Mapping the Future: An Examination of Texas’s Standardized Testing Landscape
Related Articles: Mapping the Future: An Examination of Texas’s Standardized Testing Landscape
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Future: An Examination of Texas’s Standardized Testing Landscape. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Future: An Examination of Texas’s Standardized Testing Landscape
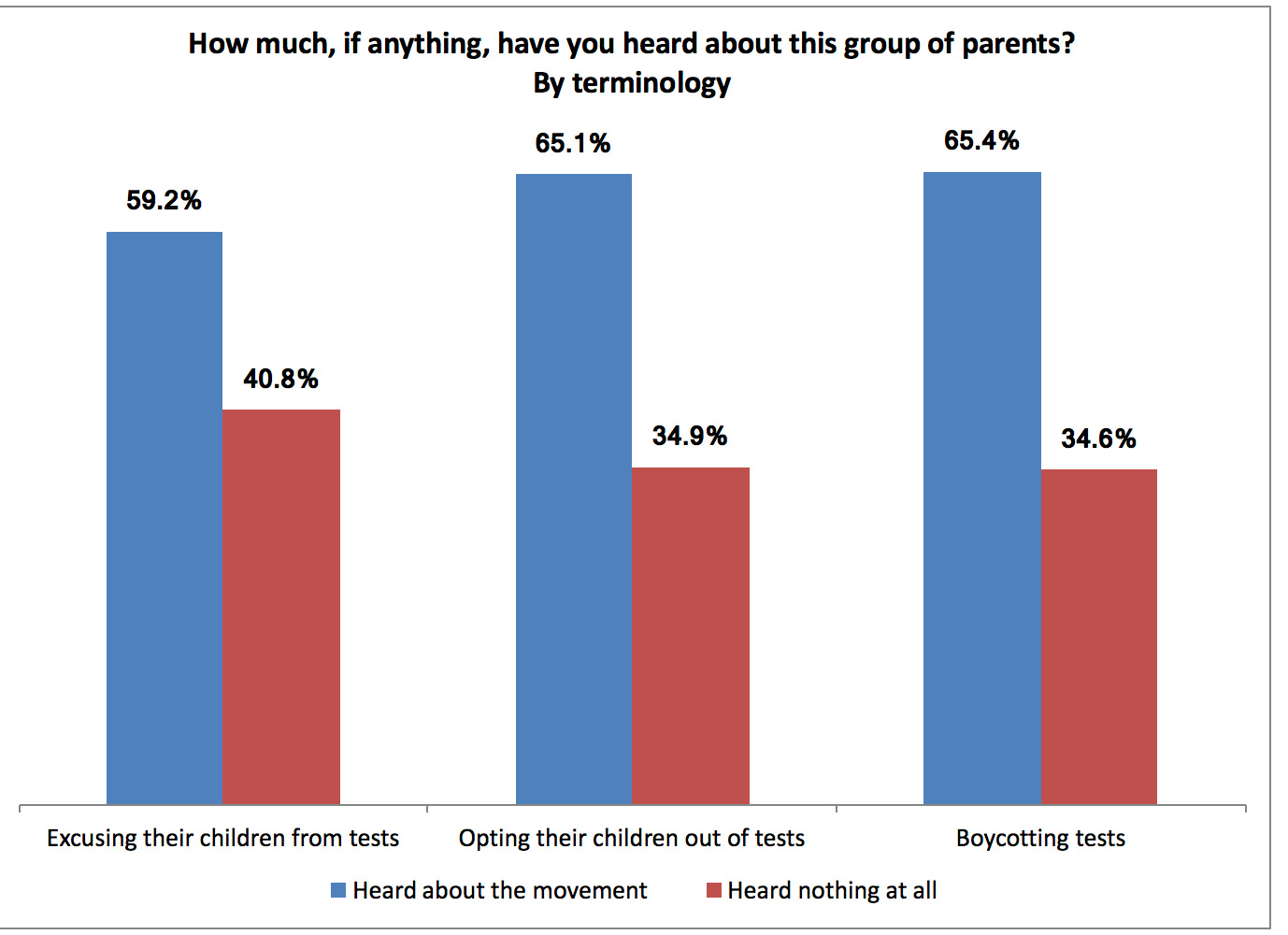
Texas, a state known for its vastness and entrepreneurial spirit, also boasts a robust educational system. Central to this system is the use of standardized testing, a practice that has evolved significantly over the years. Understanding the intricacies of Texas’s standardized testing landscape, often referred to as "map testing," is crucial for comprehending the state’s educational policies and their impact on students, teachers, and schools.
