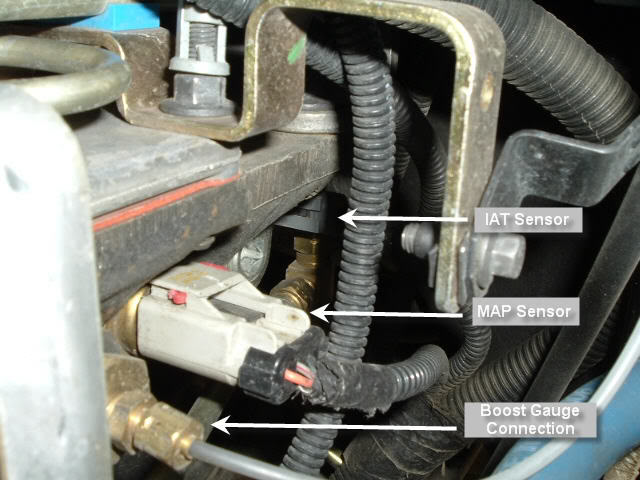
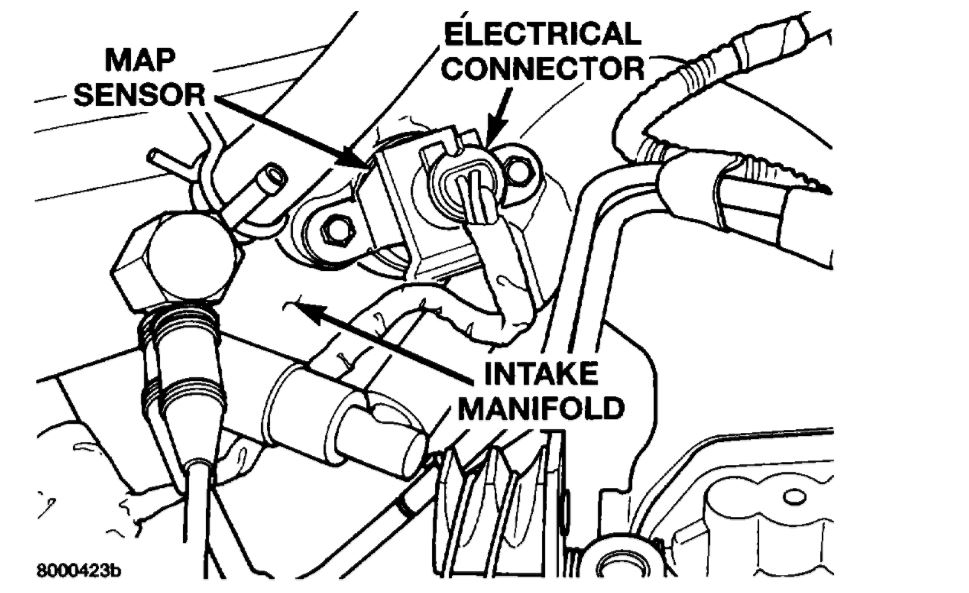
map sensor 6.7 powerstroke
Related Articles: map sensor 6.7 powerstroke
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to map sensor 6.7 powerstroke. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor: A Vital Component in the 6.7 Powerstroke Engine

The 6.7 Powerstroke engine, renowned for its robust performance and durability, relies on a sophisticated array of sensors to ensure optimal operation. One crucial component within this intricate system is the Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor. This unassuming sensor plays a vital role in engine control, influencing fuel delivery, ignition timing, and overall engine performance.
Understanding the MAP Sensor’s Function
The MAP sensor is responsible for measuring the absolute pressure within the engine’s intake manifold. This pressure, which fluctuates based on engine load and operating conditions, provides valuable information to the engine control module (ECM). The ECM uses this data to calculate various parameters, including:
- Air Mass: The MAP sensor’s reading, coupled with other sensor inputs like air temperature, allows the ECM to determine the amount of air entering the engine.
- Fuel Delivery: By accurately gauging air mass, the ECM can precisely calculate the amount of fuel required for optimal combustion. This ensures efficient fuel consumption and minimizes emissions.
