Mapping Taiwan: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Island Nation
Related Articles: Mapping Taiwan: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Island Nation
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Mapping Taiwan: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Island Nation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping Taiwan: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Island Nation

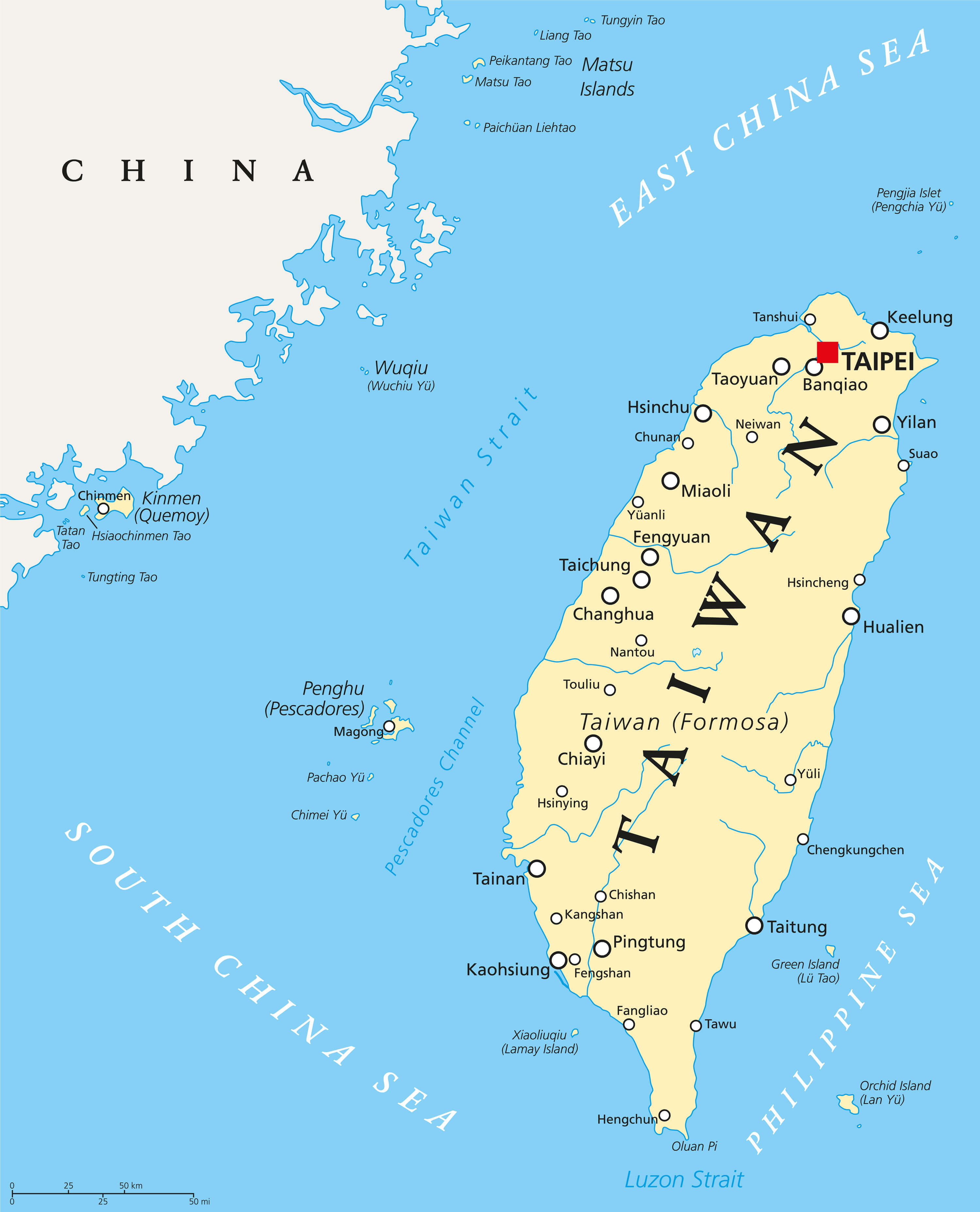
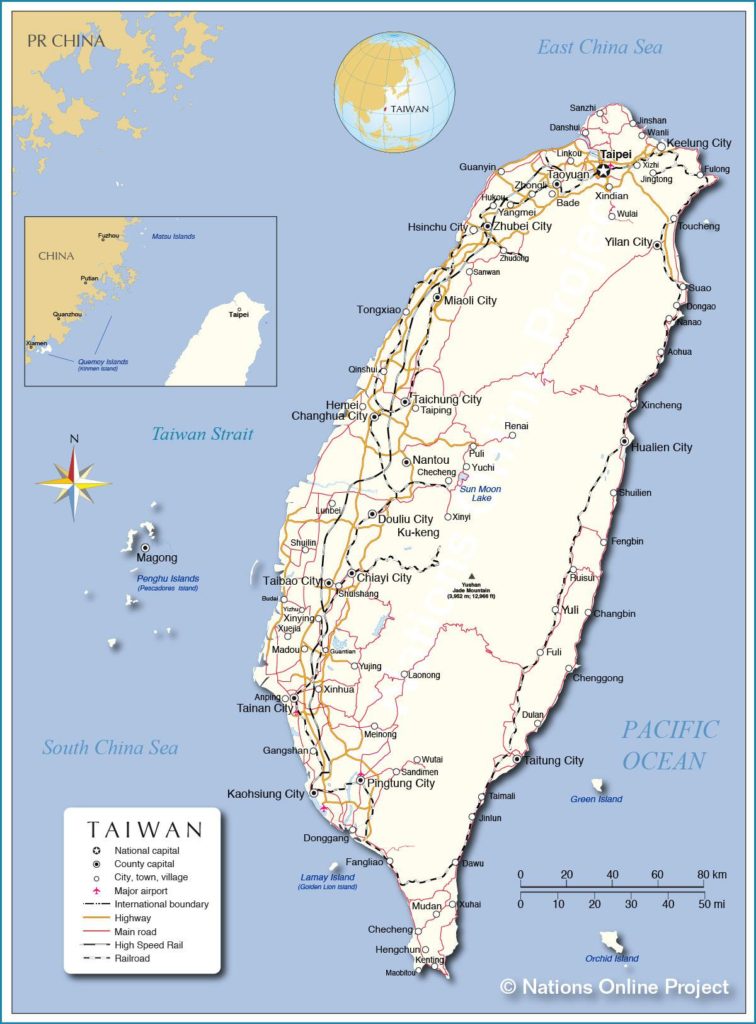
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a vibrant and dynamic island nation located off the southeastern coast of mainland China. Understanding its geography, political landscape, and cultural nuances requires a nuanced approach, and maps serve as invaluable tools for navigating this complex and fascinating territory.
