A Topographical Tapestry: Exploring the Southern California Mountains
Related Articles: A Topographical Tapestry: Exploring the Southern California Mountains
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Topographical Tapestry: Exploring the Southern California Mountains. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Topographical Tapestry: Exploring the Southern California Mountains
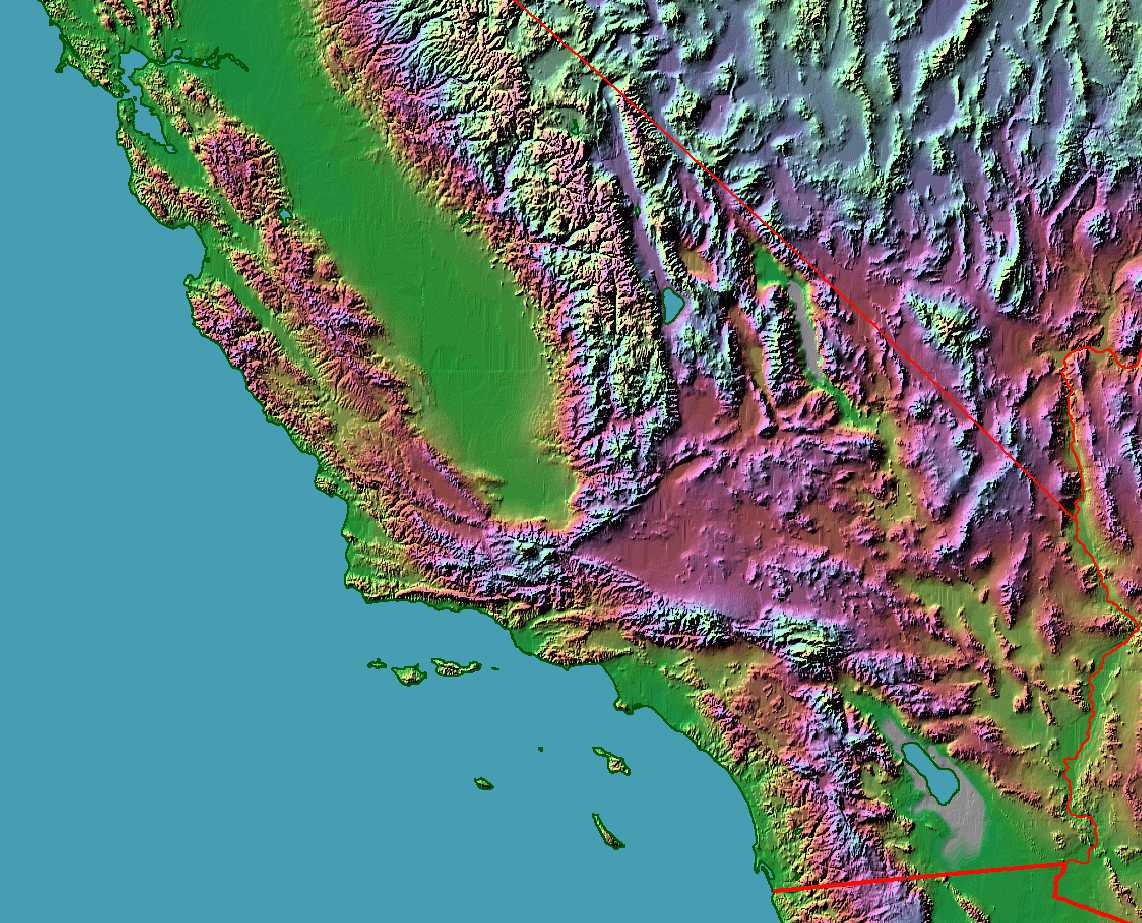
Southern California, renowned for its sun-drenched beaches and vibrant urban landscapes, also boasts a rugged and awe-inspiring mountain terrain. These peaks, canyons, and valleys, stretching from the Pacific coast to the Mojave Desert, form a captivating landscape that profoundly shapes the region’s climate, ecology, and human history. Understanding the intricate topography of these mountains is essential for comprehending the region’s unique character and appreciating the delicate balance of its natural systems.