A Historical Overview: From the Early Days to the Present
Texas’s standardized testing journey began in the 1990s with the implementation of the Texas Assessment of Academic Skills (TAAS), designed to assess student proficiency in reading, writing, mathematics, and science. This initial foray into large-scale testing marked a shift towards accountability and measurable outcomes in education.
The introduction of the Texas Assessment of Knowledge and Skills (TAKS) in 2003 further solidified the state’s commitment to standardized testing. TAKS expanded the scope of assessment to include subjects like social studies and fine arts, and introduced a higher stakes component, linking test scores to school accountability ratings.
In 2012, Texas transitioned to the State of Texas Assessments of Academic Readiness (STAAR), a comprehensive assessment system encompassing multiple grades and subject areas. STAAR aimed to align with the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS), the state’s curriculum standards, and to provide a more rigorous and comprehensive evaluation of student learning.
The Multifaceted Nature of Map Testing in Texas
Texas’s standardized testing landscape is characterized by its multifaceted nature, encompassing various tests administered at different grade levels and subject areas. This complex system serves several purposes:
- Accountability and Performance Measurement: Standardized tests provide a standardized measure of student learning, enabling educators and policymakers to track progress, identify areas for improvement, and hold schools accountable for student performance.
- Curriculum Alignment: The content of standardized tests is designed to align with the TEKS, ensuring that students are assessed on the knowledge and skills deemed essential for their grade level.
- Student Progress Monitoring: Regular testing allows teachers to monitor student progress throughout the year, identify areas where students may be struggling, and provide targeted interventions to support their learning.
- Resource Allocation: Test scores are often used to inform resource allocation decisions, ensuring that schools with greater needs receive additional support and resources.
The Impact of Map Testing: A Multifaceted Perspective
While standardized testing plays a crucial role in Texas’s educational system, its impact is complex and multifaceted.
Benefits:
- Enhanced Accountability: Standardized testing provides a quantifiable measure of student performance, fostering accountability and promoting a culture of continuous improvement within schools.
- Improved Curriculum Alignment: The alignment of standardized tests with the TEKS ensures that students are assessed on the knowledge and skills deemed essential for their grade level, fostering consistency and rigor in curriculum development.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: Standardized test scores provide valuable data that can inform instructional decisions, resource allocation, and policy development, enabling a more data-driven approach to education.
Challenges:
- Narrow Focus: Critics argue that standardized tests often focus on a narrow range of skills and knowledge, potentially neglecting other important aspects of learning, such as creativity, critical thinking, and social-emotional development.
- Teaching to the Test: There is concern that teachers may prioritize test preparation over broader educational goals, leading to a "teaching to the test" phenomenon that can limit students’ exposure to a wider range of learning experiences.
- High-Stakes Pressure: The high-stakes nature of standardized testing can create significant pressure on students, teachers, and schools, leading to anxiety and stress.
- Equity Concerns: There are concerns that standardized tests may not accurately reflect the learning experiences of all students, potentially exacerbating existing inequalities and disadvantages.
Addressing the Challenges: A Balanced Approach
Recognizing the multifaceted nature of standardized testing, Texas has implemented measures to address the challenges associated with its use. These include:
- Diversifying Assessments: Texas has expanded the types of assessments used, incorporating performance-based assessments and projects that evaluate a broader range of skills and knowledge.
- Reducing the Emphasis on High-Stakes Testing: The state has moved away from solely relying on high-stakes testing for accountability purposes, incorporating other measures such as student growth and school climate into the accountability framework.
- Providing Professional Development: Texas has invested in professional development for teachers to help them understand the nuances of standardized testing and develop effective strategies for preparing students for assessments while maintaining a focus on broader educational goals.
FAQs Regarding Map Testing in Texas
1. What are the different types of standardized tests administered in Texas?
Texas administers several standardized tests, including the STAAR (State of Texas Assessments of Academic Readiness) for grades 3-8 and end-of-course exams for high school students.
2. How are standardized test scores used to determine school accountability ratings?
Texas uses a multi-faceted accountability system that includes student performance on standardized tests, student growth, and other factors such as college readiness and graduation rates.
3. How can parents access their child’s standardized test scores?
Parents can access their child’s standardized test scores through their school’s website or by contacting the school directly.
4. What are the implications of standardized test scores for students?
Standardized test scores can impact students’ academic progress, their access to advanced coursework, and even their future college and career opportunities.
5. What are the ethical considerations associated with standardized testing?
Ethical considerations related to standardized testing include ensuring fairness, equity, and the use of test scores in a responsible and ethical manner.
Tips for Success in Map Testing
- Understand the Content: Students should familiarize themselves with the TEKS and the content covered on the standardized tests.
- Practice Regularly: Regular practice with test-like questions can help students build confidence and improve their performance.