A Geographical Overview: The Island and its Environs
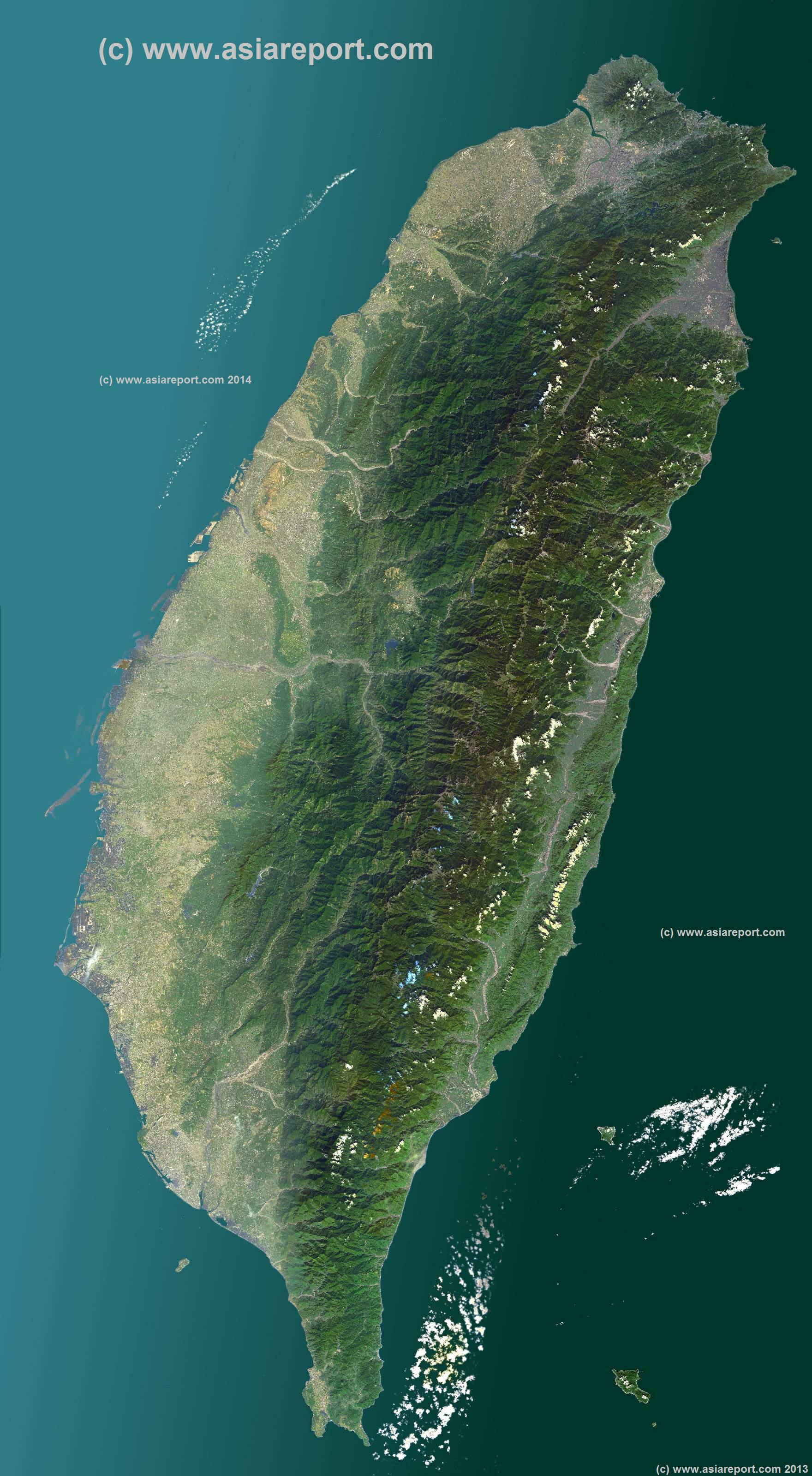
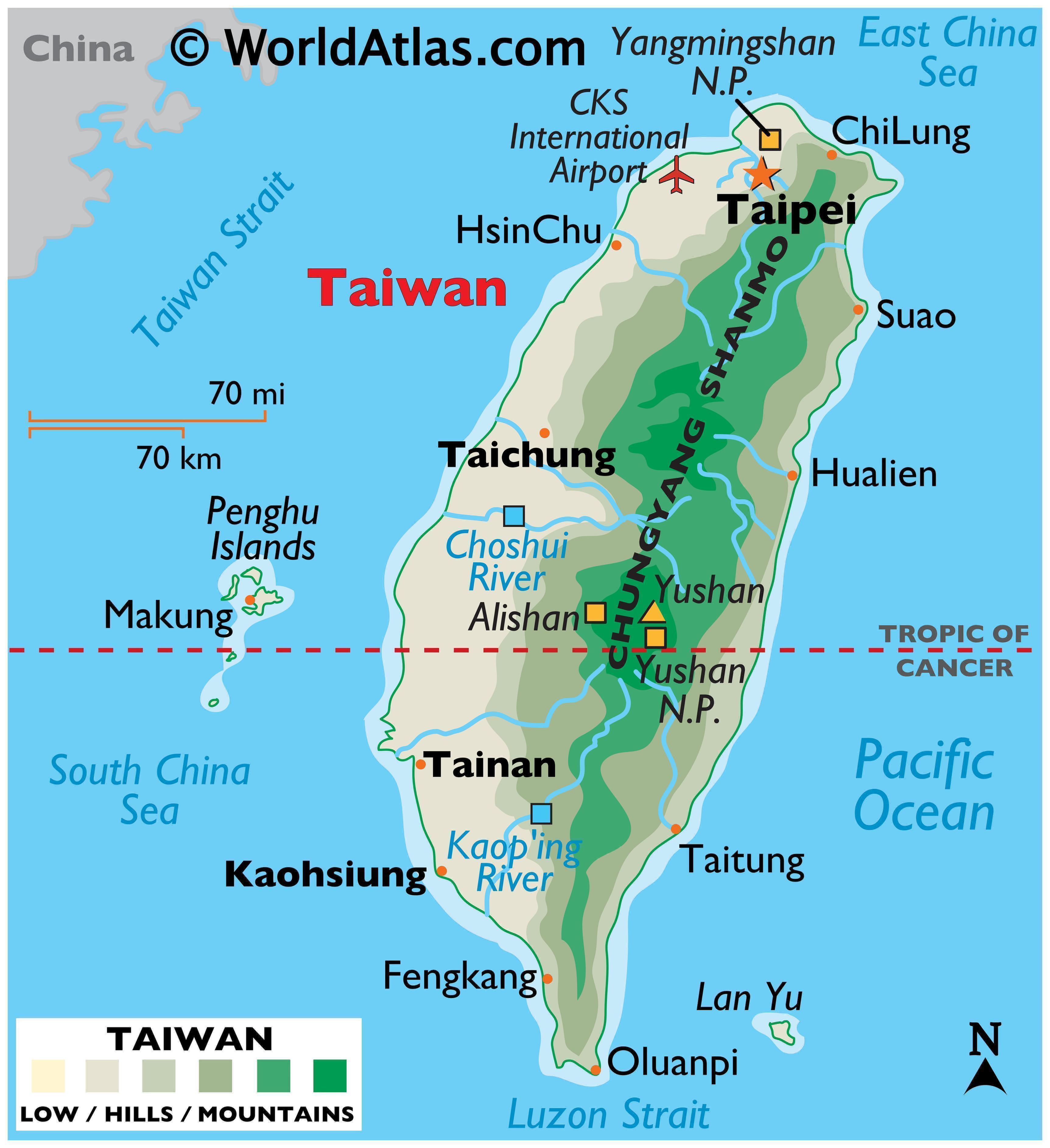
Taiwan’s physical geography is characterized by its mountainous terrain, fertile plains, and coastal regions. The island is dominated by the Central Mountain Range, which runs along its length, creating a dramatic and diverse landscape. The highest peak, Yushan (Jade Mountain), stands at 3,952 meters, making it the tallest mountain in East Asia.
Maps Depicting Physical Features:
- Topographic Maps: These maps showcase the island’s elevation, highlighting the Central Mountain Range, its numerous peaks, and the surrounding plains and coastal areas.
- Geological Maps: These maps provide insights into the island’s rock formations, fault lines, and mineral resources, illustrating the geological processes that have shaped Taiwan’s landscape.
- Hydrological Maps: These maps depict Taiwan’s rivers, lakes, and reservoirs, showcasing the island’s water resources and their distribution.
Beyond the Island: The Spratly Islands and the Taiwan Strait
Taiwan’s geographic significance extends beyond its island boundaries. The Spratly Islands, a group of small islands and reefs in the South China Sea, are claimed by Taiwan, China, Vietnam, the Philippines, Malaysia, and Brunei. These islands hold strategic importance due to their potential oil and gas reserves and their location within crucial shipping lanes.
The Taiwan Strait, separating Taiwan from mainland China, is another area of significant geopolitical importance. This narrow waterway serves as a vital trade route and is a potential flashpoint for tensions between the two sides.
