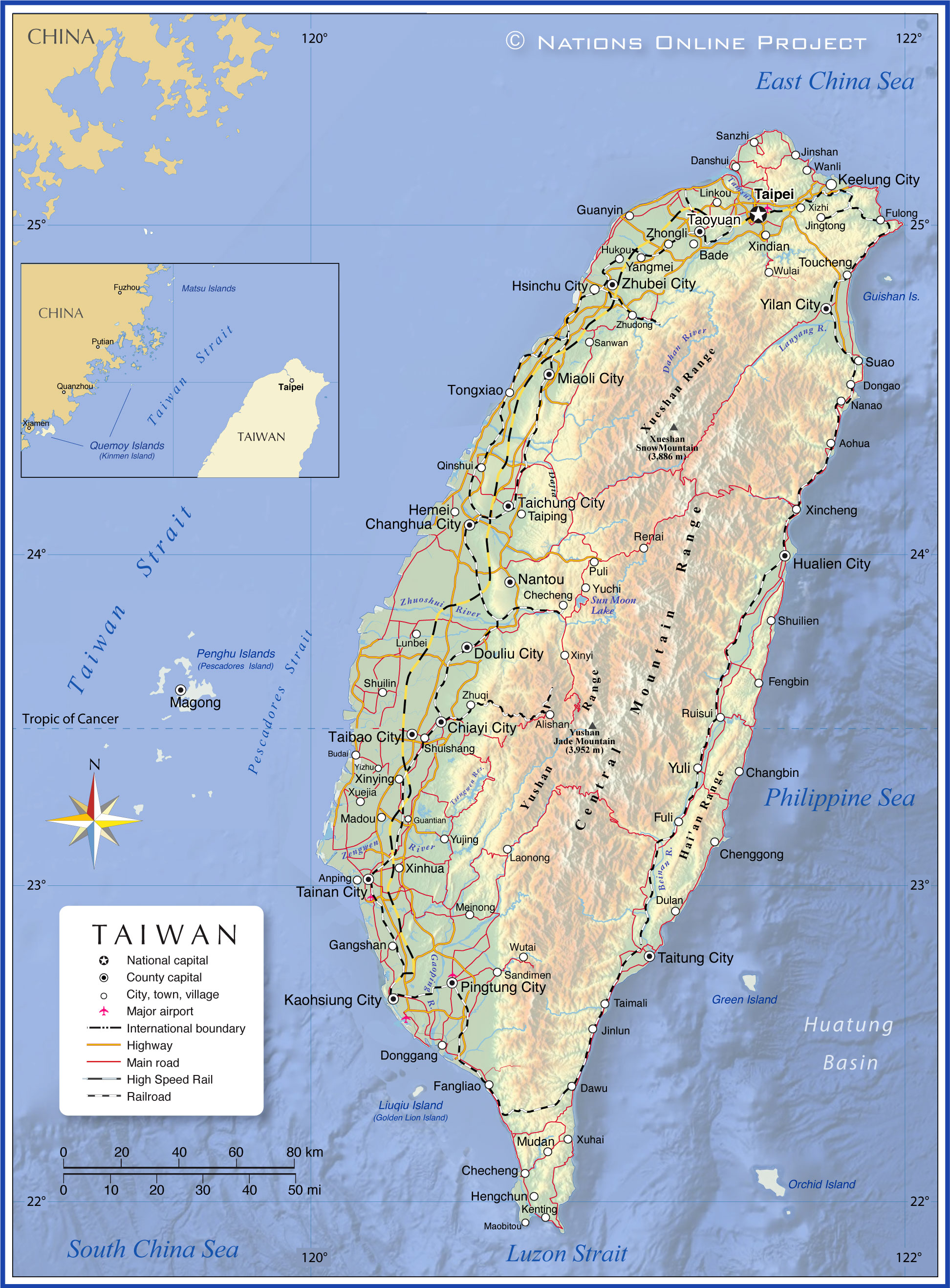
Taiwan’s island geography is characterized by a diverse and mountainous terrain. The island is dominated by the Central Mountain Range, which runs roughly north-south, dividing the island into a western coastal plain and an eastern mountainous region. The highest peak, Yushan (Jade Mountain), reaches an elevation of 3,952 meters, making it the highest point in East Asia.
