Mapping Malaria in Thailand: Understanding the Landscape of a Persistent Threat
Related Articles: Mapping Malaria in Thailand: Understanding the Landscape of a Persistent Threat
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Mapping Malaria in Thailand: Understanding the Landscape of a Persistent Threat. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping Malaria in Thailand: Understanding the Landscape of a Persistent Threat
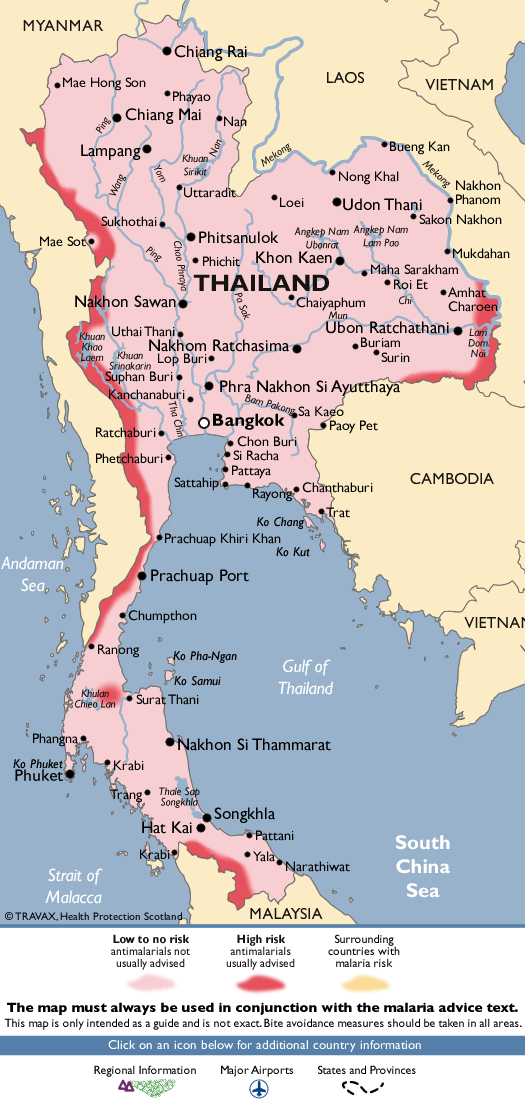
Malaria, a mosquito-borne disease caused by parasites of the Plasmodium genus, remains a significant public health concern in Thailand. While the country has made remarkable progress in reducing malaria incidence over the past decades, the disease persists in specific regions, posing a continuous challenge for health authorities. Understanding the geographical distribution of malaria is crucial for effective prevention, treatment, and control efforts.
This article delves into the intricacies of malaria areas in Thailand, analyzing the factors that influence its prevalence, examining the current map of malaria transmission, and exploring the implications for public health.
The Enduring Presence of Malaria in Thailand
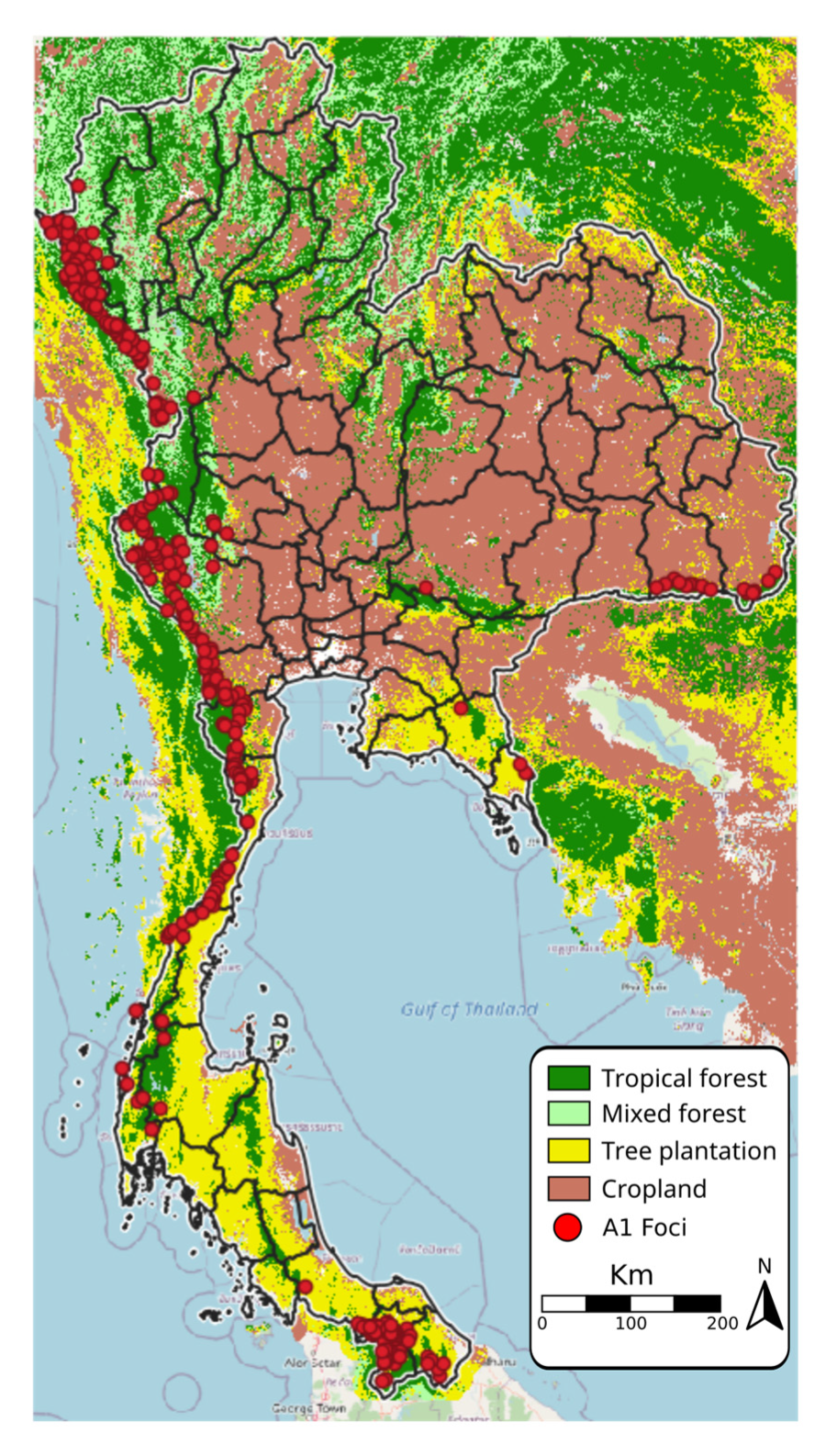
Thailand’s geography, characterized by diverse ecosystems ranging from dense rainforests to mountainous terrains, provides ideal breeding grounds for Anopheles mosquitoes, the primary vectors of malaria. The country’s proximity to malaria-endemic regions in Southeast Asia further complicates the situation.
Malaria transmission in Thailand is primarily caused by Plasmodium falciparum, the most dangerous species, and Plasmodium vivax, which can cause relapses. Other species, such as Plasmodium knowlesi, are also present, although less prevalent.
Factors Influencing Malaria Transmission
Several factors contribute to the spatial distribution of malaria in Thailand:
- Environmental Factors: Rainfall patterns, temperature, humidity, and vegetation cover all play a crucial role in mosquito breeding and survival. Regions with high rainfall, dense vegetation, and suitable temperatures are more prone to malaria transmission.
- Socioeconomic Factors: Poverty, limited access to healthcare, and inadequate housing conditions contribute to increased vulnerability to malaria.
- Human Population Movements: Migratory workers and travelers can introduce malaria into areas with low transmission rates, leading to outbreaks.
- Drug Resistance: The emergence of drug-resistant strains of Plasmodium parasites poses a significant threat, making treatment more challenging.