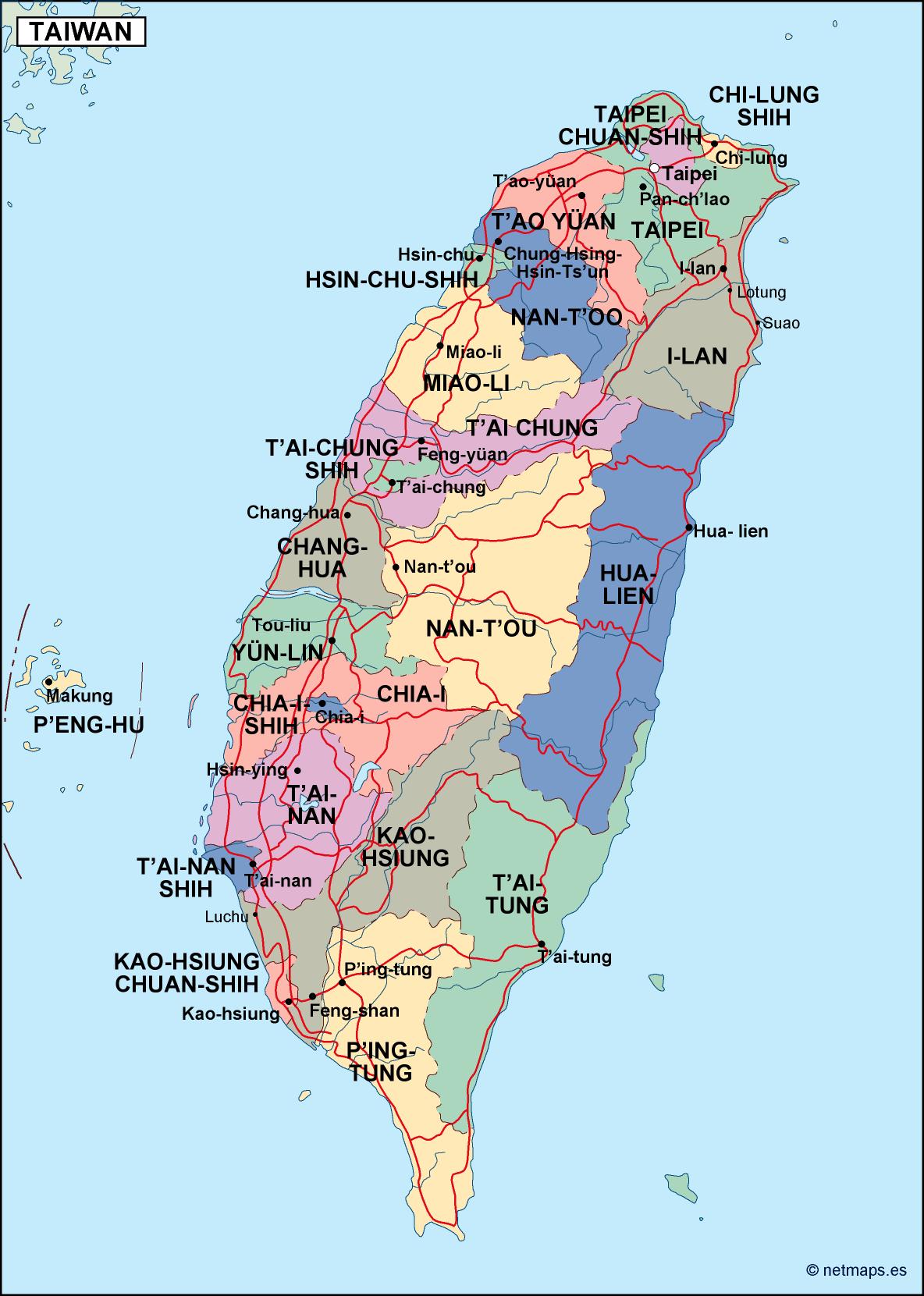
Political and Administrative Divisions: A Complex Landscape
Taiwan’s political and administrative landscape is complex, reflecting its unique history and current status. The island is divided into 22 counties and 6 municipalities, each with its own local government and administrative structures.
