Decoding Southern California’s Climate: A Comprehensive Guide to the Regional Climate Zones
Related Articles: Decoding Southern California’s Climate: A Comprehensive Guide to the Regional Climate Zones
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Decoding Southern California’s Climate: A Comprehensive Guide to the Regional Climate Zones. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Decoding Southern California’s Climate: A Comprehensive Guide to the Regional Climate Zones
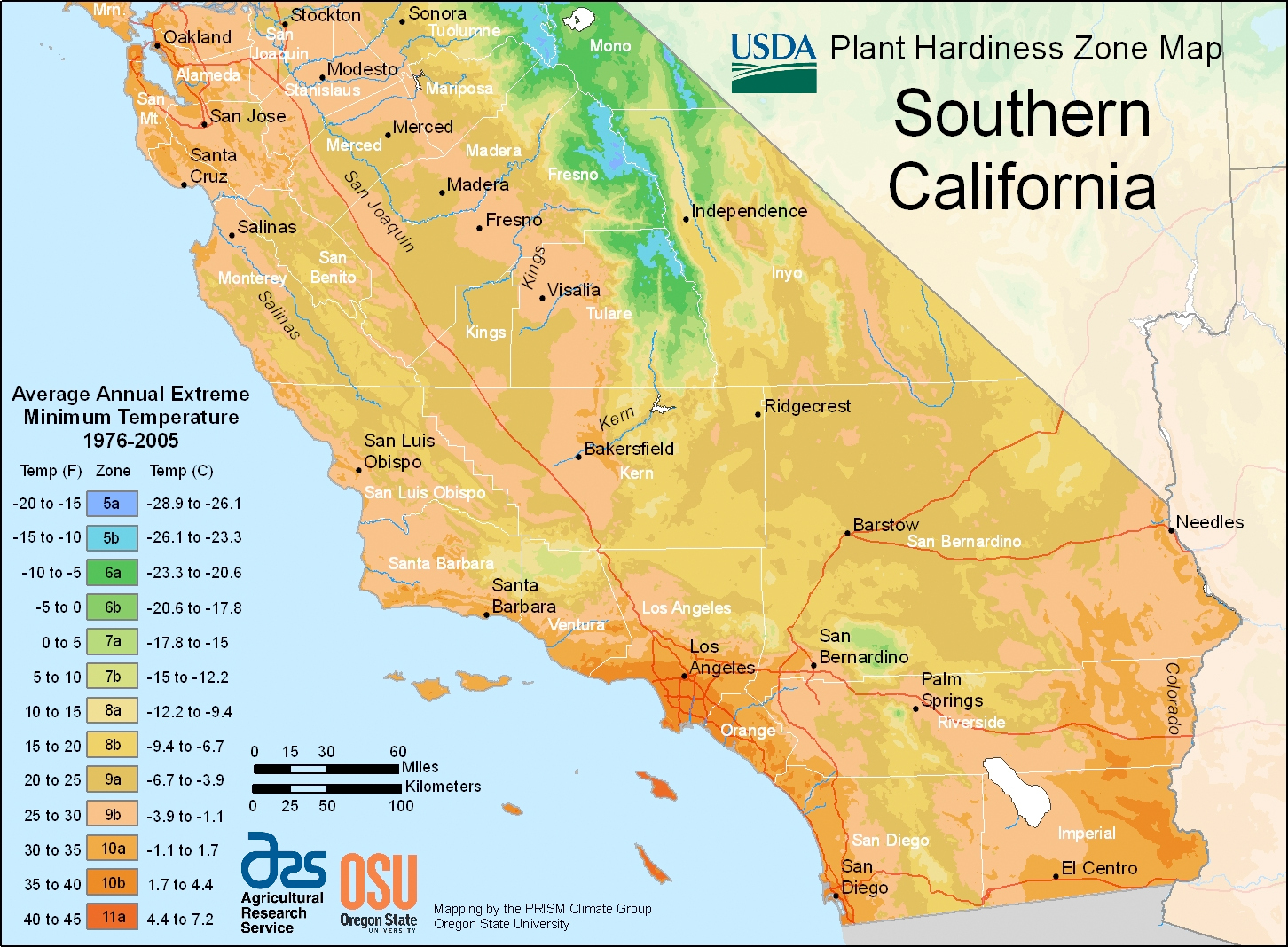