A Diverse and Dramatic Landscape
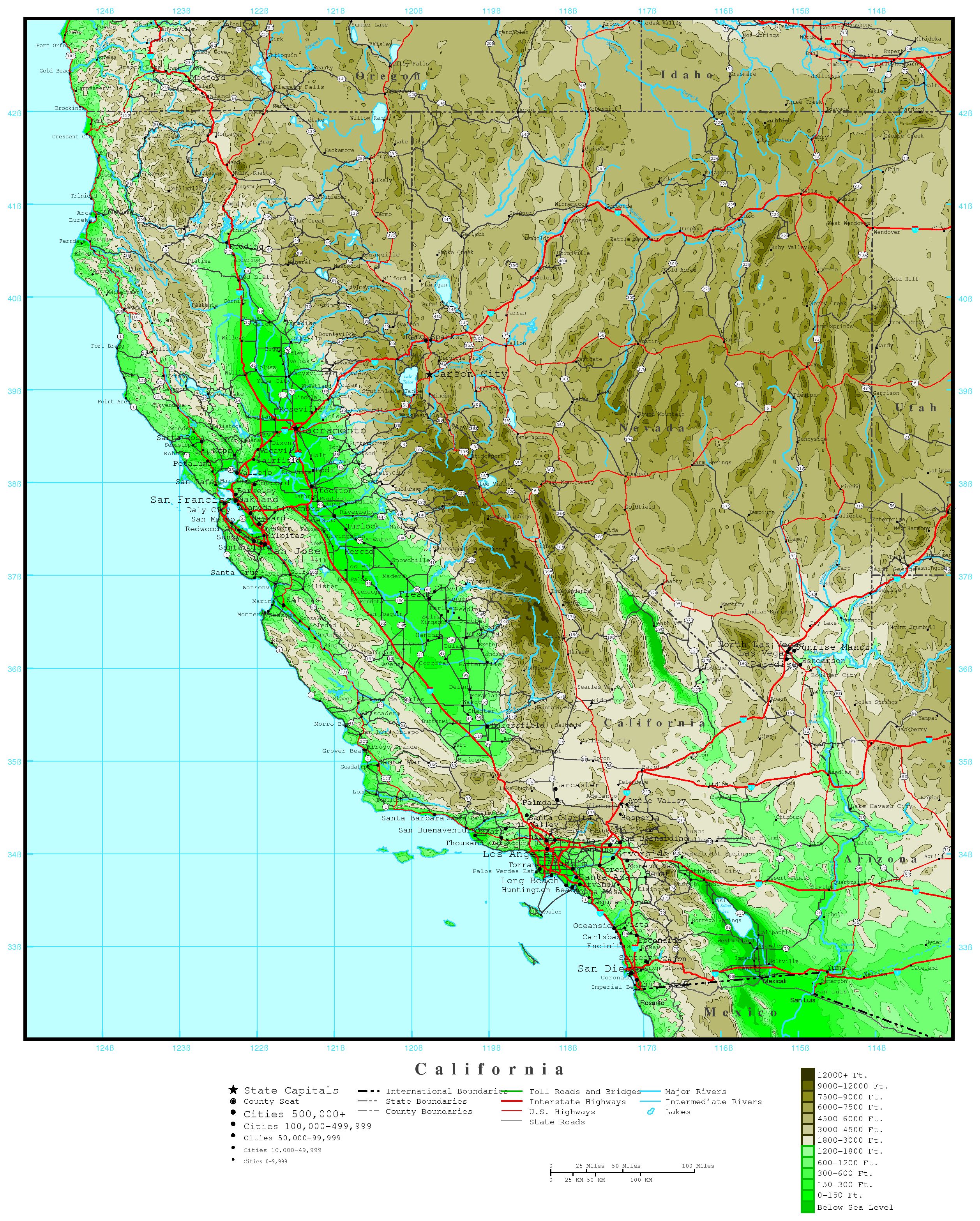
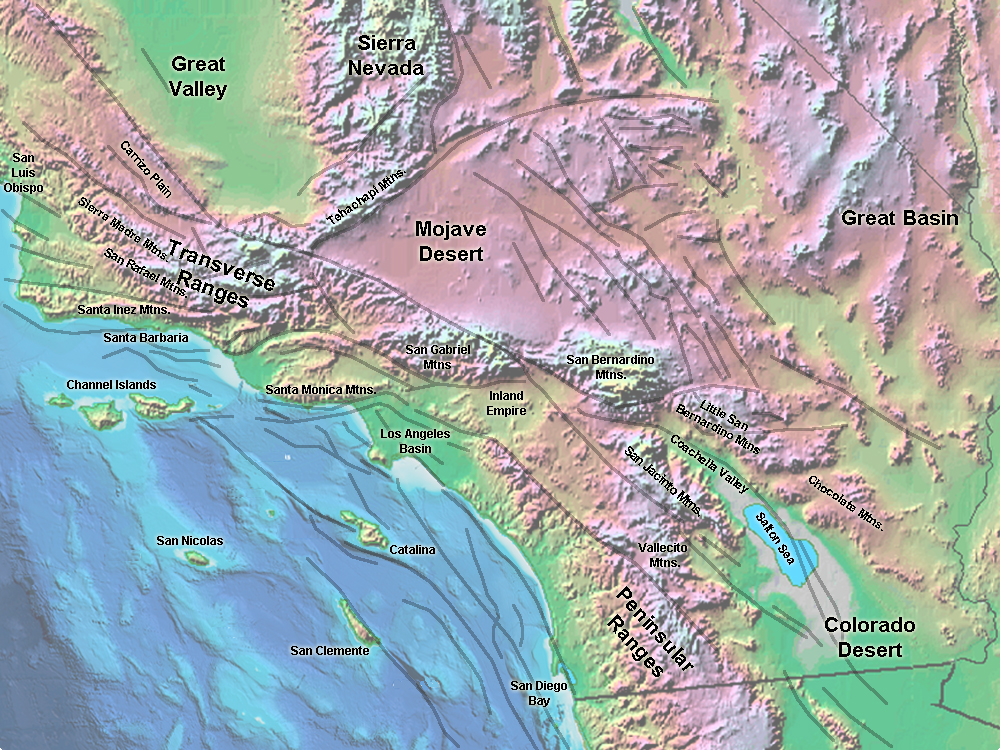
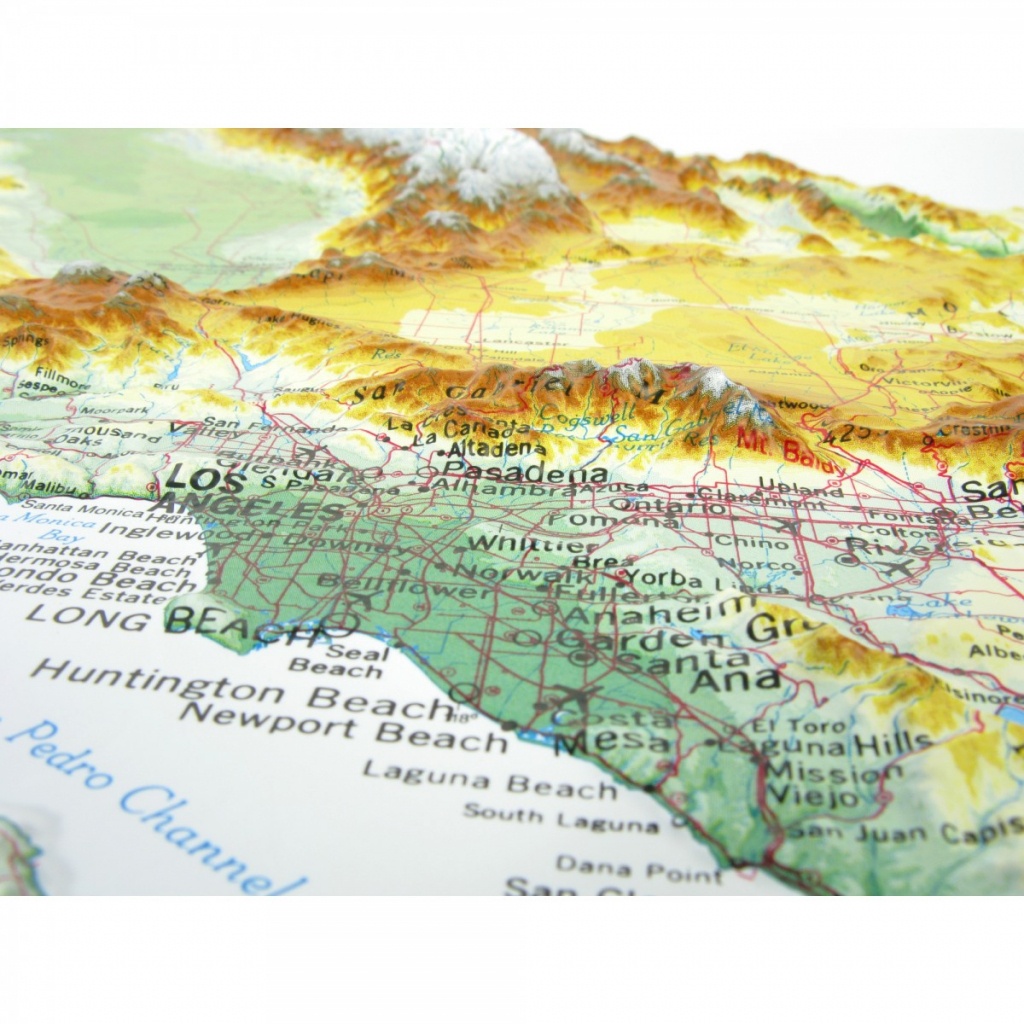
The Southern California mountains are a mosaic of diverse geological formations, each contributing to the region’s distinctive topography. The San Gabriel Mountains, rising east of Los Angeles, are part of the Transverse Ranges, a unique geological feature that runs perpendicular to the dominant north-south trend of the Pacific Coast Ranges. This unusual orientation is a result of tectonic forces that have shaped the region over millions of years. The San Gabriel Mountains are characterized by granite peaks, deep canyons, and rugged slopes, their highest point being Mount San Antonio (also known as Mount Baldy), reaching over 10,000 feet.
