mazda 6 2.2 map sensor
Related Articles: mazda 6 2.2 map sensor
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to mazda 6 2.2 map sensor. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Crucial Role of the MAP Sensor in Mazda 6 2.2 Engine Performance
The Mazda 6 2.2, known for its robust engine and reliable performance, relies heavily on a component often overlooked by many: the Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor. This seemingly small sensor plays a pivotal role in regulating the engine’s air intake, directly impacting fuel efficiency, power delivery, and overall drivability. Understanding the function of the MAP sensor and its potential issues is essential for any Mazda 6 2.2 owner seeking to maintain optimal engine performance.
Unveiling the MAP Sensor’s Function
The MAP sensor serves as a vital link between the engine’s intake manifold and the engine control unit (ECU). Its primary responsibility is to measure the absolute pressure within the intake manifold, providing the ECU with crucial data for fuel-air mixture calculations.
How the MAP Sensor Works
The MAP sensor is typically a diaphragm-based device. The diaphragm is sensitive to pressure changes within the intake manifold. As pressure increases, the diaphragm deflects, altering the resistance within the sensor. This change in resistance is translated into an electrical signal by the sensor’s internal circuitry. The ECU then receives this signal and interprets it as the absolute pressure in the intake manifold.
Impact on Engine Performance
The information provided by the MAP sensor is crucial for the ECU to accurately determine the amount of fuel needed to be injected into the engine for optimal combustion. A malfunctioning MAP sensor can lead to a variety of issues, including:
- Poor Fuel Economy: An inaccurate pressure reading from the MAP sensor can cause the ECU to inject too much or too little fuel, leading to inefficient combustion and reduced fuel economy.
- Engine Stalling: If the ECU receives an incorrect pressure reading, it may fail to provide the appropriate amount of fuel, leading to engine stalling, particularly during acceleration or idle.
- Rough Idle: Erratic fuel delivery due to a faulty MAP sensor can result in a rough idle, characterized by engine vibrations and instability.
- Reduced Power Output: An incorrect fuel-air mixture can hinder combustion efficiency, leading to reduced engine power and sluggish acceleration.
- Check Engine Light: A faulty MAP sensor will typically trigger the check engine light on the dashboard, alerting the driver to a potential issue.
Common MAP Sensor Issues
While MAP sensors are generally durable components, they can be susceptible to a few common issues:
- Contamination: Dirt, debris, or oil buildup on the sensor’s diaphragm can obstruct its movement and affect its ability to provide accurate pressure readings.
- Electrical Faults: Worn or damaged wiring, loose connections, or internal sensor circuitry failure can disrupt the flow of electrical signals from the sensor to the ECU.
- Diaphragm Damage: Physical damage to the diaphragm, such as punctures or tears, can compromise its ability to respond accurately to pressure changes.
Diagnosing MAP Sensor Issues
Identifying a faulty MAP sensor can be done through a combination of observation and diagnostic tools:
- Check Engine Light: A check engine light accompanied by symptoms like poor fuel economy, rough idle, or reduced power output can be a strong indicator of a MAP sensor issue.
- Visual Inspection: Inspect the MAP sensor for signs of contamination, damage, or loose connections.
- Diagnostic Scanner: Use an OBD-II scanner to read the ECU’s diagnostic codes. A code related to the MAP sensor will confirm a potential issue.
- Pressure Testing: A specialized pressure tester can be used to verify the MAP sensor’s output against a known pressure source, confirming its accuracy.
