MAP Testing Scores by Grade Level: A Comprehensive Overview
Related Articles: MAP Testing Scores by Grade Level: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to MAP Testing Scores by Grade Level: A Comprehensive Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
MAP Testing Scores by Grade Level: A Comprehensive Overview
The Measures of Academic Progress (MAP) assessment is a standardized test widely used in the United States to measure student progress in reading and mathematics. Its adaptive nature, adjusting difficulty based on student performance, provides a more nuanced picture of individual learning than traditional paper-and-pencil tests. This comprehensive overview delves into MAP testing scores by grade level, exploring their significance and practical applications.
Understanding MAP Testing Scores
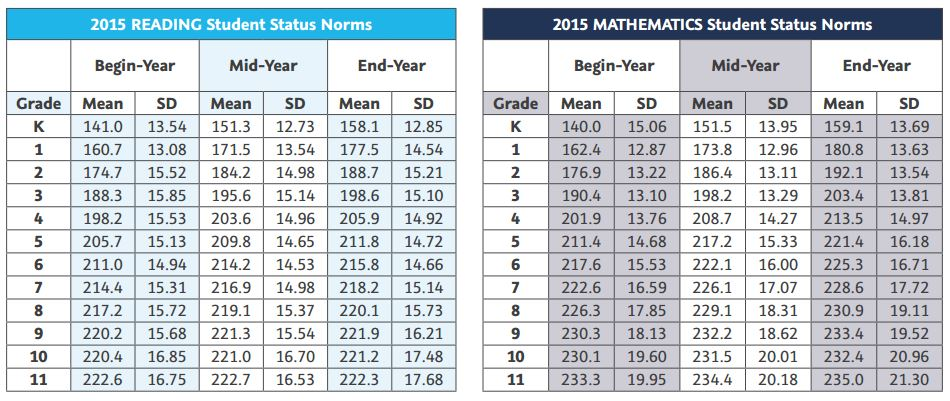
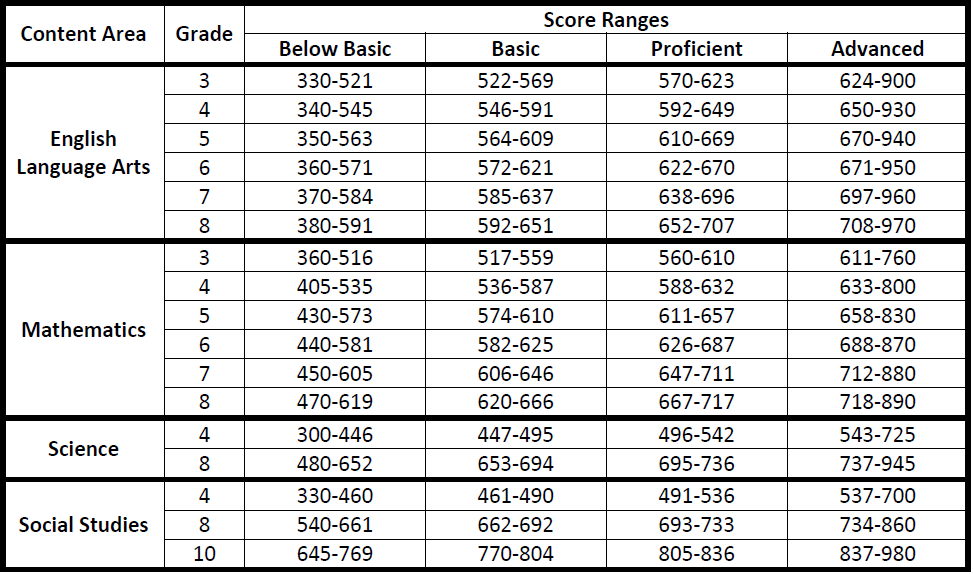
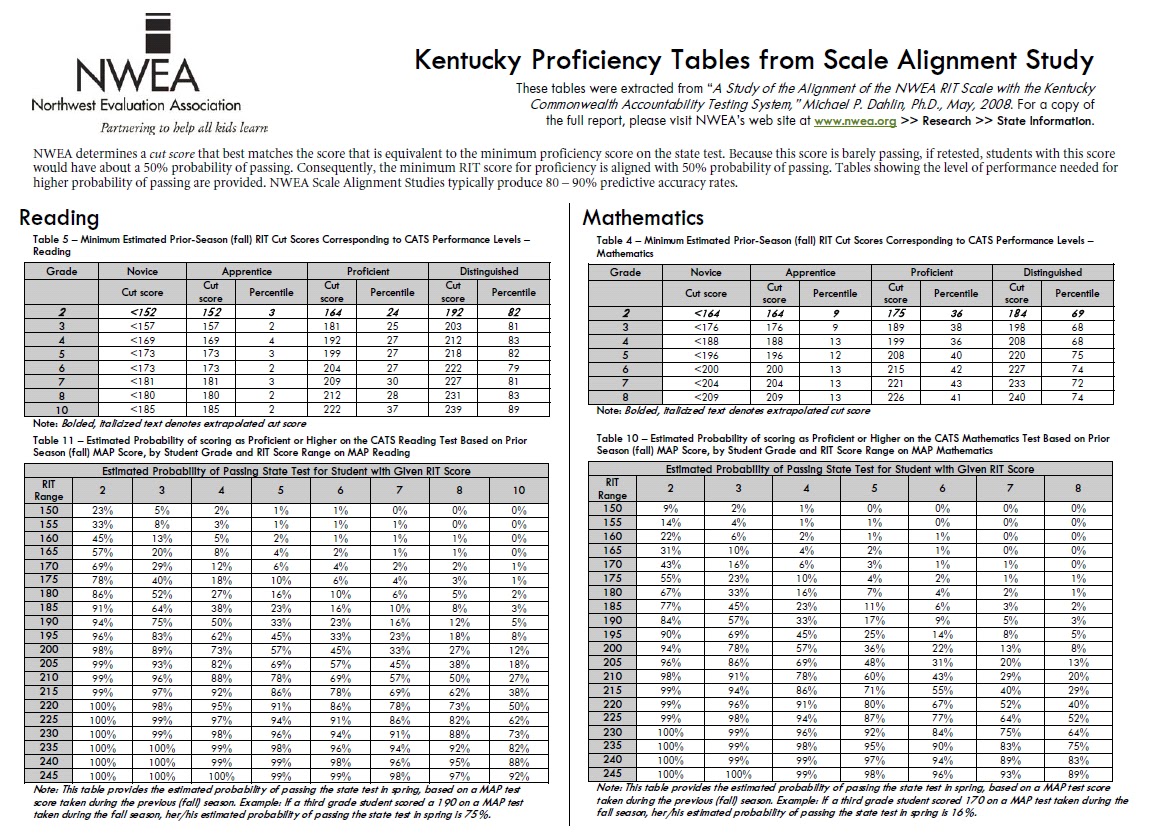
MAP tests generate RIT scores, which represent a student’s estimated proficiency level on a scale ranging from 150 to 220. Each RIT score corresponds to a specific grade level and skill set, allowing educators to pinpoint areas of strength and weakness. For instance, a student scoring 180 in reading might be at the 5th-grade level in comprehension but struggle with vocabulary at the 4th-grade level. This granular data empowers teachers to tailor instruction effectively.
MAP Testing Scores by Grade Level: A Detailed Examination
Kindergarten
MAP testing in kindergarten focuses on foundational skills crucial for later academic success. In reading, this includes letter recognition, phonics, and basic comprehension. Mathematics assessments emphasize number sense, counting, and simple addition and subtraction.
Grade 1
As students enter first grade, MAP assessments delve deeper into early literacy and numeracy. Reading comprehension, fluency, and vocabulary are evaluated alongside early decoding skills. In mathematics, students are tested on basic arithmetic, geometry, and problem-solving.
Grade 2
By second grade, MAP testing becomes more sophisticated, assessing higher-level reading comprehension and fluency, including the ability to analyze text and draw inferences. Mathematics assessments focus on multiplication and division, fractions, and basic measurement.