The western coastal plain, known as the "Taiwan Basin," is a fertile agricultural region, home to most of the island’s population and major cities. The eastern mountainous region is characterized by rugged terrain, dense forests, and numerous indigenous communities.
Historical Evolution:
Taiwan’s history is marked by a complex interplay of indigenous cultures, colonial influences, and political transformations. The island was originally inhabited by various indigenous tribes before the arrival of the Dutch in the 17th century. The Dutch established settlements along the coast, but their rule was short-lived, replaced by the arrival of the Qing dynasty in 1683.
During the Qing period, Taiwan was incorporated into the Chinese empire as a province. However, in 1895, after the First Sino-Japanese War, Taiwan was ceded to Japan. The Japanese era saw significant modernization and development of the island, but also experienced resistance from the Taiwanese population.
Following World War II, Japan returned Taiwan to China. However, the ensuing Chinese Civil War resulted in the retreat of the Kuomintang (KMT) to Taiwan in 1949, establishing the Republic of China (ROC) on the island. The People’s Republic of China (PRC), established on the mainland, claims sovereignty over Taiwan, leading to a complex political situation that continues to this day.
Political Context and Geopolitical Significance:
The relationship between Taiwan and mainland China is a major geopolitical issue. The PRC’s claim over Taiwan is based on the "One China" principle, which asserts that there is only one sovereign state called China. However, Taiwan maintains its own government, military, and democratic system, operating independently from mainland China.
The "Taiwan issue" has been a source of tension between the PRC and the ROC, with the PRC repeatedly threatening military action if Taiwan declares independence. The United States, which maintains close ties with Taiwan, has adopted a policy of "strategic ambiguity," neither formally recognizing Taiwan as a sovereign state nor explicitly endorsing its independence.
Importance and Benefits of Understanding the Map of Taiwan:
The map of Taiwan provides a crucial visual representation of the island’s geography, history, and political context. Understanding its physical features allows for a better grasp of the island’s natural resources, agricultural potential, and challenges posed by its terrain.
The historical evolution of Taiwan, as depicted on the map, highlights the island’s diverse cultural heritage and the complex political dynamics that have shaped its present-day reality. Studying the map also reveals the geopolitical significance of Taiwan, its strategic location, and the ongoing tensions between the PRC and ROC.
FAQs:
1. What is the current political status of Taiwan?
Taiwan is currently governed by the Republic of China (ROC), which maintains its own government, military, and democratic system, operating independently from mainland China. However, the People’s Republic of China (PRC) claims sovereignty over Taiwan.
2. Is Taiwan a sovereign nation?
The political status of Taiwan is complex and contested. While it maintains its own government and operates independently, it is not formally recognized as a sovereign nation by most countries, including the United States.
3. What are the key geographical features of Taiwan?
Taiwan is characterized by a mountainous terrain, with the Central Mountain Range dividing the island into a western coastal plain and an eastern mountainous region. The highest peak, Yushan (Jade Mountain), is the highest point in East Asia.
4. What is the relationship between Taiwan and China?
The relationship between Taiwan and mainland China is characterized by political tension and ongoing claims of sovereignty. The PRC claims Taiwan as part of its territory, while Taiwan maintains its own independent government.
5. What is the "One China" principle?
The "One China" principle asserts that there is only one sovereign state called China, and Taiwan is a part of it. This principle is recognized by many countries, including the United States, but it is contested by Taiwan.
Tips:
1. Utilize online maps and resources: Numerous online platforms, such as Google Maps and Wikipedia, offer detailed maps of Taiwan, providing geographical information, historical context, and political boundaries.
