Navigating the Arteries of Southern California: A Comprehensive Guide to the Freeway Network
Related Articles: Navigating the Arteries of Southern California: A Comprehensive Guide to the Freeway Network
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Arteries of Southern California: A Comprehensive Guide to the Freeway Network. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Arteries of Southern California: A Comprehensive Guide to the Freeway Network
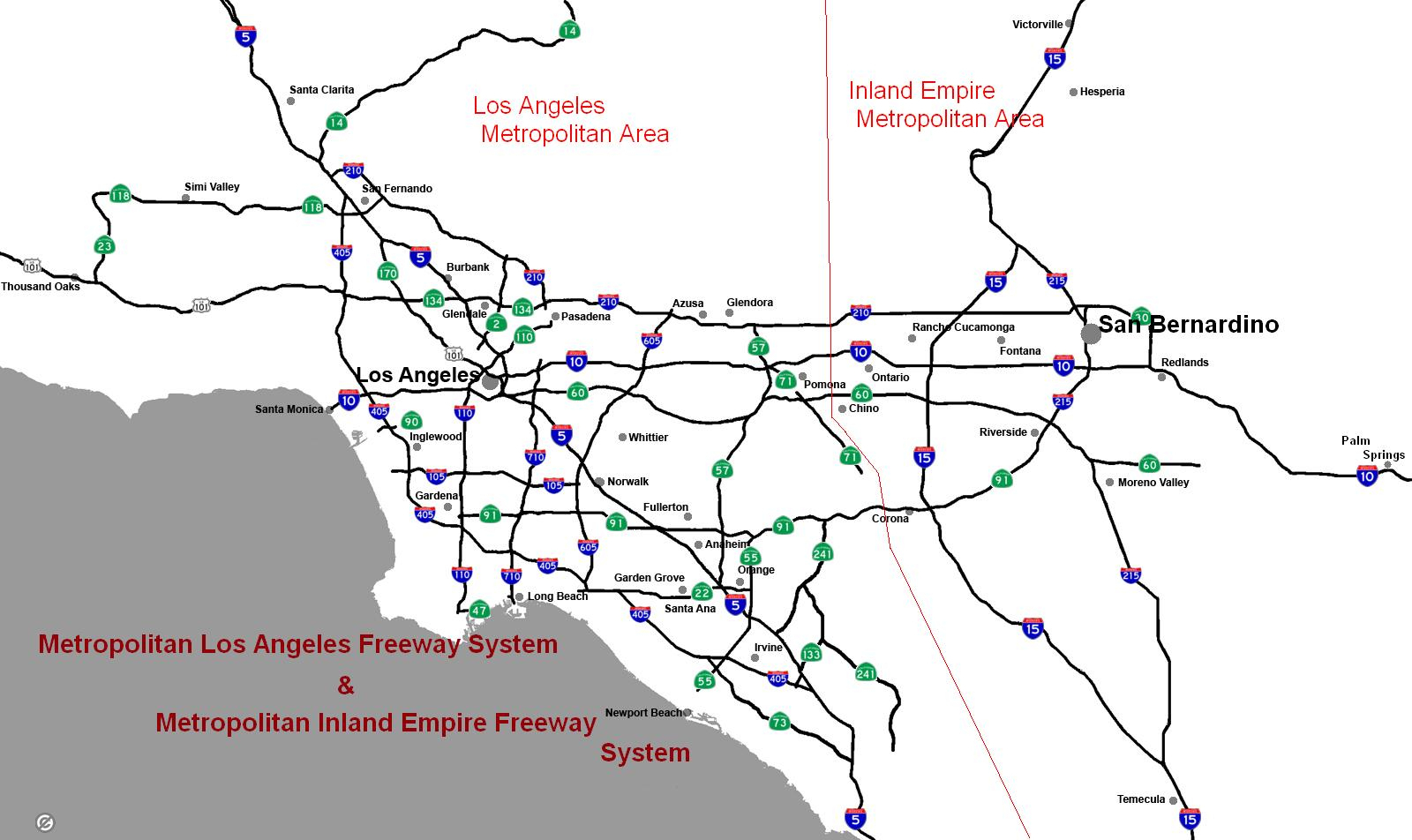
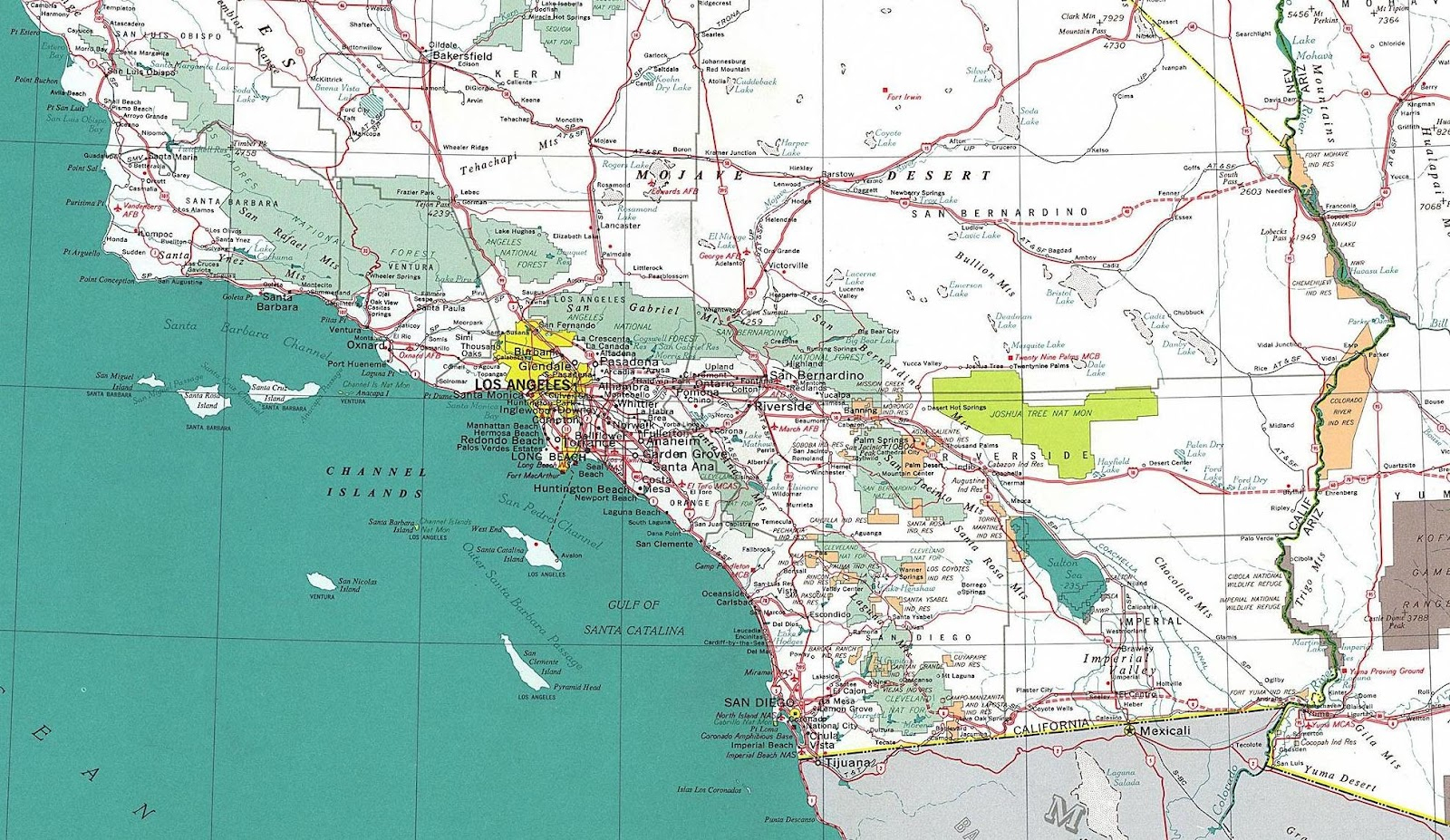