To the north, the San Bernardino Mountains, also part of the Transverse Ranges, are a vast and imposing mountain range. Their highest peak, San Gorgonio Mountain, stands at over 11,500 feet, making it the highest peak in Southern California. These mountains are known for their dense forests, alpine meadows, and numerous lakes and streams, providing a haven for diverse wildlife.
Further east, the Mojave Desert transitions into the San Jacinto Mountains, part of the Peninsular Ranges. These mountains, running parallel to the coast, are characterized by steep slopes, deep canyons, and dramatic granite peaks, including the iconic San Jacinto Peak, reaching over 10,800 feet. The San Jacinto Mountains are a critical water source for the region, with numerous springs and streams feeding into the Coachella Valley below.
A Tapestry of Ecosystems
The Southern California mountains are home to a stunning array of ecosystems, each adapted to the unique conditions of elevation, rainfall, and exposure. At lower elevations, chaparral, a dense scrubland of drought-tolerant shrubs, dominates the landscape. This ecosystem is fire-adapted, with frequent wildfires playing a crucial role in its regeneration and biodiversity.
As elevation increases, the chaparral transitions into coniferous forests, dominated by ponderosa pine, Jeffrey pine, and white fir. These forests, with their towering trees and dense undergrowth, provide habitat for a wide variety of animals, including black bears, mountain lions, and various bird species.
