Navigating the Arteries of Southern California: A Comprehensive Guide to its Highway Network
Related Articles: Navigating the Arteries of Southern California: A Comprehensive Guide to its Highway Network
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Arteries of Southern California: A Comprehensive Guide to its Highway Network. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Arteries of Southern California: A Comprehensive Guide to its Highway Network

Southern California’s sprawling landscape, characterized by its diverse topography, thriving urban centers, and iconic destinations, is intricately connected by a vast and complex highway network. This intricate web of asphalt and concrete serves as the lifeblood of the region, facilitating the movement of people, goods, and services, and playing a vital role in the economic and social fabric of Southern California. Understanding this network is essential for anyone navigating the region, whether for commuting, exploring its diverse attractions, or simply understanding the geographical context of this dynamic area.
A Journey Through the Arteries: Exploring the Major Highways
The Southern California highway system is a tapestry woven from a series of interconnected freeways, each serving a unique purpose and catering to specific traffic patterns. Some of the most prominent arteries, forming the backbone of the region’s transportation infrastructure, include:
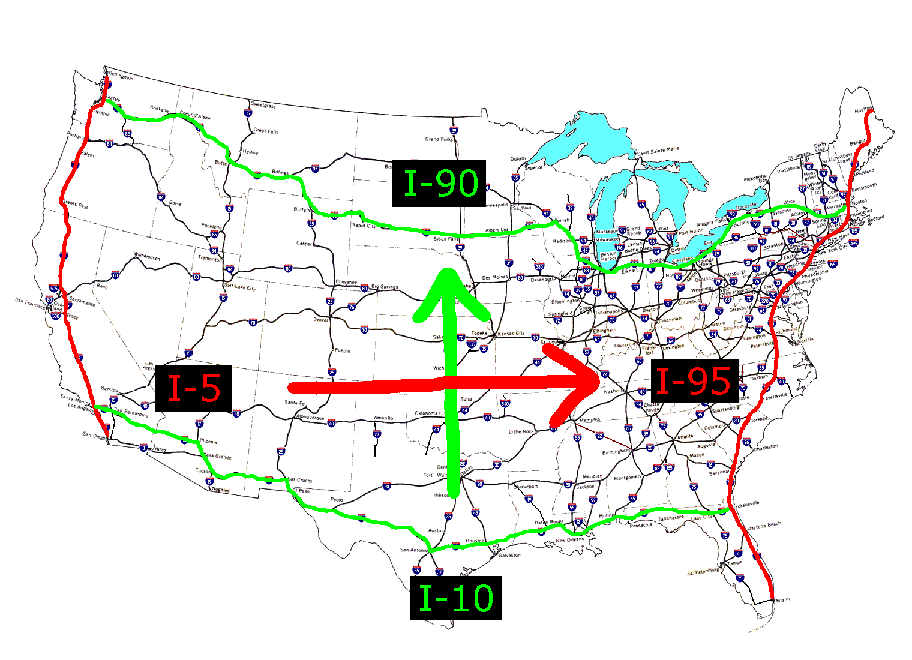
- Interstate 5 (I-5): This north-south freeway, often referred to as the "Golden State Freeway," traverses the entire length of California, connecting Southern California to the rest of the state and beyond. It is a major artery for commerce and tourism, carrying significant traffic volumes, particularly in the Los Angeles metropolitan area.
- Interstate 10 (I-10): This east-west freeway, known as the "San Bernardino Freeway" in Southern California, runs from the Pacific Ocean to the Arizona border. It is a vital route for regional and national transportation, connecting Los Angeles to Phoenix, Arizona, and other key destinations in the Southwest.
- Interstate 405 (I-405): This north-south freeway, commonly called the "San Diego Freeway," is a critical route for traffic between Los Angeles and Orange County, connecting the San Fernando Valley to the coastal cities of Orange County. It is notorious for its heavy traffic congestion, particularly during peak hours.
- Interstate 605 (I-605): This north-south freeway, known as the "San Gabriel Freeway," serves as a major connector between the San Fernando Valley and the San Gabriel Valley, offering an alternative route to I-5.
- Interstate 110 (I-110): This north-south freeway, called the "Harbor Freeway," connects downtown Los Angeles to the Port of Los Angeles and Long Beach, serving as a vital artery for the region’s shipping and logistics industry.
- Interstate 210 (I-210): This east-west freeway, known as the "Foothill Freeway," traverses the San Gabriel Valley, connecting Pasadena, Glendale, and other cities to the San Fernando Valley.
- Interstate 105 (I-105): This east-west freeway, known as the "Century Freeway," connects the San Gabriel Valley to the South Bay region of Los Angeles County, serving as a key route for commuters and travelers.
- Interstate 40 (I-40): This east-west freeway, known as the "Historic Route 66" in Southern California, runs from Barstow to the Arizona border. It is a major route for travelers seeking a historic and scenic driving experience.