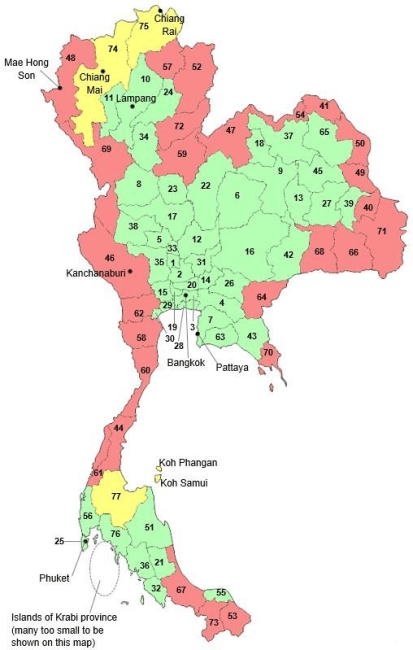
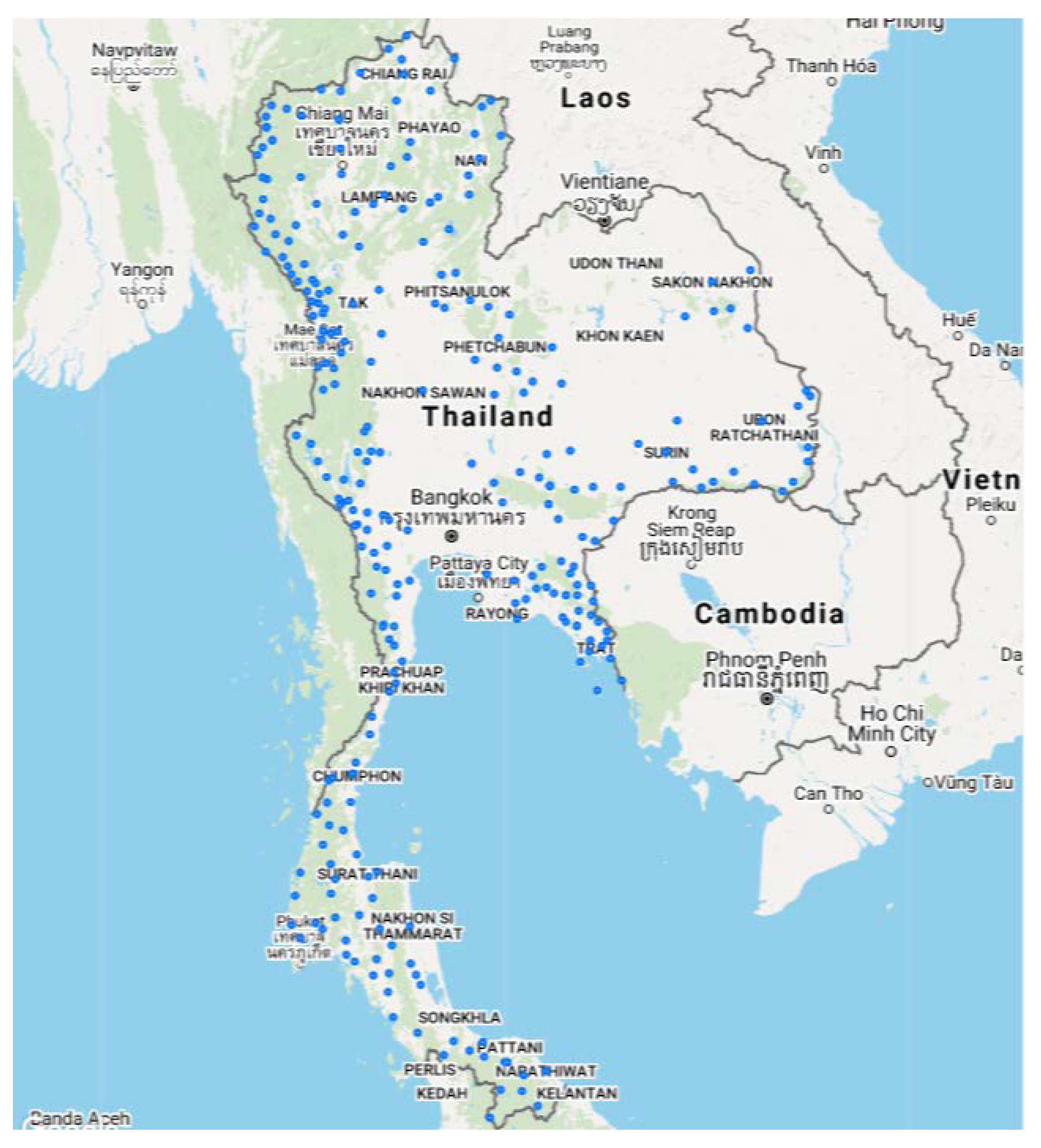
The Malaria Map of Thailand
The malaria map of Thailand reflects the complex interplay of these factors. The Ministry of Public Health regularly updates the map, providing a visual representation of areas with different levels of malaria transmission. This map serves as a crucial tool for:
- Targeted Prevention and Control: Identifying high-risk areas allows for the allocation of resources for mosquito control measures, such as insecticide-treated nets, indoor residual spraying, and larviciding.