Maps Depicting Political Divisions:
- Political Maps: These maps show the boundaries of Taiwan’s counties and municipalities, providing a clear visual representation of the island’s administrative divisions.
- Election Maps: These maps highlight the results of various elections, illustrating the distribution of political power and voter preferences across the island.
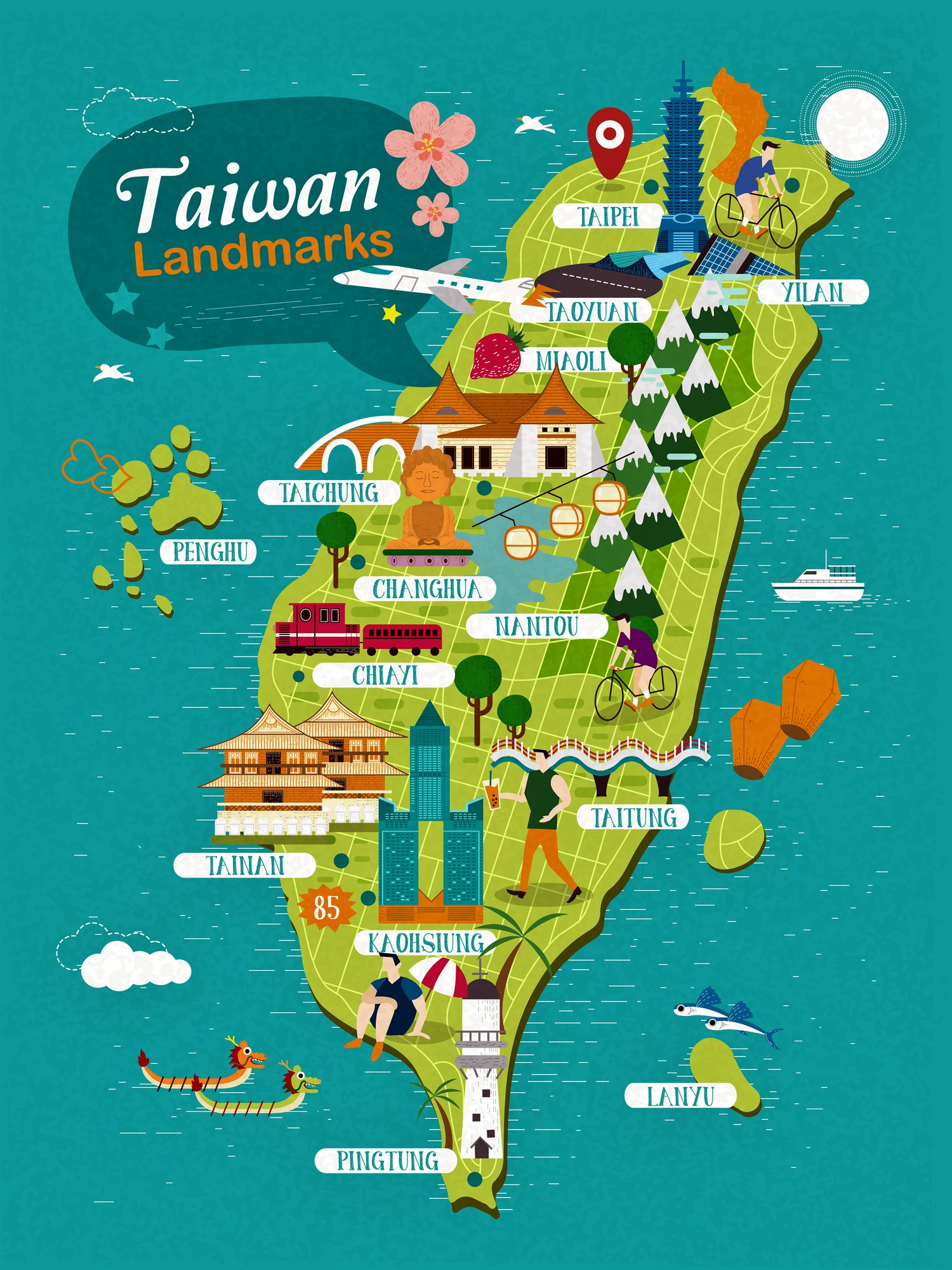
Cultural and Ethnic Diversity: A Mosaic of Identities
Taiwan’s cultural landscape is a vibrant tapestry woven from diverse threads. The island’s indigenous peoples, who have inhabited Taiwan for centuries, represent a rich and diverse cultural heritage. The Han Chinese population, who arrived in successive waves of migration, have also contributed significantly to Taiwan’s cultural identity.