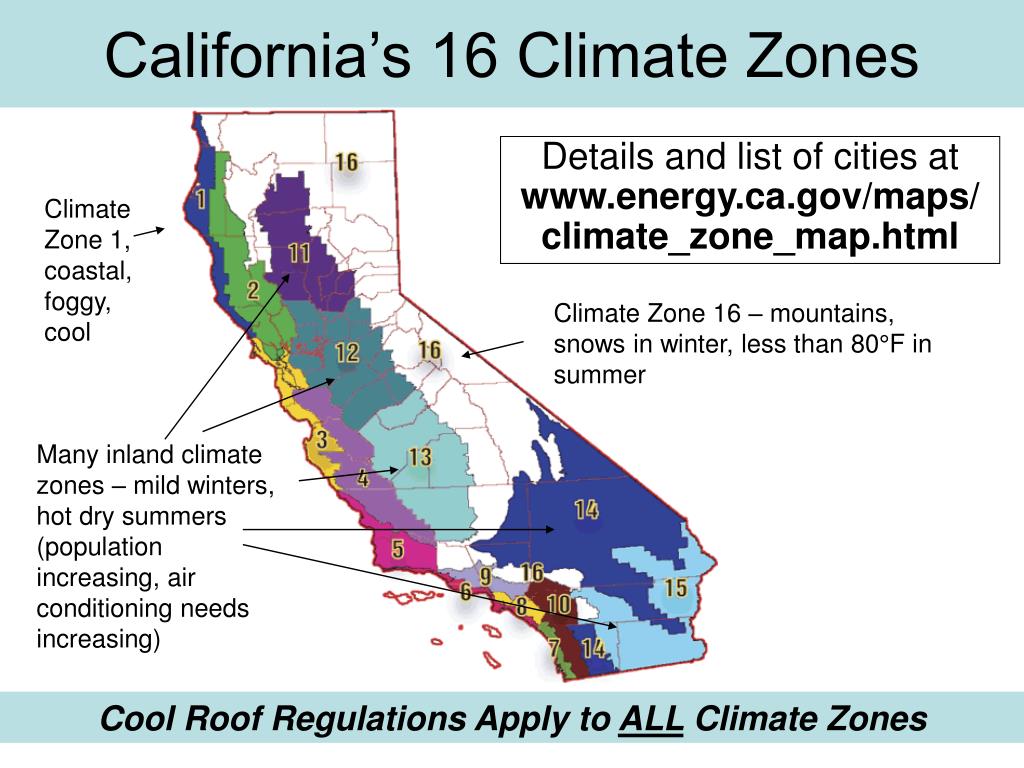
Southern California, renowned for its sun-drenched beaches and diverse landscapes, is a region shaped by a complex interplay of climate factors. Understanding the nuances of its climate zones is crucial for a myriad of applications, from informed land use planning and agricultural practices to effective water management and disaster preparedness. This article delves into the intricacies of the Southern California climate zone map, exploring its significance and providing a comprehensive guide to its utilization.
