A Network of Seismic Scars: Understanding Southern California’s Fault Lines
Related Articles: A Network of Seismic Scars: Understanding Southern California’s Fault Lines
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Network of Seismic Scars: Understanding Southern California’s Fault Lines. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Network of Seismic Scars: Understanding Southern California’s Fault Lines
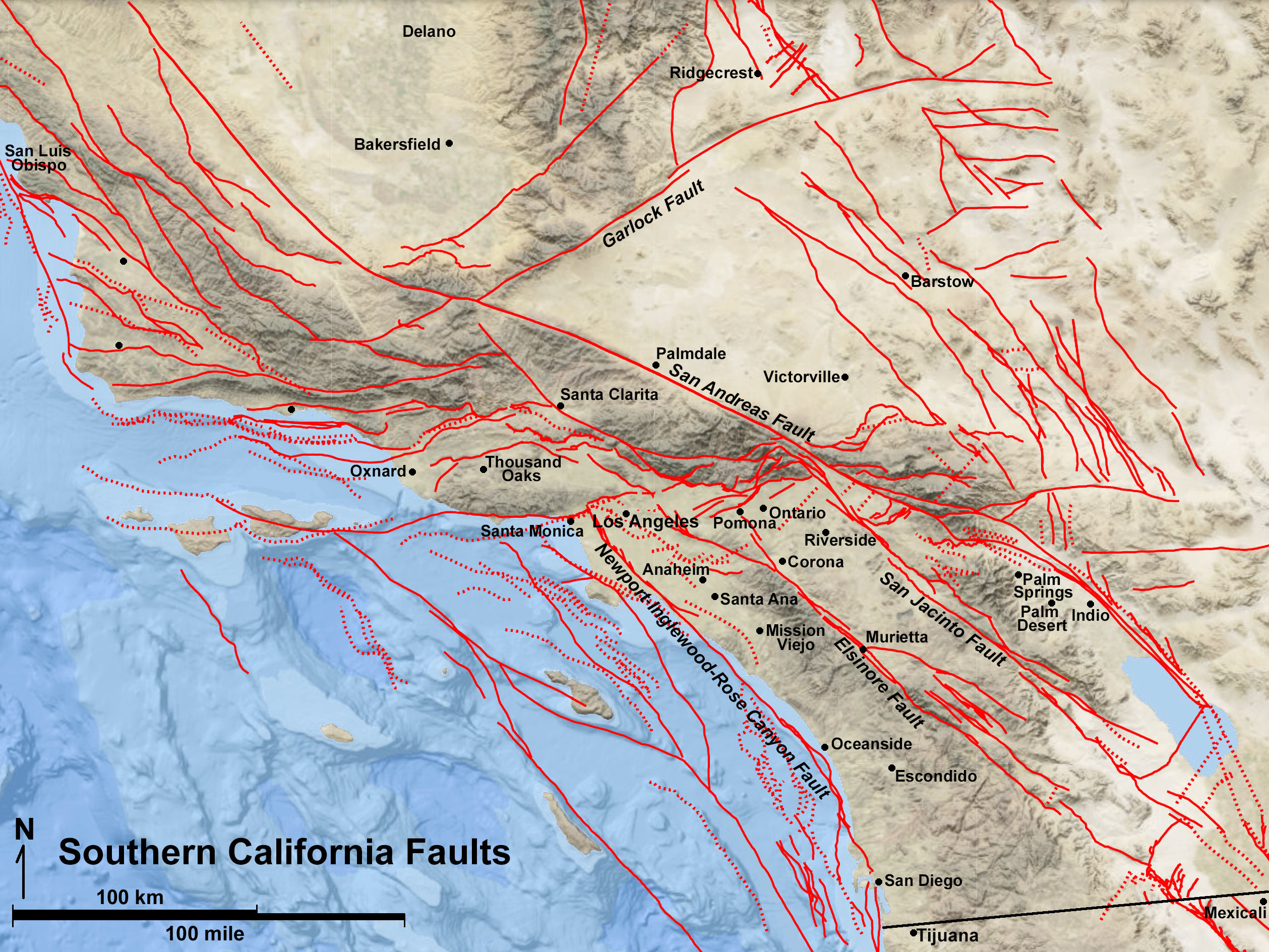
Southern California, a region renowned for its stunning landscapes and vibrant cities, sits atop a complex network of fault lines. These geological fractures, remnants of tectonic plate interactions, are responsible for shaping the region’s geography and, unfortunately, are the source of its seismic vulnerability. Understanding the intricate map of these fault lines is paramount for mitigating the risks associated with earthquakes and ensuring the safety of its inhabitants.
