A Geographic Tapestry: Unveiling the Southern California Valleys
Related Articles: A Geographic Tapestry: Unveiling the Southern California Valleys
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Geographic Tapestry: Unveiling the Southern California Valleys. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographic Tapestry: Unveiling the Southern California Valleys

Southern California, a region renowned for its diverse landscapes, vibrant cities, and captivating coastline, also boasts a network of fertile valleys that have played a pivotal role in shaping its history, culture, and economy. These valleys, carved by ancient forces and nurtured by a unique climate, offer a compelling glimpse into the region’s geological past, agricultural present, and urban future.
A Geological Odyssey: The Formation of Southern California Valleys
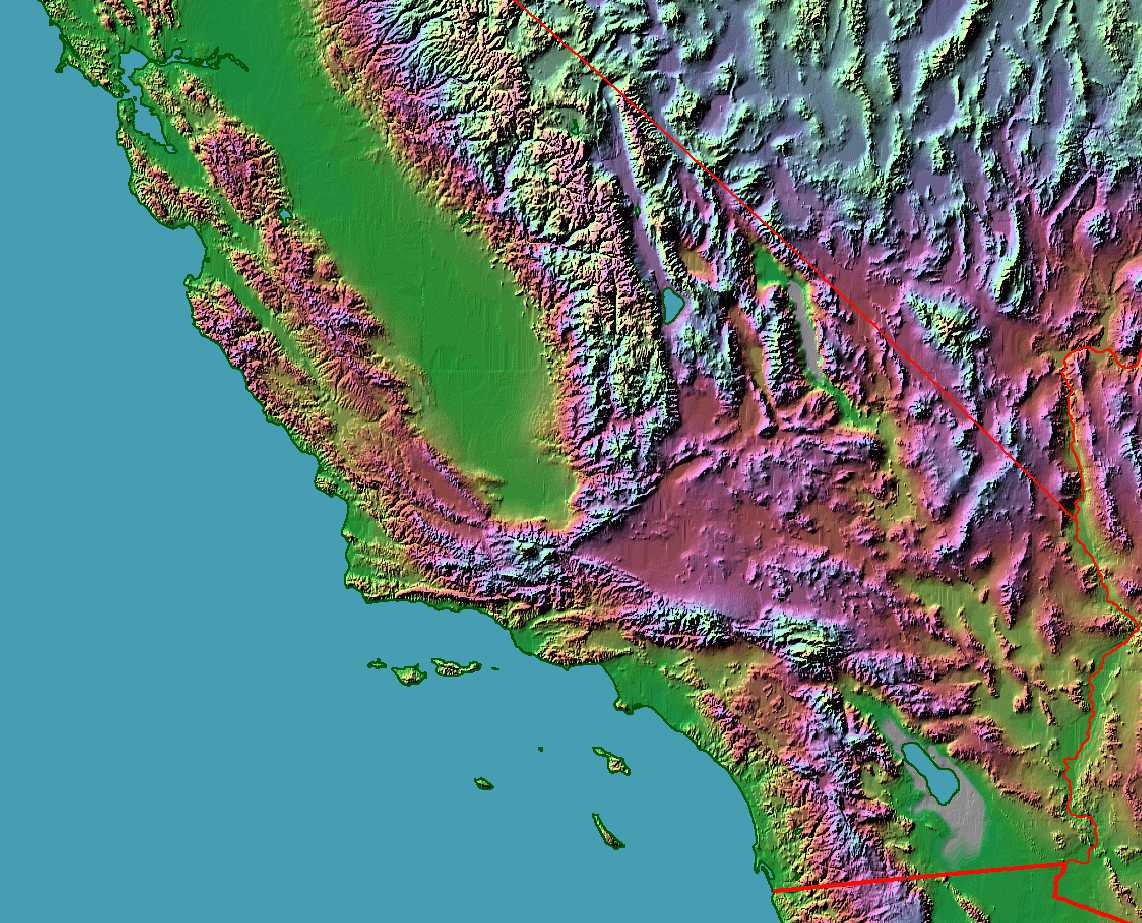