Above the treeline, alpine meadows and rocky summits offer a unique environment. These high-altitude ecosystems, exposed to harsh weather conditions, are home to specialized plants and animals adapted to extreme cold and limited growing seasons.
The Importance of Water
The Southern California mountains play a vital role in the region’s water supply. Snowfall in the higher elevations accumulates as a vast reservoir of water, slowly melting throughout the spring and summer months. This meltwater feeds numerous rivers and streams, providing drinking water for millions of residents and supporting agriculture in the region.
The mountains also act as a natural filter, purifying the water that flows through them. The dense vegetation and rocky terrain slow the flow of water, allowing sediments and pollutants to settle out. This natural filtration process ensures a clean and reliable water supply for the region.
Human Impact and Conservation
The Southern California mountains have been shaped by human activity for centuries. Native American tribes have lived in and around these mountains for thousands of years, utilizing their resources sustainably. European settlement brought significant changes, with logging, mining, and agriculture transforming the landscape.
Today, these mountains face challenges related to urbanization, climate change, and invasive species. The growing population of Southern California puts pressure on water resources, leading to competition for water rights and concerns about drought. Climate change is altering the frequency and intensity of wildfires, posing risks to human communities and natural ecosystems. Invasive species, introduced through human activities, threaten native biodiversity and ecosystem balance.
Conservation efforts are crucial to protect the Southern California mountains. National parks, wilderness areas, and conservation organizations work to preserve the region’s natural beauty and ecological integrity. These efforts focus on protecting water resources, managing wildfires, controlling invasive species, and promoting sustainable land use practices.
FAQs
Q: What are the major mountain ranges in Southern California?
A: The major mountain ranges in Southern California include the Transverse Ranges (San Gabriel Mountains, San Bernardino Mountains), the Peninsular Ranges (San Jacinto Mountains), and the Santa Monica Mountains.
Q: What are the highest peaks in Southern California?
A: The highest peak in Southern California is San Gorgonio Mountain in the San Bernardino Mountains, reaching over 11,500 feet. Other notable peaks include Mount San Antonio (Mount Baldy) in the San Gabriel Mountains and San Jacinto Peak in the San Jacinto Mountains.
Q: What are the main ecosystems found in the Southern California mountains?
A: The Southern California mountains support a diversity of ecosystems, including chaparral, coniferous forests, alpine meadows, and rocky summits. Each ecosystem is adapted to specific elevation, rainfall, and exposure conditions.
Q: How do the Southern California mountains influence the region’s water supply?
A: The mountains play a vital role in water supply by acting as a natural reservoir for snowmelt, providing drinking water for millions of residents and supporting agriculture. They also act as a natural filter, purifying water that flows through them.
Q: What are the challenges facing the Southern California mountains?
A: The mountains face challenges related to urbanization, climate change, and invasive species. These challenges threaten water resources, biodiversity, and human communities.
Tips
- Explore the mountains: Hike, camp, or explore the numerous trails and parks in the Southern California mountains. Experience the diverse landscapes and ecosystems firsthand.
- Learn about conservation efforts: Support organizations working to protect the region’s natural resources and promote sustainable land use practices.
- Be a responsible visitor: Follow Leave No Trace principles when visiting the mountains, minimizing your impact on the environment.
- Educate yourself about the region’s history: Learn about the indigenous cultures that have inhabited these mountains for centuries and the impact of European settlement.
Conclusion
The Southern California mountains are a vital part of the region’s natural and cultural heritage. Their rugged beauty, diverse ecosystems, and essential role in water supply make them a treasure to be cherished and protected. Understanding the intricate topography and ecological dynamics of these mountains is crucial for appreciating their value and ensuring their continued health for future generations. By embracing responsible stewardship and supporting conservation efforts, we can preserve the unique and awe-inspiring character of the Southern California mountains for years to come.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Topographical Tapestry: Exploring the Southern California Mountains. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