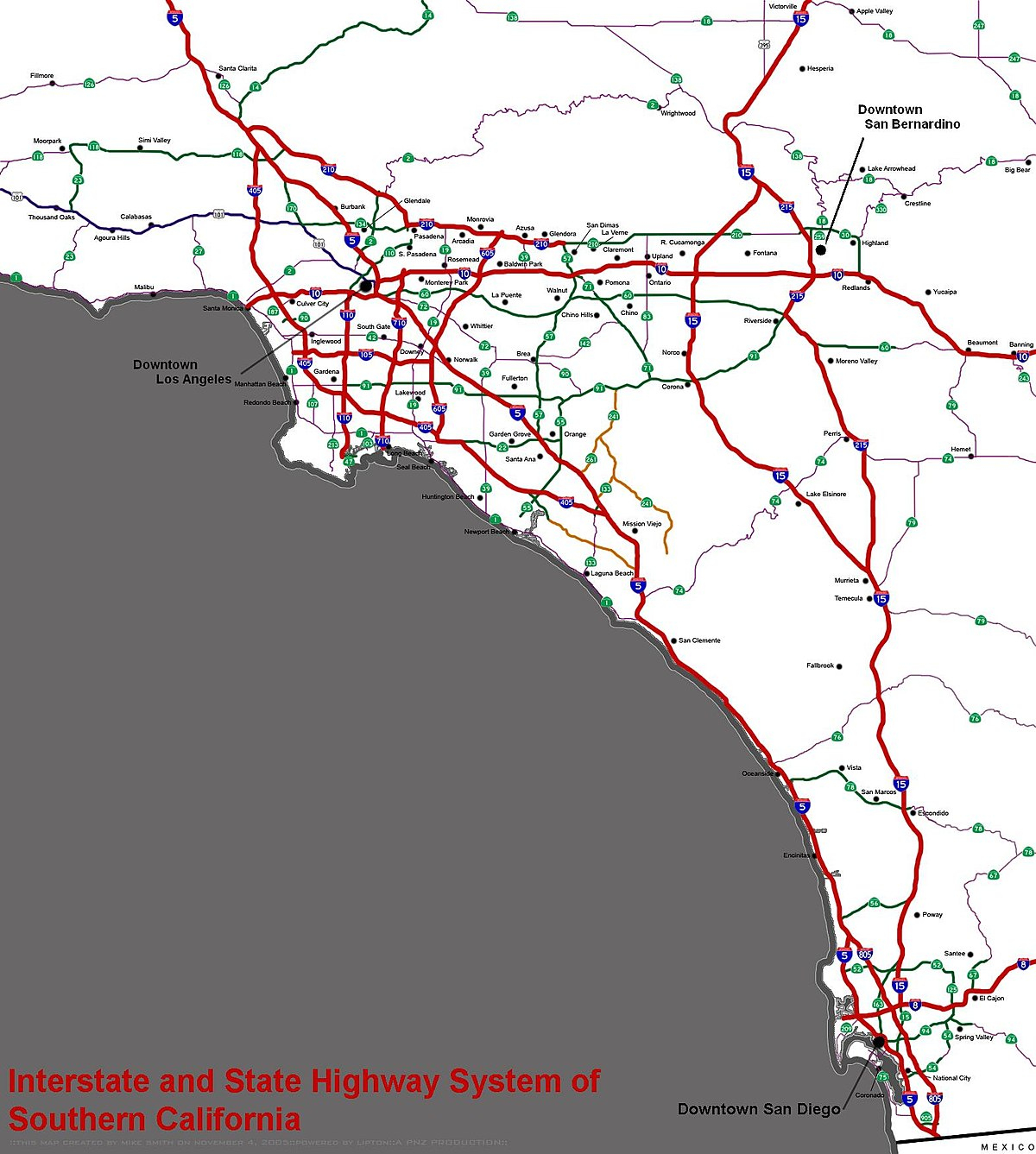
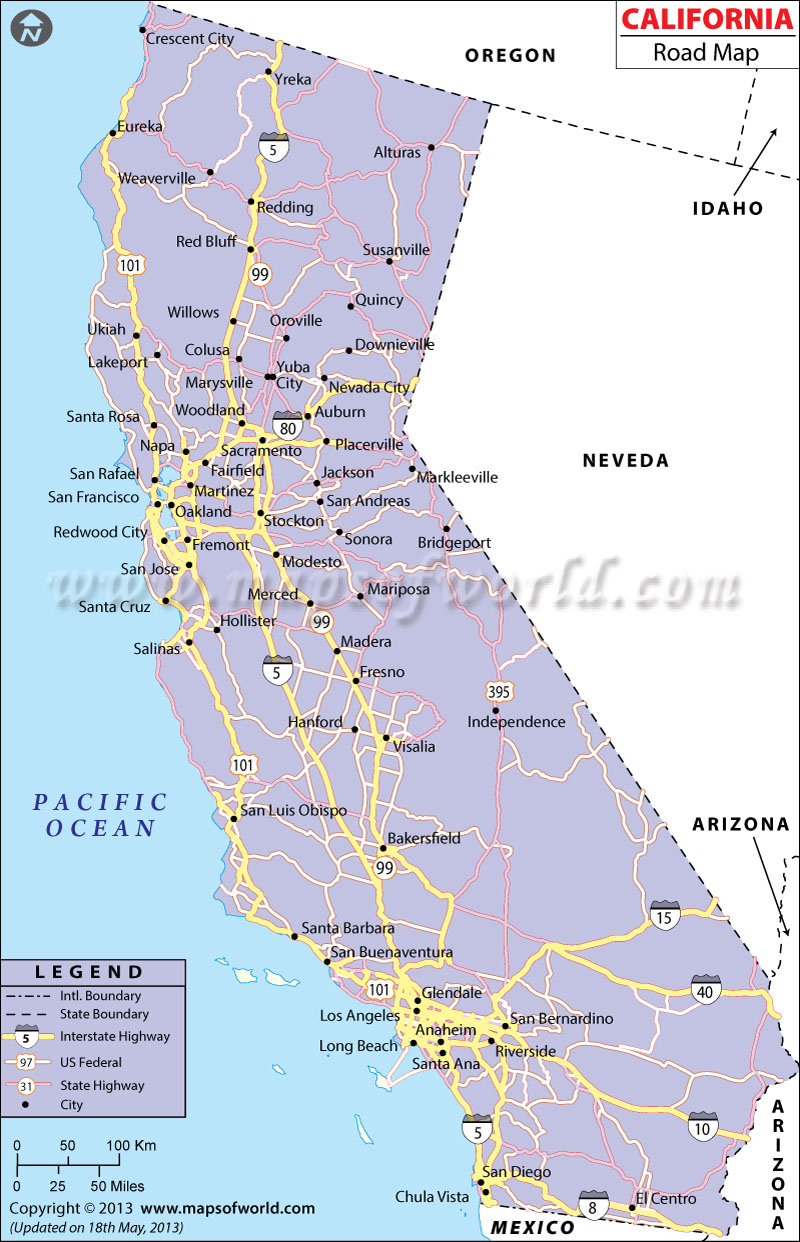
Southern California, a region renowned for its diverse landscape, vibrant culture, and bustling economy, is also defined by its sprawling network of freeways. This intricate web of asphalt ribbons, stretching across hundreds of miles, acts as the lifeblood of the region, facilitating the movement of millions of people and goods daily. Understanding this intricate system is essential for anyone navigating the region, whether they are a seasoned resident or a first-time visitor.
