map sensor location 4.6 ford
Related Articles: map sensor location 4.6 ford
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to map sensor location 4.6 ford. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
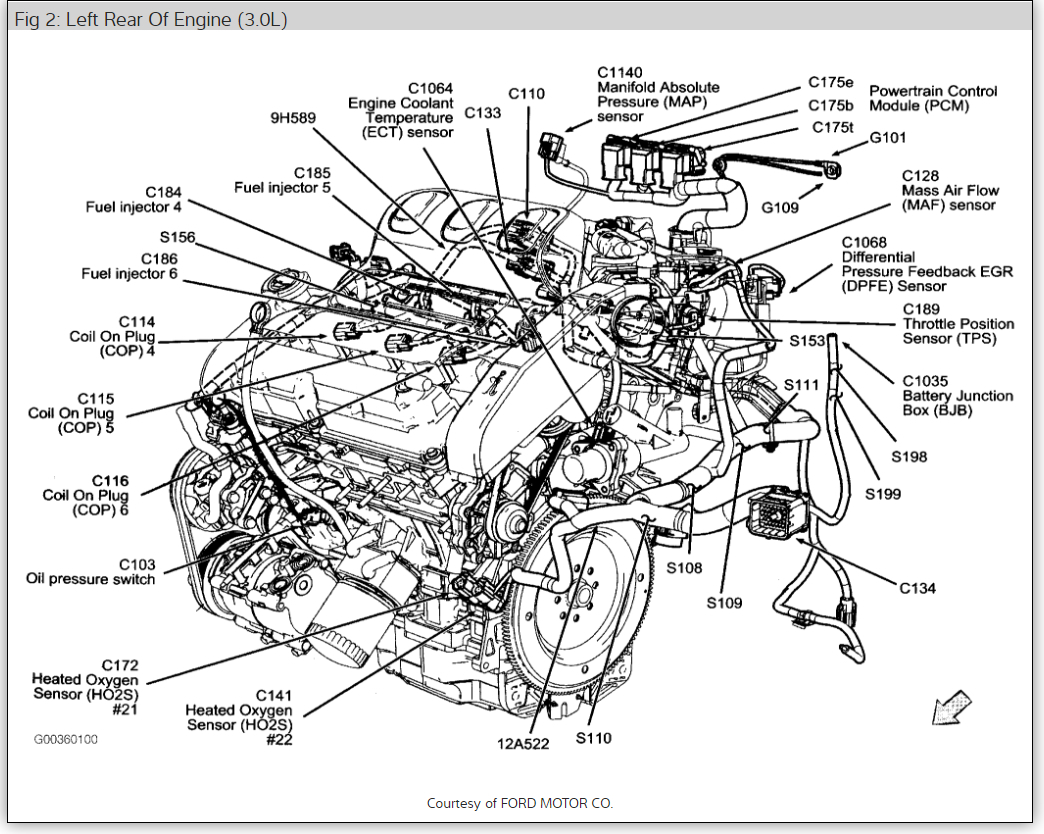
Unraveling the Mystery: Locating the MAP Sensor in a 2000 Ford 4.6L Engine

The 2000 Ford 4.6L engine, a mainstay in various Ford models, relies on a crucial component known as the Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor. This sensor plays a vital role in ensuring optimal engine performance by providing the engine control module (ECM) with critical information about the pressure within the intake manifold. This article will guide you through the process of locating this essential sensor, explaining its significance and offering insights into its proper function.
Navigating the Engine Bay: A Step-by-Step Guide to Finding the MAP Sensor
-
Engine Identification: Begin by identifying the 4.6L V8 engine within your Ford vehicle. The engine compartment is typically located under the hood, accessible by releasing the hood latch and lifting the hood.
-
Intake Manifold Location: Locate the intake manifold, the large metal component that sits atop the engine, housing the intake runners through which air enters the cylinders. The MAP sensor is usually situated on the intake manifold itself.
-
Sensor Identification: The MAP sensor is typically a small, cylindrical device with a single electrical connector. It might be attached to the manifold using a bracket or a bolt.
-
Common Locations: The MAP sensor’s exact position can vary slightly depending on the specific Ford model. However, it is often found on the driver’s side of the intake manifold, near the throttle body.
The MAP Sensor’s Crucial Role in Engine Performance
The MAP sensor is a vital component within the engine’s intricate control system. Its primary function is to measure the absolute pressure within the intake manifold, providing the ECM with crucial data about the engine’s load and air density.