Maps Depicting Cultural Diversity:
- Ethnic Maps: These maps illustrate the distribution of different ethnic groups across the island, providing insights into Taiwan’s cultural mosaic.
- Language Maps: These maps depict the different languages spoken in Taiwan, highlighting the prevalence of Mandarin Chinese, Taiwanese Hokkien, Hakka, and indigenous languages.
Economic Landscape: A Thriving Economy and Major Industries
Taiwan’s economy is highly developed, characterized by a strong manufacturing sector, advanced technology, and a vibrant service industry. The island is a major producer of electronics, semiconductors, and other high-tech goods, playing a significant role in global supply chains.
Maps Depicting Economic Activity:
- Industrial Maps: These maps show the distribution of major industries across Taiwan, highlighting the concentration of manufacturing hubs and technological centers.
- Trade Maps: These maps illustrate Taiwan’s trade relationships with other countries, showcasing the island’s position as a major player in global trade.
Beyond the Physical: The Importance of Mapping Taiwan’s Identity
Maps serve as powerful tools for understanding not only Taiwan’s physical and political geography but also its cultural and historical identity.
- Historical Maps: These maps provide insights into Taiwan’s historical development, tracing the island’s changing borders, political structures, and cultural influences over time.
- Cultural Maps: These maps showcase the distribution of different cultural traditions, languages, and religious practices across the island, providing a visual representation of Taiwan’s rich cultural heritage.
FAQs about Mapping Taiwan
1. Why are maps important for understanding Taiwan?
Maps provide a visual representation of Taiwan’s complex geography, political landscape, and cultural diversity, facilitating a deeper understanding of the island nation.
2. What types of maps are most useful for studying Taiwan?
Various maps, including topographic, geological, political, economic, historical, and cultural maps, offer valuable insights into different aspects of Taiwan.
3. How do maps help us understand Taiwan’s relationship with mainland China?
Maps illustrating the Taiwan Strait, the Spratly Islands, and historical boundaries help us visualize the geopolitical complexities and historical tensions between Taiwan and mainland China.
4. What are some of the challenges in mapping Taiwan?
Challenges include the ongoing political dispute over Taiwan’s status, the dynamic nature of the island’s political and economic landscape, and the need to accurately represent Taiwan’s diverse cultural heritage.
Tips for Using Maps to Understand Taiwan
- Choose the right map: Select maps that address the specific aspects of Taiwan you wish to understand.
- Compare and contrast: Analyze multiple maps to gain a comprehensive understanding of different perspectives and interpretations.
- Consider historical context: Integrate historical maps into your analysis to understand how Taiwan’s geography and political landscape have evolved over time.
- Engage with cultural nuances: Utilize cultural maps to appreciate the island’s diverse ethnicities, languages, and cultural practices.
Conclusion: A Vital Tool for Understanding Taiwan
Maps are essential tools for navigating the complexities of Taiwan. They provide a visual framework for understanding the island’s geography, politics, culture, and economy, allowing us to appreciate the depth and richness of this unique nation. By engaging with maps and their diverse representations, we can gain a more nuanced and informed perspective on Taiwan’s place in the world.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping Taiwan: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Island Nation. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