Grade 3
MAP testing in third grade delves into multi-syllabic words, complex sentence structures, and informational text comprehension. Mathematics assessments incorporate multi-step word problems, geometry, and data analysis.
Grade 4
Fourth-grade MAP testing emphasizes reading comprehension of increasingly challenging texts, including literary analysis and persuasive writing. In mathematics, students are assessed on decimals, fractions, and algebraic thinking.
Grade 5
Fifth-grade MAP assessments evaluate students’ ability to analyze complex text, make inferences, and synthesize information. Mathematics assessments focus on advanced arithmetic, geometry, and pre-algebra concepts.
Grade 6
MAP testing in sixth grade focuses on reading comprehension of more complex literary and informational texts, including advanced vocabulary and critical analysis. Mathematics assessments include advanced algebra, geometry, and data analysis.
Grade 7
Seventh-grade MAP testing focuses on reading comprehension, including analyzing complex text, identifying themes, and understanding author’s purpose. Mathematics assessments delve deeper into algebra, geometry, and probability.
Grade 8
Eighth-grade MAP testing assesses advanced reading comprehension, including the ability to interpret complex literary devices and analyze arguments. Mathematics assessments include advanced algebra, geometry, and trigonometry.
The Significance of MAP Testing Scores
MAP testing scores provide valuable insights into student learning and progress. They enable teachers to:
- Identify individual student strengths and weaknesses: This allows for tailored instruction and differentiated learning, ensuring every student receives the appropriate support.
- Monitor student growth over time: Comparing scores across different testing periods reveals areas of improvement and challenges, informing instructional adjustments.
- Track progress against grade-level benchmarks: This helps educators understand how students are performing relative to their peers and identify areas requiring additional focus.
- Inform instructional decisions: Data from MAP testing can guide curriculum development and resource allocation, ensuring students receive the most effective instruction.
- Communicate with parents and guardians: Clear and concise reports provide parents with a comprehensive understanding of their child’s academic progress and areas needing attention.
Utilizing MAP Testing Scores Effectively
While MAP testing scores provide valuable data, it is crucial to interpret them within a broader context. Factors like individual learning styles, cultural background, and socioeconomic status can influence performance. Educators should use MAP scores as a tool to guide instruction, not as a sole measure of student success.
FAQs Regarding MAP Testing Scores
Q: How often should students take the MAP test?
A: The frequency of MAP testing varies based on school policy and individual student needs. Typically, students take the test three times a year: at the beginning, middle, and end of the school year.
Q: What should parents do if their child’s MAP scores are below grade level?
A: Parents should communicate with their child’s teacher to discuss the results and develop a plan for supporting their child’s academic progress. This may involve additional tutoring, targeted interventions, or adjustments to homework assignments.
Q: How can teachers use MAP testing scores to differentiate instruction?
A: By analyzing individual student scores, teachers can create small groups for targeted instruction, provide individualized support, and assign differentiated activities based on specific areas of need.
Q: Can MAP testing scores be used to predict future academic success?
A: While MAP testing scores can provide valuable insights into current academic performance, they are not a foolproof predictor of future success. Other factors, such as motivation, work ethic, and social-emotional development, also play a significant role.
Tips for Utilizing MAP Testing Scores
- Focus on growth: Celebrate student progress, even if scores are initially below grade level.
- Collaborate with parents: Share MAP testing results and discuss strategies for supporting student learning.
- Use data to inform instruction: Implement targeted interventions and provide differentiated learning opportunities based on individual student needs.
- Utilize technology: Leverage online resources and adaptive learning platforms to supplement instruction and address specific skill gaps.
- Maintain a positive learning environment: Foster a growth mindset and encourage students to embrace challenges as opportunities for learning.
Conclusion
MAP testing scores offer a valuable tool for educators to assess student learning and guide instruction. By understanding the nuances of these scores and utilizing them effectively, schools can create a more personalized and effective learning environment for all students. By fostering a culture of continuous improvement and focusing on individual student growth, schools can leverage MAP testing to empower students to reach their full academic potential.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into MAP Testing Scores by Grade Level: A Comprehensive Overview. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