A Tapestry of Climate Zones:
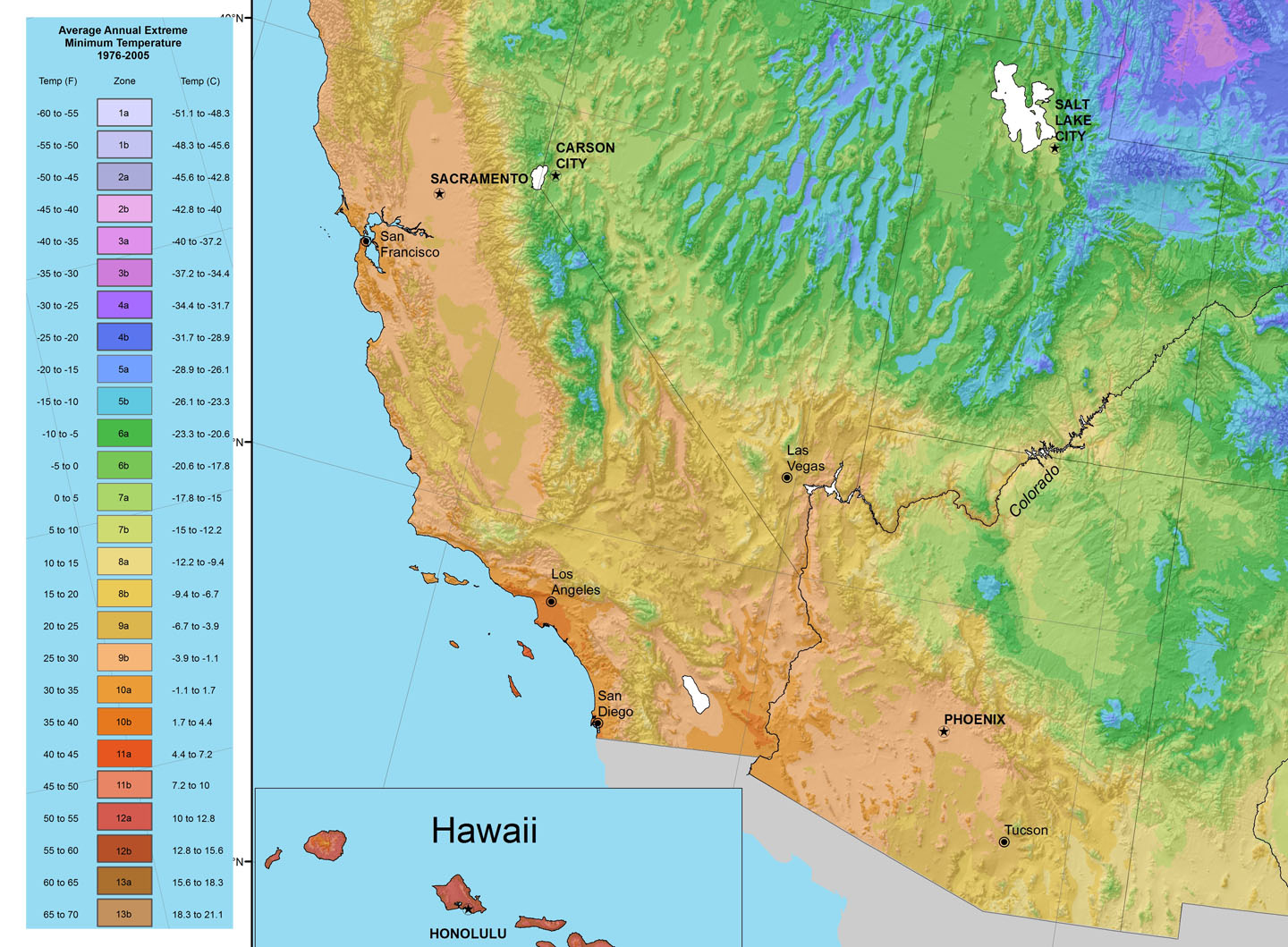
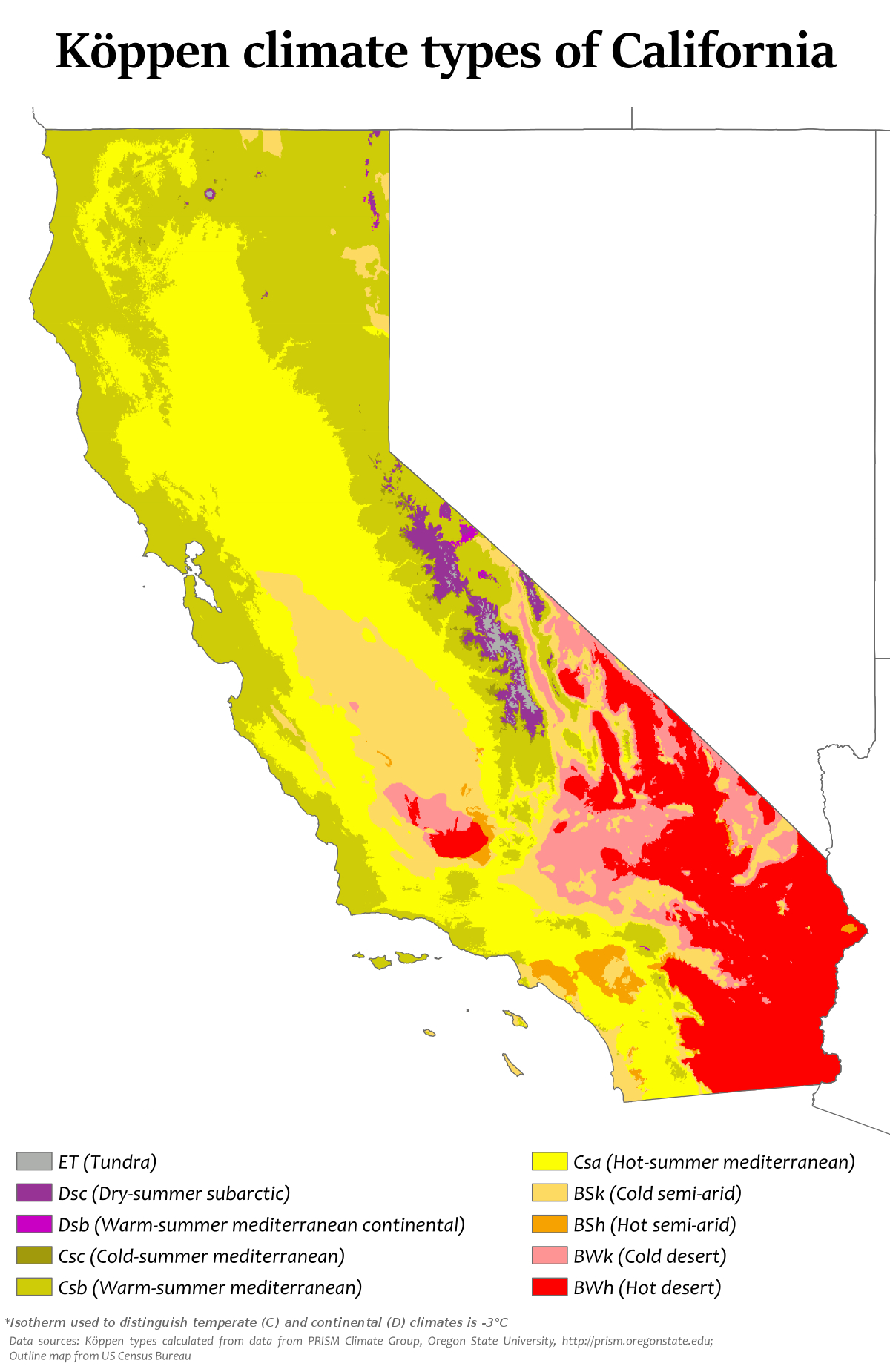
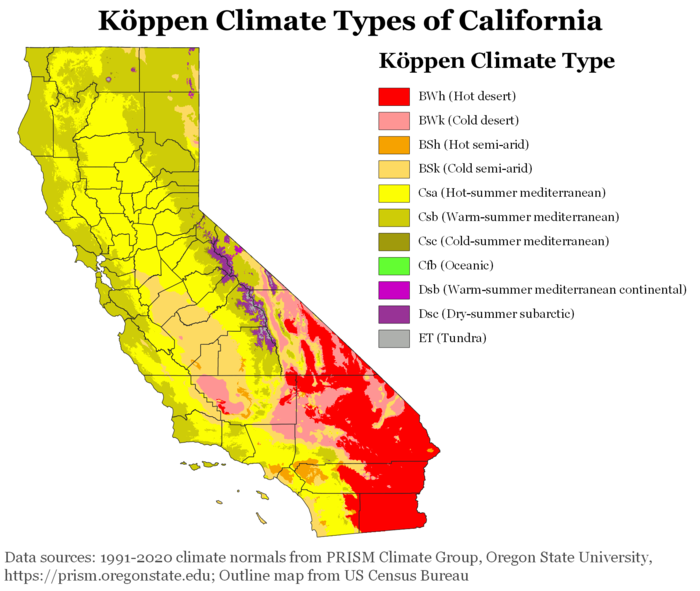
Southern California’s climate is not a monolithic entity. Instead, it is a mosaic of distinct zones, each characterized by unique temperature patterns, precipitation levels, and prevailing winds. These zones are defined by the Köppen-Geiger climate classification system, a widely recognized framework used to categorize global climates based on temperature and precipitation patterns.