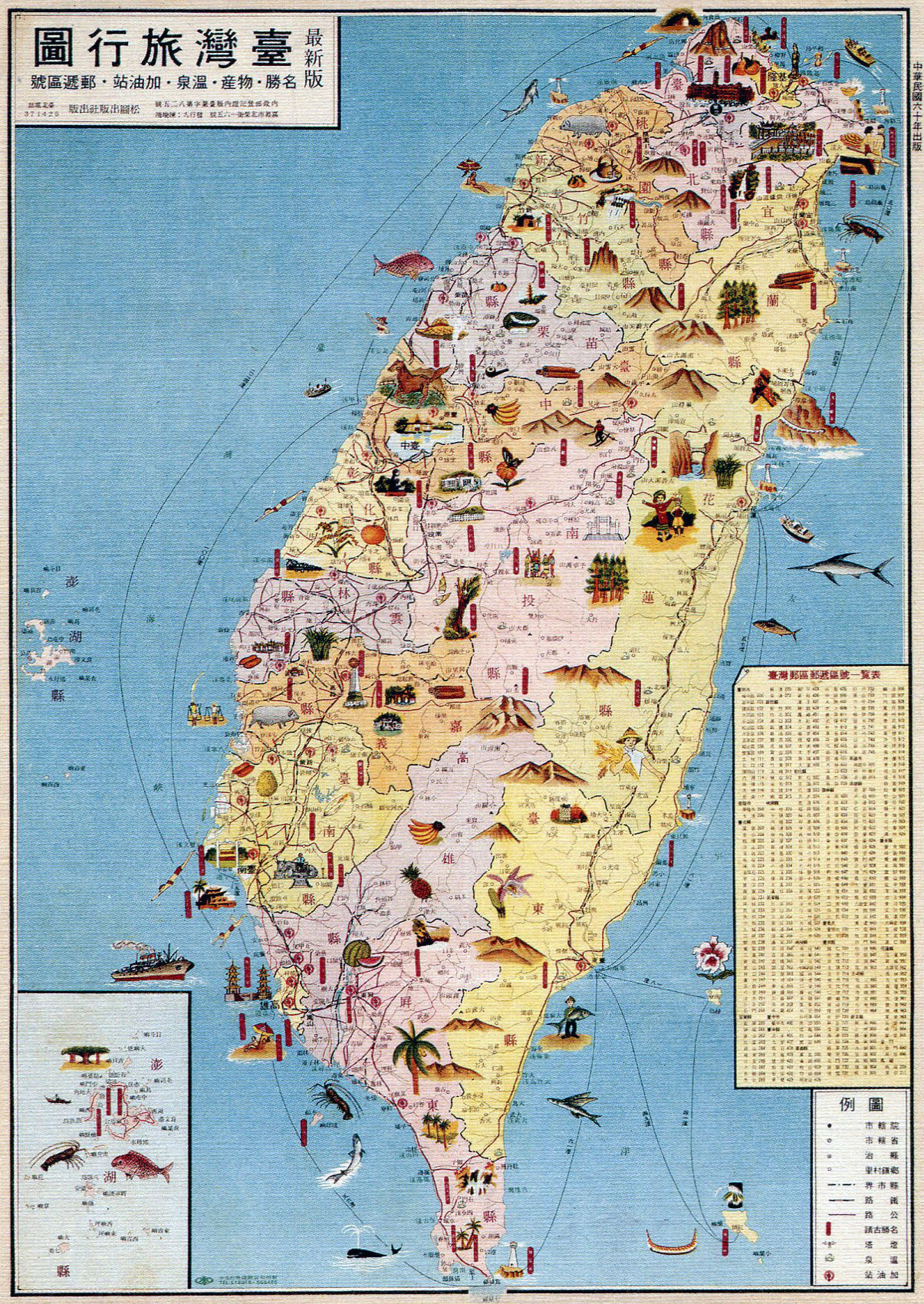
2. Explore historical maps: Examining historical maps of Taiwan can provide valuable insights into the island’s evolution over time, from colonial periods to present-day boundaries.
3. Focus on key geographical features: Pay attention to the Central Mountain Range, the western coastal plain, and major cities like Taipei and Kaohsiung, as they play crucial roles in the island’s economy, culture, and political dynamics.
4. Understand the political context: Stay informed about the ongoing political tensions between Taiwan and mainland China, as well as the international community’s response to the "Taiwan issue."
Conclusion:
The map of Taiwan serves as a powerful tool for understanding the island’s unique geography, history, and political context. It highlights the island’s natural beauty, rich cultural heritage, and the complexities of its relationship with mainland China. As a vital player in the Asia-Pacific region, Taiwan’s future remains intertwined with the evolving geopolitical landscape, making it a subject of continuous global interest.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Taiwan: Geography, History, and Significance. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