Beyond the Interstates: Exploring the Regional Highway System
In addition to the major interstates, Southern California’s highway network is further enriched by a network of state highways and local freeways, each serving specific communities and connecting them to the broader regional network. These include:
- California State Route 1 (CA-1): This scenic coastal highway, known as the "Pacific Coast Highway," traverses the California coastline, offering breathtaking views of the Pacific Ocean. It connects major coastal cities like Santa Monica, Malibu, and Santa Barbara.
- California State Route 110 (CA-110): This north-south freeway, known as the "Glendale Freeway," connects the San Fernando Valley to downtown Los Angeles, providing an alternative route to I-5.
- California State Route 101 (CA-101): This north-south freeway, known as the "Ventura Freeway," connects the San Fernando Valley to Ventura County, serving as a major route for commuters and travelers.
- California State Route 91 (CA-91): This east-west freeway, known as the "Corona Freeway," connects the Inland Empire to Orange County, serving as a major route for commuters and travelers.
- California State Route 60 (CA-60): This east-west freeway, known as the "Pomona Freeway," connects the San Gabriel Valley to the Inland Empire, serving as a major route for commuters and travelers.
Navigating the Network: Understanding the Significance
The Southern California highway network is more than just a collection of roads; it is a dynamic system that reflects the region’s growth, challenges, and aspirations. Its importance can be understood in terms of its impact on:
- Economic Development: The highway system facilitates the movement of goods and services, supporting the region’s industries, businesses, and trade. It connects major ports, airports, and industrial centers, contributing to the region’s economic vitality.
- Tourism and Recreation: The highway network provides access to Southern California’s iconic attractions, including beaches, national parks, mountains, and deserts. It allows visitors to explore the region’s diverse natural beauty and cultural heritage.
- Commuting and Transportation: The highway system connects residents to their workplaces, schools, and communities, facilitating daily commutes and regional travel. It plays a crucial role in the mobility of Southern California’s population.
- Emergency Response: The highway system provides vital access for emergency services, enabling rapid response to natural disasters, accidents, and other emergencies.
Challenges and Solutions: Addressing the Network’s Complexities
Despite its significance, the Southern California highway network faces several challenges, including:
- Traffic Congestion: The region’s dense population and growing economy lead to significant traffic congestion, particularly during peak hours. This can result in delays, frustration, and increased air pollution.
- Infrastructure Deterioration: The aging infrastructure of some highways requires maintenance and repairs to ensure safety and functionality.
- Environmental Impacts: Highway construction and traffic contribute to air pollution, noise pollution, and habitat fragmentation.
Addressing these challenges requires a comprehensive approach that involves:
- Investment in Infrastructure: Investing in road improvements, expanding capacity, and implementing innovative traffic management solutions can help alleviate congestion.
- Promoting Alternative Transportation: Encouraging the use of public transportation, cycling, and walking can reduce reliance on cars and improve air quality.
- Sustainable Design and Construction: Implementing environmentally friendly design and construction practices can minimize the environmental impact of highway projects.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
Q: What are the most congested highways in Southern California?
A: The most congested highways in Southern California include I-405 (San Diego Freeway), I-5 (Golden State Freeway), and I-10 (San Bernardino Freeway), particularly during peak hours.
Q: What are the best ways to avoid traffic congestion?
A: Utilizing alternative routes, avoiding peak travel times, using public transportation, and carpooling are effective ways to mitigate traffic congestion.
Q: How can I find real-time traffic information?
A: Several online resources and mobile apps provide real-time traffic information, including Google Maps, Waze, and the California Department of Transportation (Caltrans) website.
Q: What are the major road construction projects currently underway in Southern California?
A: Caltrans’ website provides updates on major road construction projects across the state, including those in Southern California.
Tips for Navigating the Southern California Highway Network
- Plan your route in advance: Utilize online mapping tools to plan your route and estimate travel time, taking into account potential traffic delays.
- Check for traffic updates: Monitor real-time traffic information to avoid congested areas and adjust your route accordingly.
- Consider alternative transportation: Explore public transportation options, such as buses, trains, or ride-sharing services, to avoid traffic congestion.
- Be aware of weather conditions: Weather can significantly impact road conditions, so check for weather forecasts before traveling.
- Drive defensively: Be aware of your surroundings, maintain a safe following distance, and obey all traffic laws.
Conclusion: A Vital Network for a Dynamic Region
The Southern California highway network is a testament to the region’s growth and dynamism. It connects communities, drives economic activity, and provides access to the region’s diverse attractions. While facing challenges related to congestion, infrastructure, and environmental impact, the network remains a vital resource for the region’s future. By investing in infrastructure, promoting alternative transportation, and embracing sustainable practices, Southern California can ensure its highway system continues to serve as a robust and resilient artery for its vibrant communities.
![Day 717 [6-6-15] "New Heights" - Day 1 of our trip showed us how roads are the arteries of](https://i.pinimg.com/originals/0d/51/87/0d518724fb36ae7c7717e61998360ca8.jpg)




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Arteries of Southern California: A Comprehensive Guide to its Highway Network. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