The Origins of a Network:
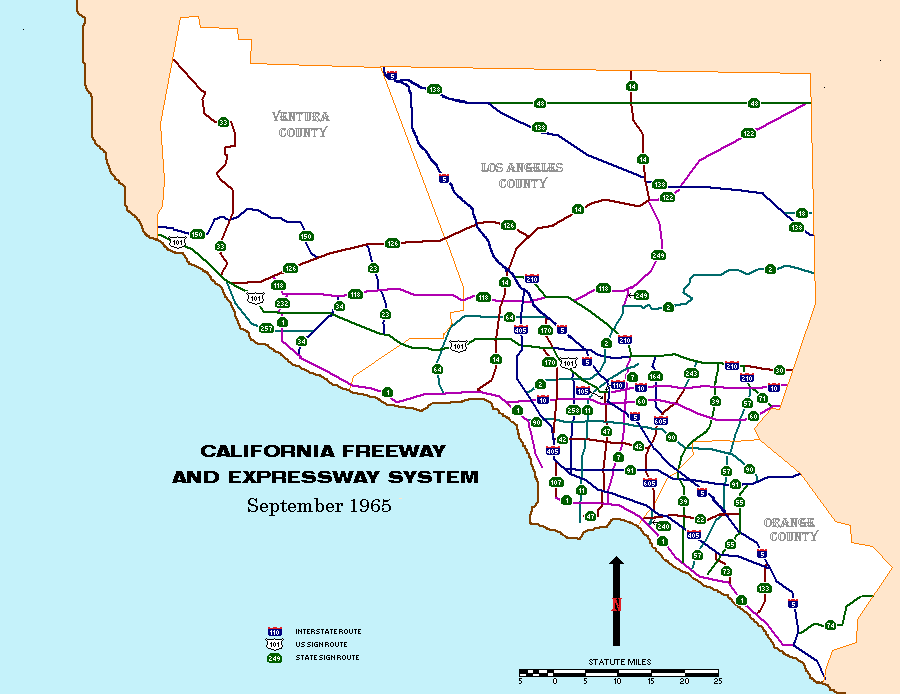
The development of Southern California’s freeway system began in the early 20th century, driven by the rapid growth of the region’s population and the rise of the automobile. The first freeway, the Pasadena Freeway (now the 110 Freeway), opened in 1940, marking the beginning of a major infrastructure project that would reshape the region.
The post-World War II era saw an explosion in freeway construction, fueled by the availability of federal funding and the increasing demand for efficient transportation. Key freeways, such as the 405 Freeway (San Diego Freeway) and the 10 Freeway (Santa Monica Freeway), were built during this period, forming the backbone of the current freeway network.
The Anatomy of the Network:
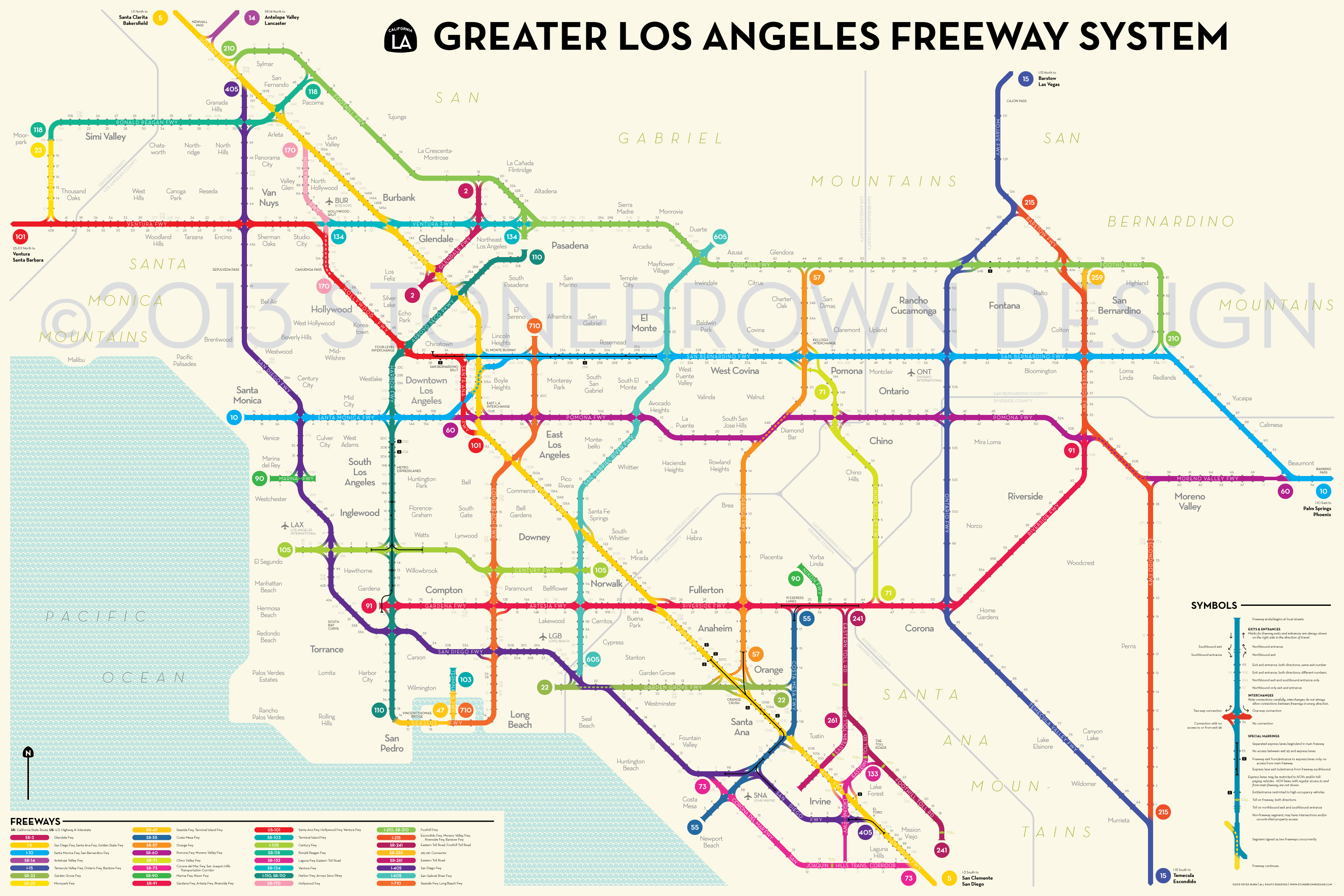
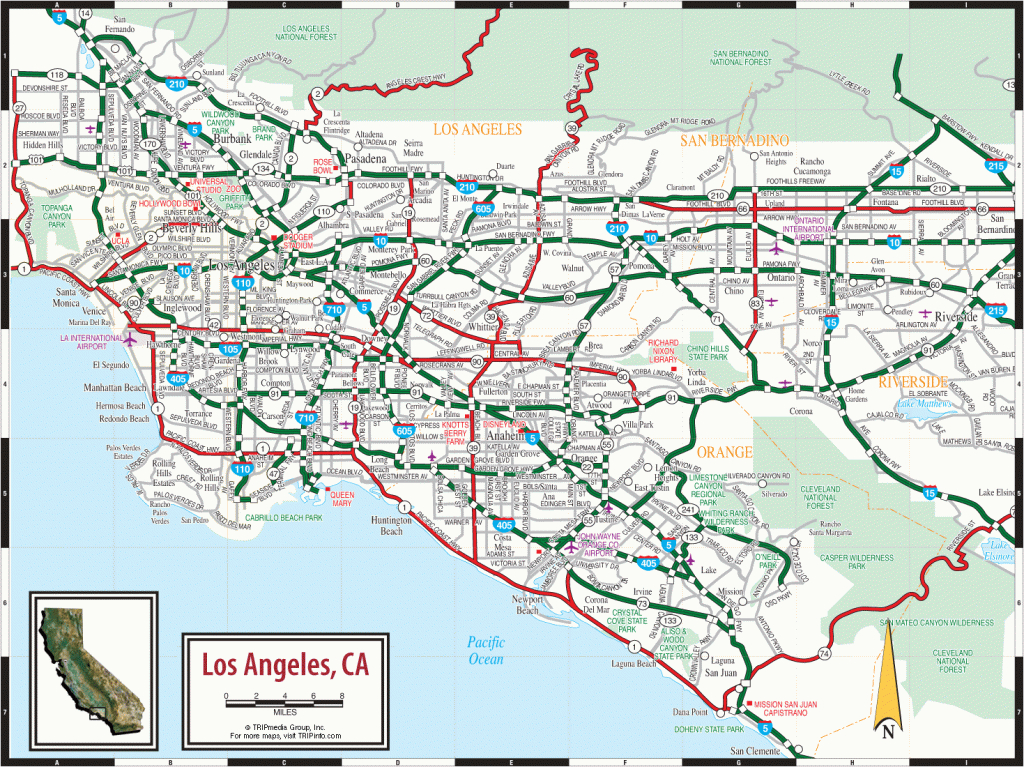
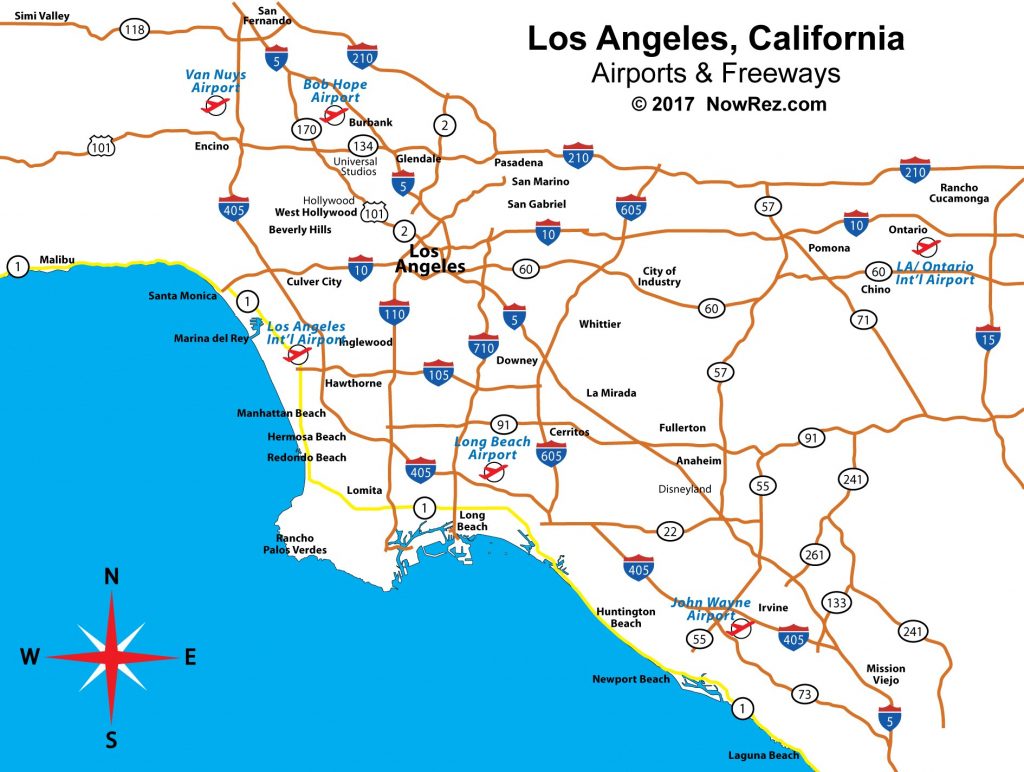
The Southern California freeway system is comprised of a complex network of interconnected highways, encompassing both interstate and state routes. The primary freeways, designated