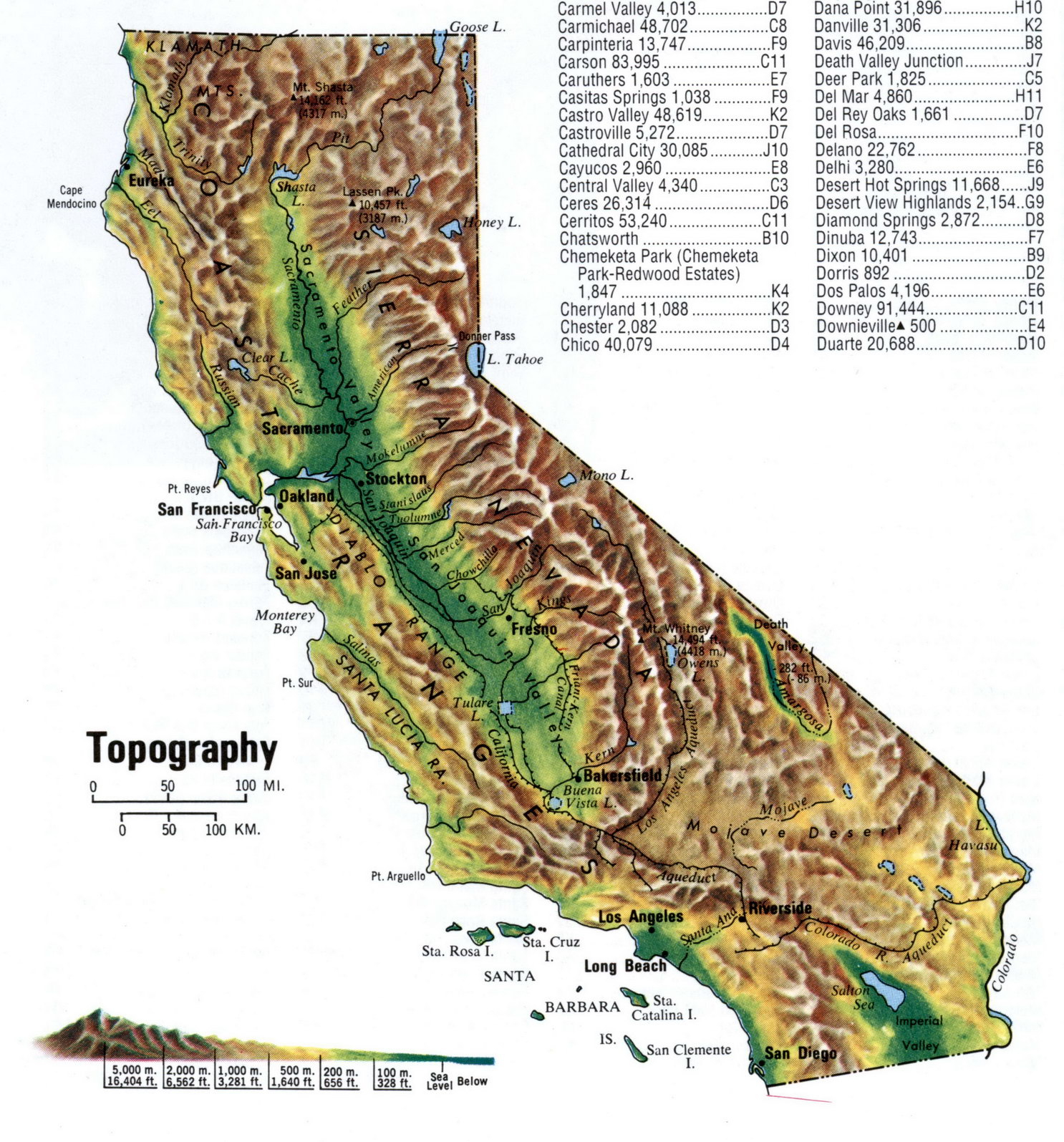
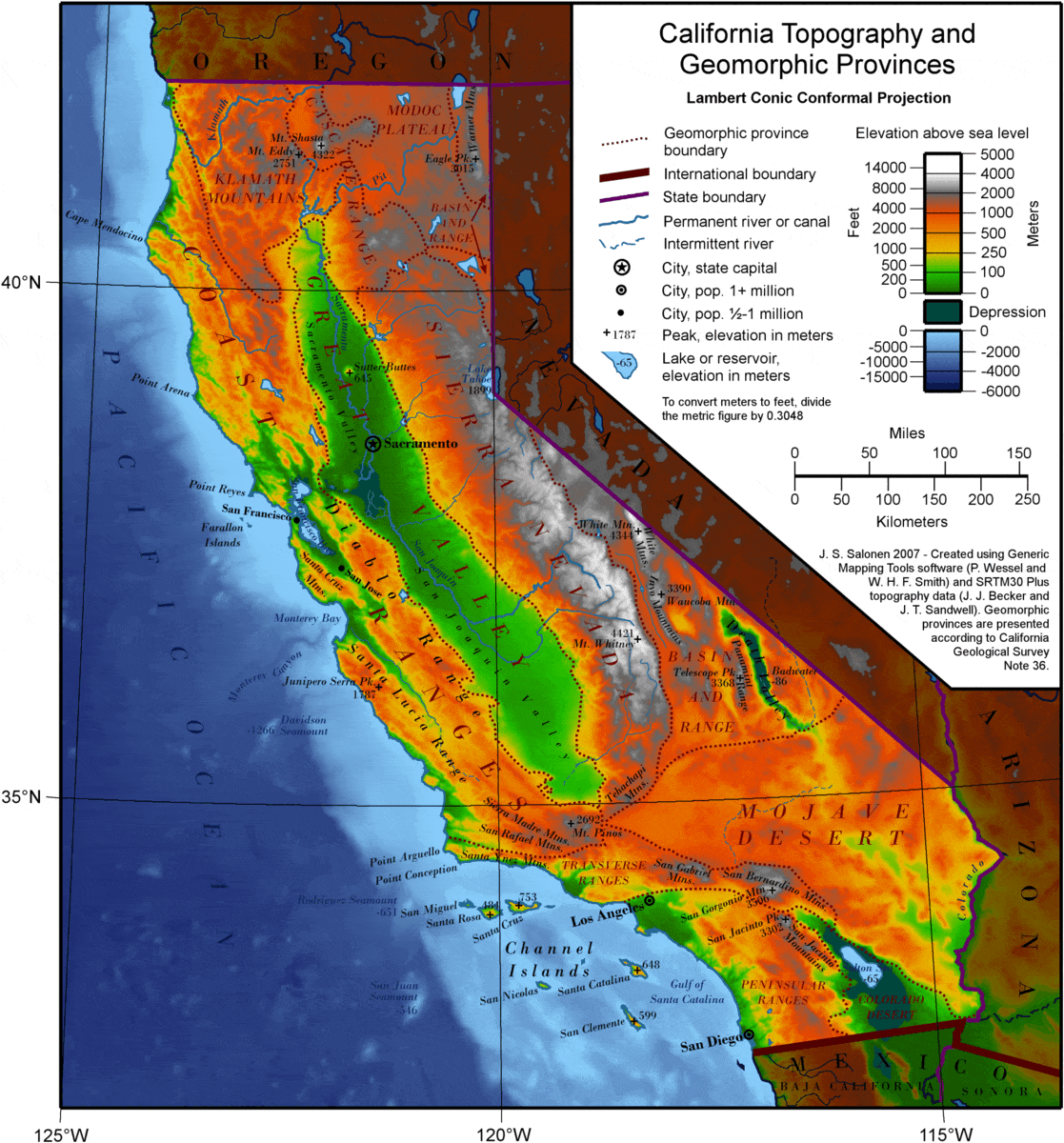
The valleys of Southern California are a testament to the dynamic geological forces that have shaped the region over millions of years. The San Andreas Fault, a major tectonic boundary, traverses the region, creating a complex interplay of uplift, subsidence, and faulting. This geological activity has resulted in the formation of distinct valleys, each with its own unique characteristics.