- Early Diagnosis and Treatment: Knowing the areas with high malaria prevalence helps healthcare providers focus on early detection and prompt treatment, preventing severe complications.
- Surveillance and Monitoring: The map facilitates continuous monitoring of malaria trends, enabling early detection of outbreaks and prompt response.
Understanding the Map: Key Areas of Concern
The malaria map of Thailand typically categorizes areas into:
- High Transmission Areas: These regions, often located in remote areas with dense forests and high rainfall, experience the highest incidence of malaria cases.
- Moderate Transmission Areas: These areas exhibit a moderate level of malaria transmission, with cases occurring more sporadically.
- Low Transmission Areas: These regions experience a low number of malaria cases, often due to factors such as lower mosquito density or improved access to healthcare.
The Importance of the Malaria Map
The malaria map of Thailand is a powerful tool for public health officials, researchers, and healthcare providers. It allows them to:
- Prioritize Resources: By focusing efforts on high-risk areas, resources can be used more effectively to reduce malaria transmission.
- Develop Targeted Interventions: Tailored interventions can be implemented based on the specific characteristics of each area, ensuring maximum impact.
- Track Progress and Evaluate Interventions: The map provides a baseline for monitoring the effectiveness of malaria control programs and identifying areas requiring additional attention.
- Raise Public Awareness: The map can be used to educate the public about malaria risks, promoting preventative measures and seeking prompt medical attention.
FAQs on Malaria Areas in Thailand
Q: Where in Thailand is malaria most prevalent?
A: Malaria transmission is highest in the northern, northeastern, and western regions of Thailand, particularly in mountainous areas with dense forests and high rainfall.
Q: Are there specific areas to avoid due to malaria risk?
A: While there are no specific areas to completely avoid, it is advisable to exercise caution in regions identified as high-risk areas on the malaria map.
Q: What should travelers do to protect themselves from malaria?
A: Travelers should consult their healthcare provider for advice on malaria prophylaxis, use mosquito repellents, wear protective clothing, and sleep under mosquito nets.
Q: What are the symptoms of malaria?
A: Symptoms include fever, chills, sweating, headache, muscle aches, fatigue, and nausea. If you experience these symptoms after traveling to a malaria-endemic area, seek medical attention immediately.
Q: Is there a cure for malaria?
A: Malaria is treatable with antimalarial medications. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent complications.
Tips for Staying Safe from Malaria in Thailand
- Consult Your Doctor: Before traveling to Thailand, consult your healthcare provider about the malaria risk and appropriate preventative measures.
- Stay Informed: Familiarize yourself with the malaria map of Thailand and the specific areas with higher transmission rates.
- Use Mosquito Repellents: Apply DEET-based mosquito repellents regularly, especially during dusk and dawn when mosquitoes are most active.
- Wear Protective Clothing: Cover exposed skin with long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and socks.
- Sleep Under Mosquito Nets: Use insecticide-treated nets when sleeping, both indoors and outdoors.
- Take Antimalarial Medication: If prescribed by your doctor, take antimalarial medication as directed.
- Seek Medical Attention Immediately: If you experience any symptoms of malaria, seek medical attention promptly.
Conclusion
The malaria map of Thailand is a valuable tool for understanding the geographical distribution of this preventable disease. By utilizing this map and implementing effective control measures, Thailand has made significant strides in reducing malaria incidence. However, continued vigilance and sustained efforts are essential to further decrease malaria transmission and ultimately eliminate the disease.
Through continued research, public health initiatives, and collaborative efforts, Thailand can move towards a future where malaria is no longer a threat to its people.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping Malaria in Thailand: Understanding the Landscape of a Persistent Threat. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