- Develop Effective Test-Taking Strategies: Students should learn effective test-taking strategies, such as time management, pacing, and eliminating answer choices.
- Seek Support: Students should not hesitate to seek support from teachers, parents, or tutors if they are struggling with the material or the test format.
Conclusion
Standardized testing in Texas, commonly known as "map testing," plays a significant role in the state’s educational system. While it provides valuable data for accountability and performance measurement, its impact is complex and multifaceted. The state has implemented measures to address the challenges associated with standardized testing, striving for a balanced approach that fosters both academic achievement and well-rounded student development. The future of standardized testing in Texas will likely continue to evolve, with ongoing efforts to ensure that these assessments remain a valuable tool for improving student outcomes and creating a more equitable and effective education system for all.

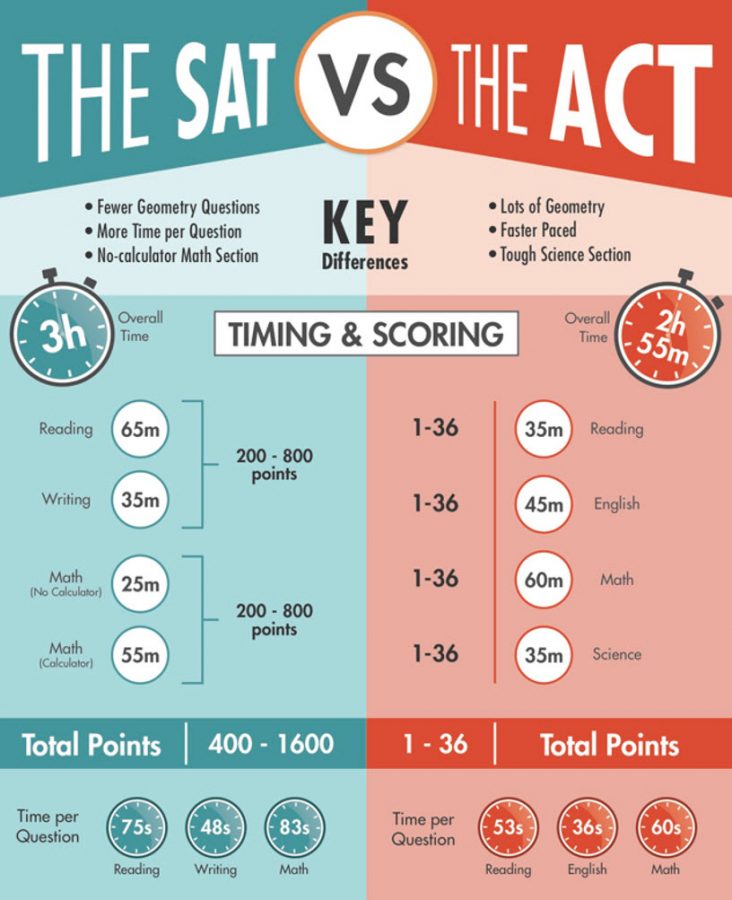





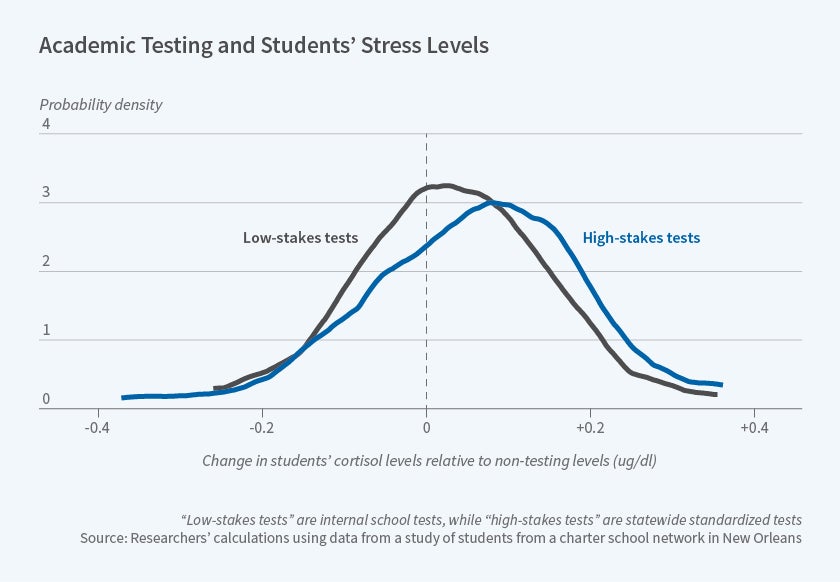
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Future: An Examination of Texas’s Standardized Testing Landscape. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
