Harnessing the Winds of Change: A Comprehensive Look at Taiwan’s Wind Farm Map
Related Articles: Harnessing the Winds of Change: A Comprehensive Look at Taiwan’s Wind Farm Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Harnessing the Winds of Change: A Comprehensive Look at Taiwan’s Wind Farm Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Harnessing the Winds of Change: A Comprehensive Look at Taiwan’s Wind Farm Map
Taiwan, an island nation situated in the East China Sea, is a global leader in renewable energy development, particularly in the field of wind power. The island’s strategic location, characterized by strong and consistent winds, has made it an ideal location for harnessing wind energy. This article delves into the intricate landscape of Taiwan’s wind farm map, examining its evolution, geographical distribution, and the multifaceted benefits it brings to the nation.
Mapping the Winds of Progress: A Historical Perspective
Taiwan’s foray into wind energy began in the early 1990s, with the installation of a few small-scale wind farms. However, the true catalyst for large-scale development came in the late 1990s and early 2000s, driven by the government’s commitment to reducing reliance on fossil fuels and promoting sustainable energy sources. This period saw the establishment of several significant wind farms, primarily in the western and northern coastal regions, where wind speeds are generally higher.
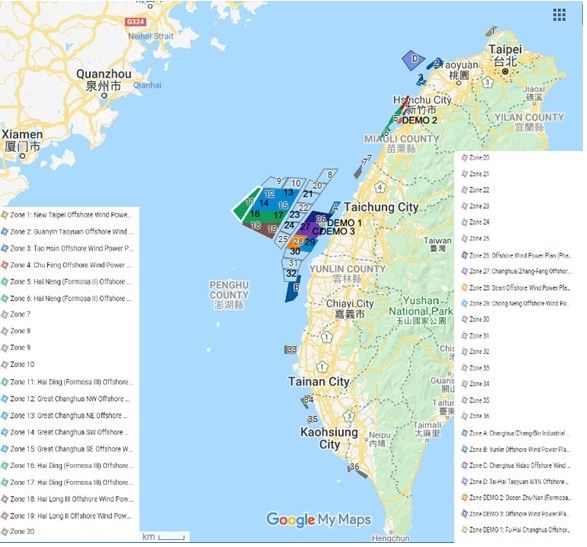
A Geographical Mosaic: Exploring the Distribution of Wind Farms
Taiwan’s wind farm map is a testament to the diverse wind resources across the island. The distribution of wind farms is heavily influenced by geographical factors, including:
- Coastal Regions: The western and northern coasts of Taiwan, exposed to the prevailing monsoon winds, are home to the majority of wind farms. These areas, including the Penghu Islands and Changhua County, benefit from strong and consistent wind speeds.
- Offshore Locations: Recognizing the potential of offshore wind resources, Taiwan has actively developed offshore wind farms in recent years. These installations, located in the Taiwan Strait and the East China Sea, are strategically positioned to capitalize on the stronger and more consistent winds found at sea.
- Mountainous Terrain: While less common, some wind farms have been established in mountainous regions, particularly in the eastern part of the island. These locations, while offering less consistent wind speeds, provide a valuable alternative for expanding wind power capacity.
The Multifaceted Benefits of Taiwan’s Wind Farm Map
Taiwan’s wind farm map is not just a geographical representation; it embodies the nation’s commitment to sustainable development and its pursuit of a cleaner energy future. The benefits of this map extend far beyond the generation of renewable electricity:
- Energy Security: Wind power significantly reduces Taiwan’s dependence on imported fossil fuels, enhancing energy security and mitigating the risks associated with volatile global energy markets.
- Environmental Sustainability: By displacing fossil fuel-based power generation, wind farms contribute to a cleaner environment, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating the impacts of climate change.
- Economic Growth: The wind energy sector has created numerous job opportunities in manufacturing, installation, maintenance, and research and development, stimulating economic growth and diversifying the economy.
- Technological Advancement: The development of wind farms has spurred innovation in renewable energy technologies, leading to advancements in turbine design, energy storage, and grid integration.
- Community Engagement: Wind farms often foster strong community partnerships, promoting local economic development and supporting environmental conservation initiatives.
Navigating the Future: Challenges and Opportunities
While Taiwan’s wind farm map showcases remarkable progress in renewable energy development, it also highlights certain challenges and opportunities for the future:
- Grid Integration: Integrating large-scale wind power into the existing electricity grid requires sophisticated infrastructure and advanced grid management systems.
- Environmental Concerns: While wind energy is generally considered environmentally friendly, potential impacts on bird and bat populations require careful mitigation measures.
- Public Acceptance: Public perception of wind farms can vary, necessitating open communication and community engagement to address concerns and ensure project acceptance.
- Technological Innovation: Continuous research and development are crucial for improving wind turbine efficiency, reducing costs, and enhancing the reliability of wind power generation.