The Dominant Zones:
-
Mediterranean Climate (Csa): This zone, encompassing coastal areas and the inland valleys, experiences warm, dry summers and mild, wet winters. This is the quintessential Southern California climate, characterized by sunny skies and relatively stable temperatures.
-
Semi-Arid Climate (BSk): Inland regions, particularly the eastern portions of the region, fall under this classification. These areas experience hot, dry summers and cooler, less wet winters than the Mediterranean zone.
-
Highland Climate (Dfb): The higher elevations of the San Gabriel Mountains and the San Bernardino Mountains exhibit a highland climate, with cold winters featuring snowfall and warm, dry summers.
Factors Shaping the Climate Zones:
Several factors contribute to the diverse climate zones of Southern California:
-
Latitude: Southern California’s location between 32° and 37° north latitude places it within the subtropical zone, receiving ample sunshine and warm temperatures.
-
Topography: The region’s dramatic topography, with mountain ranges running parallel to the coast, creates a rain shadow effect. Air masses moving inland from the Pacific Ocean are forced to rise, releasing moisture on the windward slopes. The leeward slopes, sheltered from the rain, experience drier conditions.
-
Ocean Currents: The California Current, a cold current flowing southward along the Pacific Coast, moderates coastal temperatures, resulting in cooler summers and warmer winters than inland regions.
-
Urban Heat Island Effect: The dense urban development in Southern California contributes to higher temperatures within cities compared to surrounding rural areas.
The Significance of the Climate Zone Map:
Understanding the nuances of Southern California’s climate zones is crucial for various applications:
-
Land Use Planning: The map guides land use decisions, ensuring that development is aligned with the specific climate conditions of each zone. For instance, areas with high fire risk might be designated for low-density development or specific vegetation types.
-
Agriculture: Farmers can tailor their crops and irrigation practices to the specific climate characteristics of their region. Knowing the water availability and temperature patterns allows for optimal crop selection and efficient water management.
-
Water Resources Management: The map helps in understanding the distribution of water resources and planning for sustainable water use. Areas with higher precipitation receive more water, while drier regions require efficient water conservation strategies.
-
Disaster Preparedness: The map provides valuable insights into potential hazards associated with each climate zone. For example, areas prone to drought require proactive fire prevention measures, while coastal zones need to be prepared for sea level rise.
FAQs about Southern California’s Climate Zone Map:
1. How does the climate zone map impact home construction?
The map influences building design choices, such as insulation levels, roof materials, and window placement. Homes in drier zones may require different ventilation strategies than those in coastal areas.
2. Can the climate zone map help in planning outdoor activities?
Yes, the map can inform outdoor activities. Knowing the temperature patterns and precipitation levels allows for planning activities that are suited to the specific climate conditions of the chosen location.
3. How can the climate zone map assist in mitigating climate change impacts?
The map helps in identifying vulnerable areas and developing targeted strategies for climate change adaptation. For example, areas with high fire risk might benefit from vegetation management programs, while coastal zones may require infrastructure improvements to mitigate sea level rise.
Tips for Using the Southern California Climate Zone Map:
-
Consult with local experts: Engage with local planners, agricultural specialists, and environmental organizations to gain deeper insights into the specific implications of the climate zones within your area.
-
Consider microclimates: While the map provides a general overview, remember that microclimates can exist within larger zones. Factors like elevation, slope, and vegetation can create localized variations.
-
Stay informed about climate change: Climate change is altering precipitation patterns and temperature regimes, potentially leading to shifts in climate zones. Stay updated on the latest research and projections to anticipate future changes.
Conclusion:
Southern California’s climate zone map is a valuable tool for understanding the region’s diverse climate conditions. By providing a framework for comprehending temperature, precipitation, and other climatic factors, the map supports informed decision-making across various sectors. From land use planning and agricultural practices to water management and disaster preparedness, the map empowers stakeholders to make informed choices that promote sustainable development and resilience in the face of climate change.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Decoding Southern California’s Climate: A Comprehensive Guide to the Regional Climate Zones. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