Replacing a Faulty MAP Sensor
If a faulty MAP sensor is identified, replacing it is a relatively straightforward process:
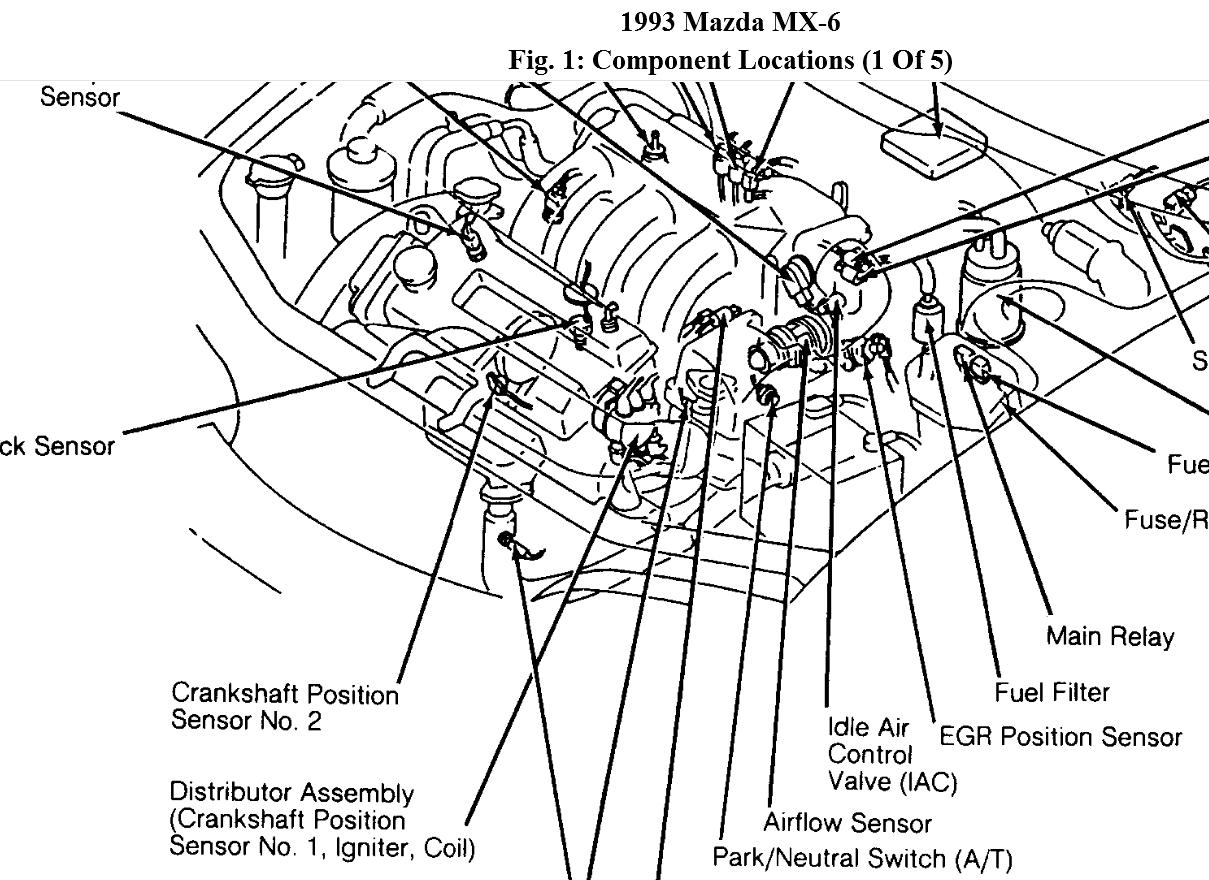
- Locate the Sensor: The MAP sensor is typically located on the intake manifold, often near the throttle body. Consult your owner’s manual or a reliable online resource for the exact location in your specific Mazda 6 2.2 model.
- Disconnect the Electrical Connector: Carefully disconnect the electrical connector leading to the MAP sensor.
- Remove the Sensor: Unscrew the MAP sensor from the intake manifold, taking care not to damage the surrounding components.
- Install the New Sensor: Install the new MAP sensor in the same position as the old one, ensuring it is securely fastened.
- Reconnect the Electrical Connector: Reconnect the electrical connector to the new MAP sensor.
- Clear Diagnostic Codes: Use an OBD-II scanner to clear the stored diagnostic codes after replacing the MAP sensor.
FAQs
Q: What are the symptoms of a bad MAP sensor?
A: Symptoms of a faulty MAP sensor can include poor fuel economy, rough idle, engine stalling, reduced power output, and a check engine light.
Q: Can I drive my car with a bad MAP sensor?
A: While you may be able to drive your car with a faulty MAP sensor, it is not recommended. The sensor plays a crucial role in engine performance, and driving with a malfunctioning sensor can lead to further damage and potentially unsafe driving conditions.
Q: How often should I replace my MAP sensor?
A: MAP sensors are generally durable and do not have a specific replacement interval. However, they can be susceptible to wear and tear, and it is advisable to replace them if they show signs of malfunction or contamination.
Q: Can I clean a MAP sensor?
A: Cleaning a contaminated MAP sensor may be possible, but it is not recommended. The sensor’s delicate diaphragm can be easily damaged during the cleaning process. It is often more advisable to replace the sensor if it is heavily contaminated.
Tips
- Regular Maintenance: Regular engine maintenance, including air filter replacement and engine cleaning, can help prevent contamination of the MAP sensor.
- Avoid Harsh Driving Conditions: Driving in extreme conditions, such as dusty environments or excessively hot climates, can increase the risk of sensor contamination or damage.
- Professional Inspection: If you suspect a MAP sensor issue, it is always best to have a professional mechanic diagnose and repair the problem.
Conclusion
The MAP sensor plays a vital role in the efficient operation of the Mazda 6 2.2 engine. By accurately measuring intake manifold pressure, it provides the ECU with essential information for fuel-air mixture calculations, impacting fuel economy, power delivery, and overall drivability. Maintaining a functional MAP sensor is crucial for ensuring optimal engine performance and preventing potential issues. Regular maintenance, awareness of common sensor problems, and prompt professional intervention when necessary are key to maximizing the performance and longevity of your Mazda 6 2.2 engine.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into mazda 6 2.2 map sensor. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