- Ignition Timing: The MAP sensor data informs the ECM about the engine’s load and speed, enabling it to adjust ignition timing for optimal performance and efficiency.
- Boost Pressure Control: In turbocharged engines, the MAP sensor plays a critical role in monitoring and controlling boost pressure, ensuring safe and efficient operation.
The MAP Sensor: A Key Player in Engine Control
The MAP sensor’s role is not limited to providing data; it actively participates in the engine control process. Its readings influence a wide range of engine parameters, including:
- Fuel Injection Timing: The MAP sensor data helps the ECM determine the optimal timing for fuel injection, maximizing combustion efficiency and power output.
- Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Control: The MAP sensor contributes to the precise control of EGR flow, reducing emissions and optimizing engine performance.
- Variable Geometry Turbocharger (VGT) Control: In engines equipped with VGTs, the MAP sensor helps manage turbine vane position, optimizing boost pressure and engine response.
The Importance of a Functional MAP Sensor
A malfunctioning MAP sensor can significantly impact engine performance and fuel efficiency. Common symptoms of a faulty MAP sensor include:
- Engine Misfire: Incorrect fuel delivery due to inaccurate air mass readings can lead to misfires, resulting in rough idling, reduced power, and increased emissions.
- Poor Fuel Economy: Inaccurate air mass readings can lead to excessive fuel consumption, impacting fuel economy.
- Check Engine Light (CEL): A malfunctioning MAP sensor will often trigger the CEL, indicating a need for diagnosis and repair.
- Hesitation and Stalling: Erratic fuel delivery caused by a faulty MAP sensor can lead to hesitation during acceleration and even stalling.
Troubleshooting a MAP Sensor Issue
Diagnosing a faulty MAP sensor requires a combination of inspection and testing:
- Visual Inspection: Check the MAP sensor for physical damage, loose connections, or signs of corrosion.
- Vacuum Test: Using a vacuum gauge, check the MAP sensor’s response to changes in vacuum pressure. This test verifies the sensor’s ability to accurately measure pressure.
- Diagnostic Scanner: Utilize a diagnostic scanner to retrieve any fault codes related to the MAP sensor. This information can pinpoint the specific issue.
Tips for Maintaining the MAP Sensor
While the MAP sensor is generally a robust component, proper maintenance can extend its lifespan and prevent premature failure:
- Regular Inspections: Visually inspect the MAP sensor for signs of wear or damage during routine maintenance.
- Clean Connections: Clean the MAP sensor’s electrical connections with a contact cleaner to ensure a reliable connection.
- Avoid Harsh Chemicals: Do not use harsh chemicals or solvents to clean the MAP sensor, as these can damage the sensor’s sensitive components.
FAQs about the MAP Sensor in the 6.7 Powerstroke Engine
Q: What are the common signs of a failing MAP sensor?
A: Common symptoms include engine misfires, reduced power, poor fuel economy, a check engine light, hesitation during acceleration, and stalling.
Q: How often should I replace the MAP sensor?
A: The MAP sensor typically has a long lifespan, but it’s recommended to replace it if it exhibits any signs of failure or if it’s over 10 years old.
Q: Can I replace the MAP sensor myself?
A: Replacing the MAP sensor is generally a straightforward process, but it requires basic mechanical knowledge and familiarity with the engine compartment. If you’re unsure, consult a qualified mechanic.
Q: Can I clean the MAP sensor?
A: While cleaning the MAP sensor’s electrical connections can help, it’s not recommended to clean the sensor itself. Cleaning can damage the sensitive internal components.
Conclusion
The MAP sensor plays a critical role in the 6.7 Powerstroke engine’s performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions control. By accurately measuring manifold pressure, it provides essential data to the ECM, enabling precise control of fuel delivery, ignition timing, and other vital engine functions. Understanding the MAP sensor’s function and importance, along with proper maintenance and troubleshooting techniques, can help ensure the long-term health and performance of your 6.7 Powerstroke engine.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into map sensor 6.7 powerstroke. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