The Tectonic Tapestry: A Complex Dance of Plates
The Earth’s crust is composed of massive plates that constantly move and interact, creating various geological phenomena. Southern California lies at the intersection of two major plates: the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate. These plates are moving in opposite directions, with the Pacific Plate sliding northward relative to the North American Plate. This movement, known as the San Andreas Fault System, is the primary driver of seismic activity in the region.
The San Andreas Fault System: A Master Fault and Its Tributaries
The San Andreas Fault, a 800-mile long fault that traverses California, is the most prominent feature of this system. It marks the boundary between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate. This fault is a "strike-slip fault," meaning that the plates slide horizontally past each other. The San Andreas Fault is responsible for some of the most significant earthquakes in California’s history, including the 1906 San Francisco earthquake and the 1989 Loma Prieta earthquake.
However, the San Andreas Fault is not the only player in this tectonic drama. A network of smaller faults, known as "tributary faults," branch off the main fault, contributing to the complex seismic landscape of Southern California. These tributary faults, such as the San Jacinto Fault, the Elsinore Fault, and the Newport-Inglewood Fault, can generate their own earthquakes, often smaller in magnitude but still capable of causing significant damage.
The Fault Line Map: A Visual Guide to Seismic Risk
The Southern California fault lines map serves as a crucial tool for understanding the region’s seismic hazard. It depicts the locations of major and minor faults, providing a visual representation of the potential for earthquakes. This map is essential for various purposes:
- Seismic Hazard Assessment: The map allows scientists and engineers to assess the likelihood and potential impact of earthquakes in different areas. This information is vital for developing building codes, designing infrastructure, and planning emergency response strategies.
- Land Use Planning: The map helps policymakers and developers make informed decisions regarding land use. Areas with high seismic risk may be designated for less dense development or require stricter building regulations to minimize potential damage.
- Public Awareness and Education: The map plays a critical role in educating the public about earthquake hazards and promoting preparedness. By understanding the location of fault lines, individuals can take steps to mitigate risks in their homes and communities.
Understanding the Map: Key Features and Interpretations
The Southern California fault lines map is a complex representation of geological data. Key features to understand include:
- Fault Lines: These are depicted as lines on the map, representing the location where the Earth’s crust has broken and moved.
- Fault Types: The map may indicate the type of fault, such as strike-slip, normal, or reverse faults, each with its own characteristic movement.
- Fault Zones: These are areas where multiple faults intersect or are closely spaced, indicating higher seismic risk.
- Magnitude and Frequency: The map may also provide information about the historical earthquake magnitudes and frequencies along specific fault lines, offering insights into potential seismic activity.
Beyond the Map: The Importance of Continuous Research
While the fault lines map provides a static representation of the region’s seismic landscape, the Earth’s crust is constantly in motion. Ongoing research and monitoring are crucial for updating the map and refining our understanding of fault behavior. Technological advancements, such as GPS measurements, seismic monitoring networks, and advanced modeling techniques, contribute to a more comprehensive picture of seismic risk.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Southern California Fault Lines
Q: How often do earthquakes occur in Southern California?
A: Southern California experiences earthquakes of varying magnitudes frequently. While large earthquakes are less common, smaller tremors occur regularly. The region averages about 10,000 earthquakes per year, most of which are too small to be felt.
Q: What is the largest earthquake recorded in Southern California?
A: The largest recorded earthquake in Southern California was the 1857 Fort Tejon earthquake, estimated to have had a magnitude of 7.9. It occurred along the San Andreas Fault and caused significant damage across a wide area.
Q: Are there any active faults in Southern California that have not ruptured in a long time?
A: Yes, there are several active faults in Southern California that have not experienced a major earthquake in recent history. These "locked" faults are considered to be at high risk for future seismic activity.
Q: How can I prepare for an earthquake in Southern California?
A: Earthquake preparedness is crucial for residents of Southern California. Key steps include:
- Securing heavy objects: Anchor furniture and appliances to prevent them from falling during an earthquake.
- Creating an emergency kit: Prepare a kit with essential supplies such as water, food, first-aid, and a flashlight.
- Developing an evacuation plan: Know where to go and how to get there in case of an earthquake.
- Staying informed: Monitor news and emergency alerts for updates on earthquake activity.
Tips for Navigating the Fault Lines Map
- Consult reputable sources: Refer to maps and information provided by organizations such as the United States Geological Survey (USGS) and the California Geological Survey (CGS).
- Understand the scale: Pay attention to the scale of the map and the relative size of fault lines.