Here’s how the MAP sensor contributes to optimal engine performance:
-
Fuel-Air Mixture Optimization: The ECM utilizes the MAP sensor readings to calculate the ideal air-fuel ratio for efficient combustion. This ensures optimal engine power output while minimizing fuel consumption and emissions.
-
Ignition Timing Adjustment: The MAP sensor’s data also helps the ECM adjust ignition timing, ensuring optimal spark timing for each cylinder based on engine load and operating conditions.
-
Throttle Response Enhancement: The ECM uses MAP sensor readings to refine throttle response, providing a smoother and more responsive driving experience.
-
Emissions Control: The MAP sensor plays a crucial role in emissions control by ensuring accurate fuel injection and ignition timing, reducing harmful emissions from the engine.
Decoding the Symptoms of a Faulty MAP Sensor
A malfunctioning MAP sensor can disrupt the engine’s delicate balance, leading to various performance issues:
-
Engine Stalling or Rough Idle: An inaccurate MAP sensor reading can result in a lean fuel mixture, causing the engine to stall or exhibit rough idle.
-
Reduced Power Output: A faulty MAP sensor can lead to an overly rich fuel mixture, resulting in decreased engine power and sluggish acceleration.
-
Increased Fuel Consumption: An inaccurate MAP sensor reading can cause the ECM to inject more fuel than necessary, leading to increased fuel consumption.
-
Check Engine Light Illumination: A malfunctioning MAP sensor will trigger the check engine light, signaling a need for diagnosis and potential replacement.
Troubleshooting and Replacement: A Step-by-Step Guide
-
Check Engine Light Diagnosis: Utilize an OBD-II scanner to retrieve diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to the MAP sensor. These codes can provide valuable insights into the sensor’s malfunction.
-
Visual Inspection: Visually inspect the MAP sensor for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
-
Voltage Check: Use a voltmeter to check the voltage supplied to the MAP sensor. A low voltage reading could indicate a wiring issue.
-
Sensor Replacement: If the sensor is found to be faulty, replace it with a new, OEM-approved MAP sensor. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper installation.
-
Clear Codes and Test Drive: After replacing the sensor, clear the DTCs using the OBD-II scanner and test drive the vehicle to ensure the problem is resolved.
FAQs: Addressing Common Concerns about the MAP Sensor
Q: What is the expected lifespan of a MAP sensor?
A: The lifespan of a MAP sensor can vary depending on factors such as driving conditions, environmental exposure, and maintenance. However, a well-maintained MAP sensor can typically last for several years or even tens of thousands of miles.
Q: Can a faulty MAP sensor cause other engine problems?
A: Yes, a faulty MAP sensor can lead to other engine problems, such as misfires, fuel system issues, and even damage to the catalytic converter due to excessive emissions.
Q: Can I clean a MAP sensor?
A: Cleaning a MAP sensor is generally not recommended. The sensor is a delicate device, and attempting to clean it can damage its internal components. Replacement is usually the best course of action for a malfunctioning MAP sensor.
Q: How can I prevent future MAP sensor issues?
A: Regular maintenance, including periodic inspections of the sensor and its wiring, can help prevent future MAP sensor issues.
Tips for Maintaining Optimal MAP Sensor Performance
-
Regular Inspections: Periodically inspect the MAP sensor for signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
-
Cleanliness: Ensure the surrounding area of the MAP sensor is clean and free of debris.
-
Wiring Checks: Inspect the sensor’s wiring for any signs of damage or chafing.
-
Professional Maintenance: Schedule regular engine maintenance with a qualified mechanic, including inspections of the MAP sensor and its associated components.
Conclusion: The MAP Sensor’s Vital Role in Engine Health
The MAP sensor is a critical component in the intricate web of systems that govern the performance of a 2000 Ford 4.6L engine. By accurately measuring intake manifold pressure, it provides the ECM with essential data for optimizing fuel-air mixture, ignition timing, throttle response, and emissions control. Understanding the MAP sensor’s function, recognizing its potential malfunctions, and implementing preventative measures will contribute to maintaining optimal engine performance and ensuring a smooth and reliable driving experience.
![[Diagram Included] Explore Ford F150 Map Sensor Location Now!](https://www.automasterx.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/ford-f150-map-sensor-location.jpg)






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into map sensor location 4.6 ford. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