-
The San Fernando Valley: Situated north of the Santa Monica Mountains, the San Fernando Valley owes its existence to the San Fernando Fault, a branch of the San Andreas Fault. This valley, once a vast plain, was gradually uplifted and tilted, creating a gentle slope towards the Pacific Ocean.
-
The Santa Clarita Valley: Located northwest of Los Angeles, the Santa Clarita Valley is a product of the Santa Susana Fault, another branch of the San Andreas Fault. This valley is characterized by a series of rolling hills and a relatively flat floor, formed by the erosion of sedimentary rocks.
-
The San Gabriel Valley: East of Los Angeles, the San Gabriel Valley is nestled between the San Gabriel Mountains and the Puente Hills. This valley was formed by the uplift of the San Gabriel Mountains, creating a natural drainage basin.
-
The Antelope Valley: Situated north of the San Gabriel Mountains, the Antelope Valley is a large, arid basin surrounded by mountains. This valley was formed by the erosion of the surrounding mountains, creating a vast expanse of alluvial deposits.
-
The Coachella Valley: Located in the southeastern portion of the state, the Coachella Valley is a desert oasis, situated in the shadow of the San Jacinto Mountains. This valley was formed by the uplift of the mountains, creating a closed basin that traps water and promotes unique ecosystems.
A Bounty of Nature: The Agricultural Significance of Southern California Valleys
The fertile soils and temperate climate of Southern California’s valleys have made them ideal for agriculture. From the early days of Spanish colonization, these valleys have provided sustenance for the region’s growing population.
-
The San Fernando Valley: Once known as "The Valley of the Sun," the San Fernando Valley was a major agricultural center, producing citrus fruits, vegetables, and dairy products. While urbanization has reduced agricultural land, remnants of this past can still be found in the region’s orchards and vineyards.
-
The Santa Clarita Valley: This valley has traditionally been a major producer of walnuts, grapes, and other agricultural products. However, with the rapid growth of the city of Santa Clarita, agricultural land has been increasingly converted to residential and commercial uses.
-
The San Gabriel Valley: This valley has historically been a significant producer of citrus fruits, avocados, and other fruits and vegetables. However, urban sprawl and changing market demands have led to a decline in agricultural activity in recent years.
-
The Antelope Valley: This valley, with its arid climate, is well-suited for the production of alfalfa, cotton, and other drought-tolerant crops. It also serves as a major center for the production of livestock feed.
-
The Coachella Valley: This valley, known for its warm climate and abundant sunshine, is a major producer of dates, citrus fruits, and other desert-adapted crops. It also plays a significant role in the region’s tourism industry.
A Tapestry of Urbanization: The Transformation of Southern California Valleys
Over the past century, the Southern California valleys have undergone a dramatic transformation from agricultural landscapes to urban centers. This urbanization has been driven by a number of factors, including population growth, economic development, and the allure of the region’s mild climate.
-
The San Fernando Valley: This valley has become a major residential and commercial center, home to a diverse population and a thriving economy. The Valley is home to numerous businesses, entertainment venues, and educational institutions.
-
The Santa Clarita Valley: This valley has experienced rapid growth in recent decades, with new residential developments, commercial centers, and entertainment venues. It has become a popular destination for families seeking a suburban lifestyle.
-
The San Gabriel Valley: This valley is home to a mix of residential neighborhoods, commercial centers, and industrial areas. It is known for its diverse cultural heritage and its strong Asian American community.