by numbered routes, form the core of the network, connecting major cities and regions. These highways are further divided into smaller, numbered routes, forming a vast web of interconnected roadways.
The system is organized around a radial pattern, with freeways radiating outward from the central Los Angeles Basin towards the surrounding areas. The 10 Freeway, running east-west, serves as the primary artery connecting the San Fernando Valley to the Westside and the Inland Empire. Other major freeways, such as the 405 Freeway, the 5 Freeway (Golden State Freeway), and the 60 Freeway (Pomona Freeway), provide crucial connections to the coastal areas, the San Gabriel Valley, and Orange County.
Navigating the Network:
The Southern California freeway system, while efficient, can be daunting for those unfamiliar with its intricacies. The sheer volume of traffic, particularly during peak hours, can lead to significant delays. Understanding the layout of the network and utilizing available resources is crucial for a smooth and stress-free journey.
Maps and Resources:
Several resources are available to assist drivers in navigating the freeway network:
- Digital Maps: Online mapping services, such as Google Maps and Waze, provide real-time traffic updates, alternative routes, and estimated travel times.
- Printed Maps: Traditional paper maps, while less dynamic, can offer a broader overview of the freeway system and provide a sense of direction.
- Traffic Reports: Radio and television stations often broadcast live traffic reports, highlighting congested areas and providing alternative routes.
- Mobile Apps: Dedicated traffic apps, like Waze and Google Maps, offer turn-by-turn navigation, real-time traffic information, and incident reports.
Tips for Freeway Navigation:
- Plan Your Route: Before embarking on a journey, plan your route using digital maps or printed maps. Consider alternative routes to avoid known congestion areas.
- Check Traffic Reports: Before setting out, check traffic reports for real-time updates and potential delays.
- Avoid Peak Hours: If possible, avoid traveling during peak hours, typically between 7:00 AM to 9:00 AM and 4:00 PM to 6:00 PM.