- Consider the context: Understand the location of major cities, infrastructure, and population centers in relation to fault lines.
- Stay updated: Regularly check for updates and revisions to the fault lines map as new data becomes available.
Conclusion: Living with Seismic Reality
Southern California’s fault lines are a constant reminder of the dynamic nature of our planet. While the threat of earthquakes is real, understanding the region’s seismic landscape empowers us to mitigate risks and build resilient communities. By utilizing the fault lines map, embracing preparedness measures, and staying informed about the latest research, we can navigate this challenging environment and ensure the safety and well-being of future generations.



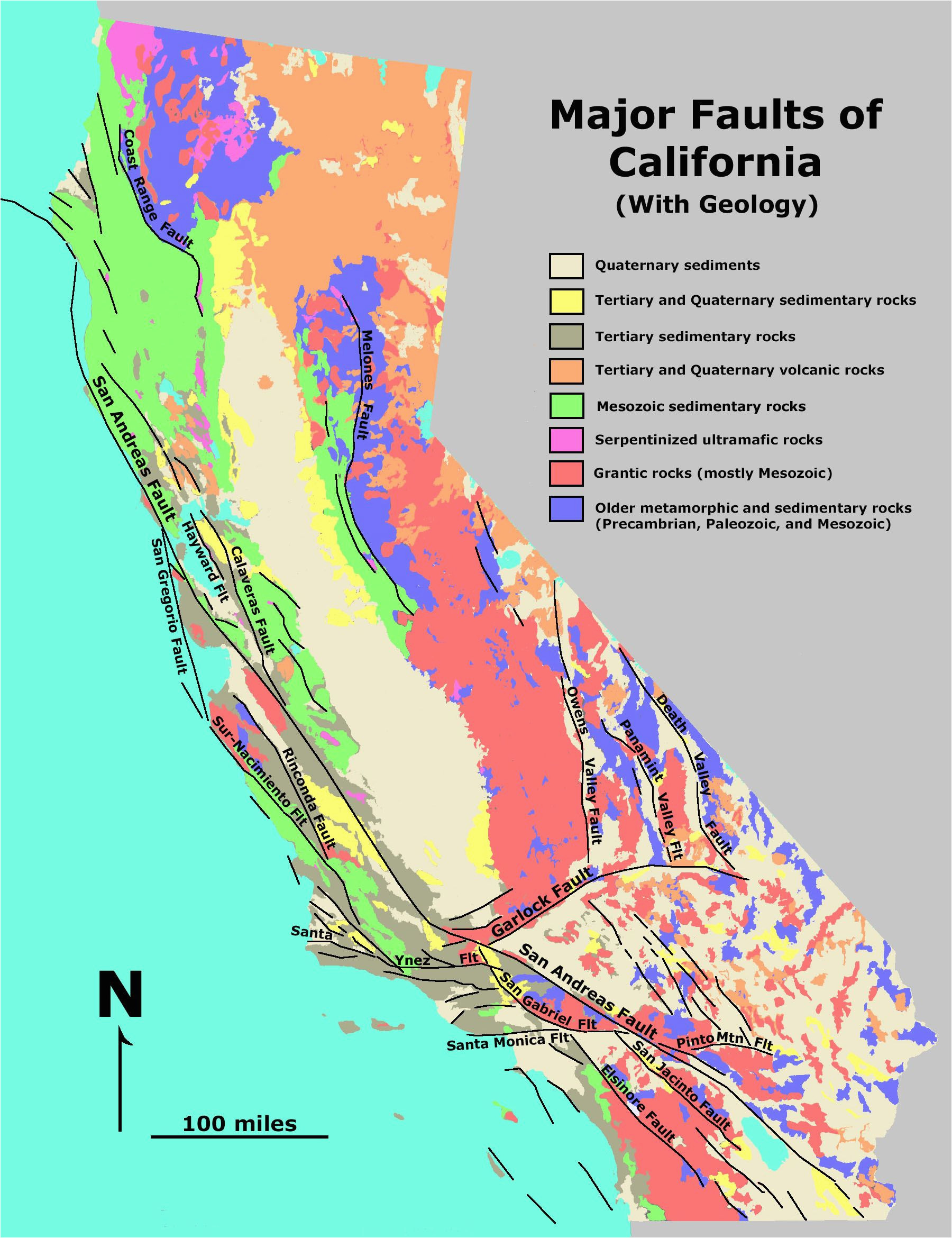


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Network of Seismic Scars: Understanding Southern California’s Fault Lines. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