-
The Antelope Valley: This valley has seen significant growth in recent years, driven by its proximity to Los Angeles and its affordable housing options. It is home to a growing aerospace industry and a number of military bases.
-
The Coachella Valley: This valley has become a popular destination for tourism, with its desert landscapes, golf courses, and resorts. It also serves as a center for the Coachella Valley Music and Arts Festival, a major cultural event.
A Balancing Act: The Challenges of Urbanization in Southern California Valleys
The urbanization of Southern California’s valleys has brought both opportunities and challenges. While the region has benefited from economic growth and population expansion, the rapid development has also led to environmental concerns, infrastructure strain, and social inequities.
-
Environmental Impacts: Urban sprawl has resulted in the loss of agricultural land, habitat fragmentation, and increased air and water pollution. The region’s water resources are also under strain as the demand for water continues to grow.
-
Infrastructure Strain: The rapid growth of Southern California’s valleys has put a strain on the region’s infrastructure, leading to traffic congestion, overcrowded schools, and inadequate public transportation.
-
Social Inequities: The rapid urbanization of the region has led to disparities in housing affordability, access to quality education, and healthcare.
A Call for Sustainable Solutions: The Future of Southern California Valleys
The future of Southern California’s valleys will depend on the region’s ability to address the challenges of urbanization while preserving the natural beauty and agricultural heritage of these important landscapes.
-
Sustainable Urban Development: The region must adopt sustainable urban development practices that promote density, mixed-use development, and public transportation.
-
Water Conservation: The region must implement water conservation measures to reduce the strain on its water resources, such as using drought-tolerant landscaping and promoting water-efficient appliances.
-
Environmental Protection: The region must prioritize the protection of natural habitats, agricultural land, and open spaces.
-
Social Equity: The region must address social inequities by promoting affordable housing, improving access to education and healthcare, and ensuring equitable distribution of resources.
FAQs About Southern California Valleys
Q: What are the main geographical features of Southern California valleys?
A: Southern California valleys are characterized by their relatively flat terrain, surrounded by mountains or hills. They are formed by geological processes such as faulting, uplift, and erosion.
Q: What are the major agricultural products grown in Southern California valleys?
A: Southern California valleys are known for their production of citrus fruits, avocados, grapes, walnuts, dates, alfalfa, and other crops.
Q: How have Southern California valleys been affected by urbanization?
A: Urbanization has led to the conversion of agricultural land to residential and commercial uses, increased traffic congestion, and environmental challenges such as air and water pollution.
Q: What are some of the challenges facing Southern California valleys in the future?
A: The region faces challenges such as water scarcity, air pollution, traffic congestion, and social inequities.
Q: What can be done to address the challenges facing Southern California valleys?
A: Solutions include promoting sustainable urban development, conserving water resources, protecting the environment, and addressing social inequities.
Tips for Exploring Southern California Valleys
-
Visit local farmers markets: Immerse yourself in the region’s agricultural heritage by visiting local farmers markets, where you can sample fresh produce and interact with local farmers.
-
Explore hiking trails: Hike through the mountains surrounding the valleys to enjoy stunning views and experience the region’s natural beauty.
-
Visit historical sites: Discover the rich history of the region by visiting historical sites, such as missions, ranchos, and old town centers.
-
Attend cultural events: Experience the diverse cultural heritage of the valleys by attending festivals, concerts, and other cultural events.
-
Support local businesses: Support the local economy by patronizing local businesses, restaurants, and shops.
Conclusion
Southern California’s valleys, shaped by geological forces, nurtured by a temperate climate, and transformed by urbanization, represent a captivating tapestry of nature, agriculture, and urban development. Their future lies in the region’s ability to balance economic growth with environmental protection and social equity. By embracing sustainable practices, preserving natural resources, and addressing social challenges, Southern California can ensure that its valleys continue to thrive as vibrant and livable landscapes for generations to come.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographic Tapestry: Unveiling the Southern California Valleys. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