- Stay Alert: Pay close attention to road signs, traffic signals, and other drivers. Distracted driving can lead to accidents.
- Use HOV Lanes: If eligible, utilize High Occupancy Vehicle (HOV) lanes to reduce travel time.
- Be Prepared for Delays: Traffic congestion is common in Southern California. Be prepared for unexpected delays and adjust your schedule accordingly.
The Impact of the Freeway System:
The Southern California freeway system has had a profound impact on the region’s development, facilitating economic growth, urbanization, and the expansion of suburban areas. However, the system has also contributed to issues like air pollution, urban sprawl, and traffic congestion.
Environmental Concerns:
The dense freeway network contributes to air pollution, as vehicles release exhaust fumes into the atmosphere. This has resulted in poor air quality, particularly in urban areas, leading to health problems for residents.
Urban Sprawl:
The accessibility provided by freeways has encouraged urban sprawl, with development extending outward from city centers. This has led to increased traffic congestion, longer commutes, and the loss of open space.
Traffic Congestion:
Despite the extensive freeway network, traffic congestion remains a persistent problem, particularly during peak hours. This can lead to increased travel times, stress, and economic losses.
Future Challenges:
The Southern California freeway system faces several challenges in the coming years:
- Aging Infrastructure: Many freeways are aging and require significant maintenance and repairs.
- Increasing Traffic Demand: The region’s population continues to grow, putting increasing pressure on the freeway system.
- Sustainability Concerns: The environmental impact of the freeway network needs to be addressed through sustainable transportation solutions.
The Importance of Public Transportation:
To address the challenges facing the freeway system, the region is investing in public transportation alternatives, such as light rail, buses, and commuter rail. These systems offer a more sustainable and efficient way to travel, reducing reliance on private vehicles and improving air quality.
Conclusion:
The Southern California freeway network, while a vital part of the region’s infrastructure, also poses significant challenges. Understanding the system, navigating it effectively, and exploring alternative transportation options are crucial for mitigating the negative impacts and ensuring the region’s continued growth and development. As the region continues to evolve, finding innovative solutions to address the challenges of traffic congestion, air pollution, and urban sprawl will be essential for maintaining the quality of life for residents and visitors alike.
FAQs:
Q: What are the most congested freeways in Southern California?
A: The 405 Freeway (San Diego Freeway) and the 10 Freeway (Santa Monica Freeway) are consistently ranked among the most congested freeways in the region, particularly during peak hours.
Q: How can I avoid traffic on the freeways?
A: Utilizing digital maps and traffic reports, avoiding peak hours, and exploring alternative routes can help minimize traffic delays.
Q: What is the best time to travel on the freeways?
A: Weekends and evenings, outside of peak hours, generally offer the least congested travel conditions.
Q: Are there any toll roads in Southern California?
A: Yes, several toll roads exist, including the 73 Toll Road (Orange County), the 91 Freeway (Corona Freeway), and the 134 Freeway (Ventura Freeway).
Q: What are the speed limits on the freeways?
A: The speed limit on most Southern California freeways is 65 miles per hour, but it can vary depending on the specific freeway and location.
Tips:
- Utilize HOV Lanes: If eligible, utilize High Occupancy Vehicle (HOV) lanes to reduce travel time.
- Use Carpool Services: Consider carpooling or using ride-sharing services to reduce traffic congestion and save on fuel costs.
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of road closures, construction projects, and other traffic disruptions through traffic reports and digital maps.
- Practice Defensive Driving: Be aware of your surroundings, maintain a safe following distance, and avoid distractions while driving.
- Consider Alternative Transportation: Explore public transportation options, such as buses, trains, and light rail, to reduce reliance on private vehicles.
Conclusion:
The Southern California freeway network is a complex and dynamic system that plays a crucial role in the region’s economy and daily life. Understanding its intricacies, navigating it effectively, and exploring alternative transportation options are essential for navigating the region’s roads and contributing to a sustainable future. As the region continues to grow and evolve, finding innovative solutions to address the challenges of traffic congestion, air pollution, and urban sprawl will be crucial for maintaining the quality of life for residents and visitors alike.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Arteries of Southern California: A Comprehensive Guide to the Freeway Network. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
