ford 6.7 map sensor
Related Articles: ford 6.7 map sensor
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to ford 6.7 map sensor. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
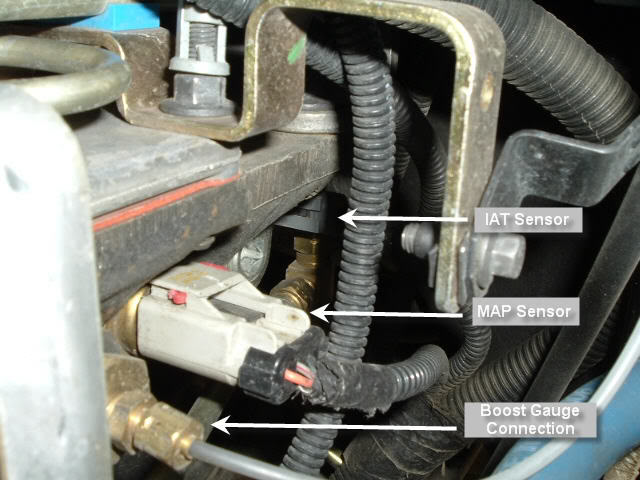
The Ford 6.7L Power Stroke: A Deep Dive into the Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor

The Ford 6.7L Power Stroke engine, a powerhouse of torque and efficiency, relies on a complex network of sensors and actuators to deliver optimal performance. One crucial component in this intricate system is the Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor. This seemingly small device plays a vital role in the engine’s ability to breathe, respond to changing conditions, and ultimately, deliver the power and fuel economy drivers expect.
The Role of the MAP Sensor: A Window into Engine Breathing
The MAP sensor is essentially the engine’s "lung capacity" gauge. It measures the absolute pressure within the intake manifold, a critical factor in determining the amount of air entering the cylinders. This information is relayed to the engine control module (ECM), the brain of the engine, which then calculates the appropriate fuel injection timing and duration.
How the MAP Sensor Works: The Science of Pressure Sensing
The MAP sensor utilizes a piezoresistive element, a material whose electrical resistance changes with applied pressure. When air pressure within the intake manifold increases, the piezoresistive element within the MAP sensor experiences a corresponding change in resistance. This change is measured by the ECM, which translates it into a precise pressure reading.
The MAP Sensor’s Importance: A Multifaceted Impact
The MAP sensor’s influence extends beyond simply measuring pressure. Its accurate readings are essential for:
- Fuel Injection Control: The ECM utilizes the MAP sensor data to calculate the precise amount of fuel required for each combustion cycle, optimizing fuel efficiency and minimizing emissions.
- Ignition Timing: By understanding the pressure within the intake manifold, the ECM can adjust the ignition timing to maximize combustion efficiency and minimize knocking.
- Boost Control: In turbocharged engines, the MAP sensor plays a critical role in monitoring and controlling boost pressure, ensuring optimal performance without exceeding safe limits.
- Emissions Control: The MAP sensor data is used to adjust emissions control systems, such as the Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) valve, to ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
Symptoms of a Faulty MAP Sensor: Recognizing the Warning Signs
A malfunctioning MAP sensor can lead to a variety of symptoms, including:
- Engine Stalling or Hesitation: An inaccurate pressure reading can disrupt the fuel injection and ignition timing, causing the engine to stall or hesitate during acceleration.
- Poor Fuel Economy: An incorrect fuel-to-air ratio, caused by a faulty MAP sensor, can significantly reduce fuel efficiency.
- Rough Idle: A fluctuating intake manifold pressure can lead to an erratic idle, characterized by vibrations and uneven engine operation.
- Check Engine Light: The ECM will detect a faulty MAP sensor and illuminate the check engine light, accompanied by a corresponding diagnostic trouble code (DTC).
Troubleshooting a Faulty MAP Sensor: A Step-by-Step Guide
Diagnosing a faulty MAP sensor typically involves the following steps:
- Visual Inspection: Examine the MAP sensor for any visible damage, such as cracks, leaks, or corrosion.
- Check for Vacuum Leaks: Inspect the vacuum lines connecting the MAP sensor to the intake manifold for any leaks or loose connections.
- Use a Scan Tool: A scan tool can retrieve diagnostic trouble codes related to the MAP sensor, providing valuable insights into the nature of the malfunction.
- Perform a Pressure Test: Using a pressure gauge, test the MAP sensor’s output against known pressure values to verify its accuracy.
- Replace the MAP Sensor: If the sensor is found to be faulty, replace it with a genuine Ford part to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
FAQs about the Ford 6.7L Power Stroke MAP Sensor
Q: How often should I replace the MAP sensor?
A: The MAP sensor is generally a durable component, but it can wear out over time due to exposure to extreme temperatures, vibrations, and contaminants. Replacing the sensor every 100,000 miles or as recommended by the manufacturer is a good practice to prevent potential issues.
Q: Can I clean the MAP sensor?
A: While cleaning the sensor may seem tempting, it’s generally not recommended. The piezoresistive element is delicate and can be easily damaged. Replacing the sensor with a new one is the most reliable solution.
Q: What is the cost of replacing the MAP sensor?
A: The cost of replacing a MAP sensor can vary depending on the specific vehicle model and the chosen parts supplier. However, the cost is generally reasonable, ranging from $50 to $150 for the sensor itself, plus labor costs for installation.
Tips for Maintaining Your MAP Sensor
- Regular Maintenance: Follow the recommended maintenance schedule for your vehicle, including air filter replacements and routine inspections of vacuum lines.
- Avoid Contaminated Air: Use a high-quality air filter to prevent dust and debris from entering the intake manifold and potentially damaging the MAP sensor.
- Use Quality Parts: When replacing the MAP sensor, always choose genuine Ford parts or high-quality aftermarket alternatives to ensure compatibility and reliability.
Conclusion: The MAP Sensor’s Unseen Importance
The MAP sensor, though small and often overlooked, plays a crucial role in the performance and efficiency of the Ford 6.7L Power Stroke engine. Its accurate pressure readings provide the ECM with vital information, enabling it to optimize fuel injection, ignition timing, and boost control, resulting in a powerful, fuel-efficient, and environmentally friendly driving experience. Understanding the MAP sensor’s function, recognizing its potential issues, and implementing preventive maintenance practices can ensure the longevity and optimal performance of this vital engine component.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into ford 6.7 map sensor. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