- International Collaboration: Sharing knowledge and expertise with other countries, particularly those pursuing wind energy development, can foster global collaboration and accelerate the transition to a clean energy future.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How much wind power does Taiwan generate?
A: Taiwan’s installed wind power capacity has grown significantly in recent years. As of 2023, the island boasts over 9 GW of installed wind power capacity, contributing a substantial portion of its electricity generation.
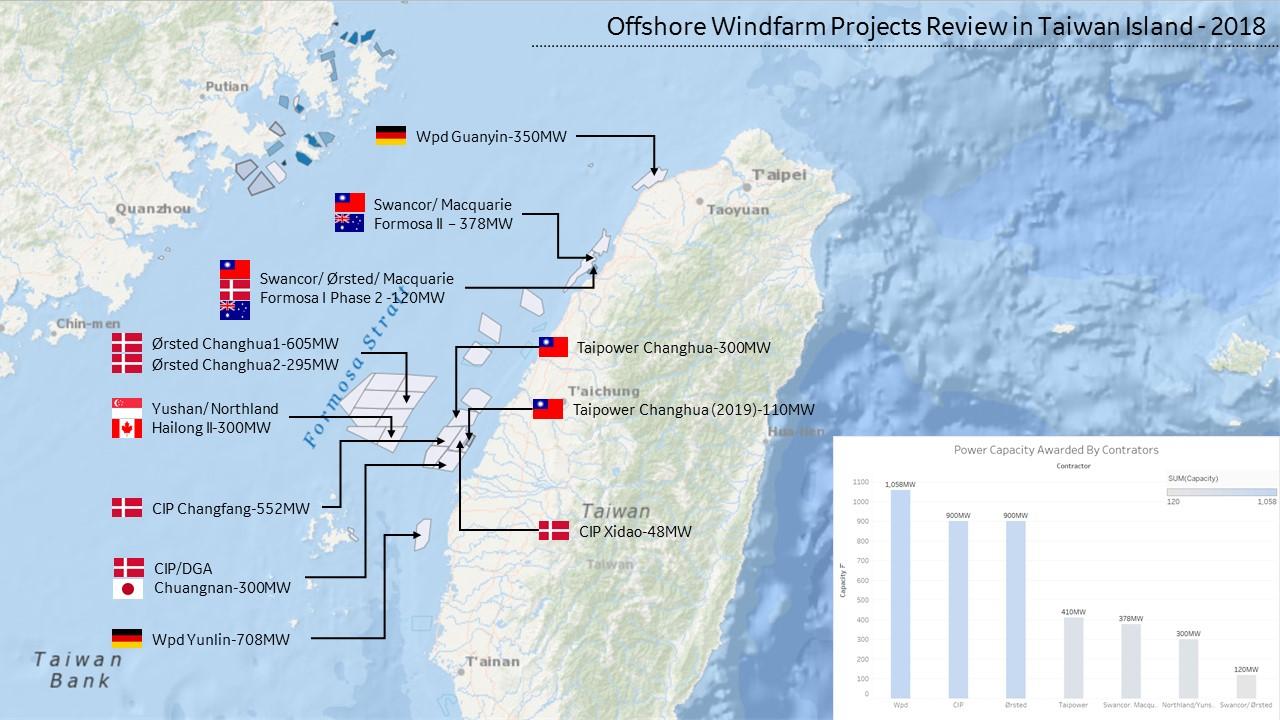
Q: What are the major wind farm projects in Taiwan?
A: Some of the most notable wind farm projects in Taiwan include the Formosa 1 and Formosa 2 offshore wind farms, the Yunlin offshore wind farm, and the Penghu wind farms.
Q: How does Taiwan’s wind farm map compare to other countries?
A: Taiwan ranks among the top countries in terms of wind power capacity per capita. The island’s commitment to renewable energy development serves as a model for other nations seeking to transition to a clean energy future.
Tips for Understanding Taiwan’s Wind Farm Map
- Explore online resources: Websites of government agencies, energy companies, and research institutions provide detailed information about wind farm locations, capacity, and development plans.
- Utilize interactive maps: Several online platforms offer interactive maps showcasing the distribution of wind farms across Taiwan, allowing users to zoom in on specific locations and explore project details.
- Read industry publications: Stay informed about the latest developments in Taiwan’s wind energy sector by reading industry publications and news articles.
Conclusion
Taiwan’s wind farm map is a testament to the nation’s commitment to sustainable energy development. It showcases the strategic use of wind resources to generate clean electricity, enhance energy security, and foster economic growth. While challenges remain, Taiwan’s ongoing investments in wind power, coupled with technological advancements and international collaboration, pave the way for a future powered by clean and sustainable energy. This map serves as a beacon of hope for a world seeking to mitigate climate change and transition to a more sustainable future.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Harnessing the Winds of Change: A Comprehensive Look at Taiwan’s Wind Farm Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!