Navigating the Educational Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Grade 6 Standardized Testing
Related Articles: Navigating the Educational Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Grade 6 Standardized Testing
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Educational Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Grade 6 Standardized Testing. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Educational Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Grade 6 Standardized Testing
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Educational Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Grade 6 Standardized Testing
- 3.1 Understanding the Purpose and Structure of Grade 6 Standardized Testing
- 3.2 Benefits and Challenges of Grade 6 Standardized Testing
- 3.3 Addressing Concerns and Ensuring Equity in Standardized Testing
- 3.4 Frequently Asked Questions about Grade 6 Standardized Testing
- 3.5 Tips for Success in Grade 6 Standardized Testing
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Educational Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Grade 6 Standardized Testing

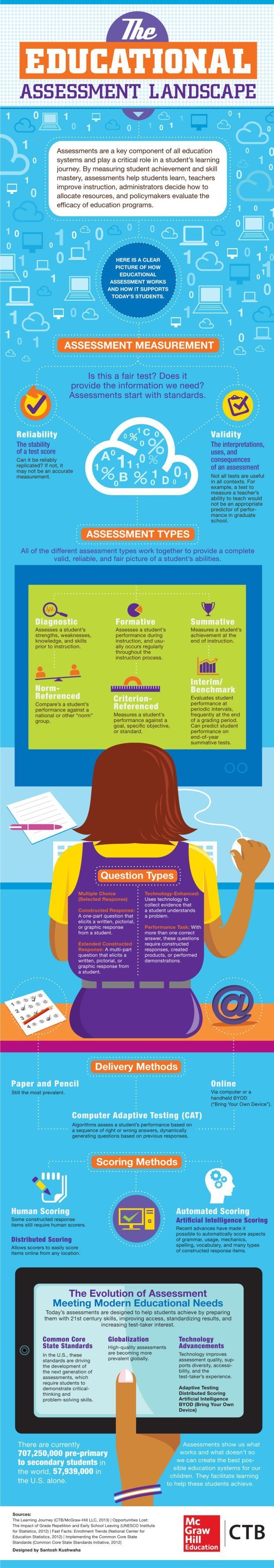
Standardized testing, a ubiquitous element of the modern educational landscape, plays a significant role in shaping curriculum, gauging student progress, and informing policy decisions. Among the various assessments administered, Grade 6 standardized tests hold a unique position, serving as a critical milestone in a student’s academic journey. This article delves into the intricacies of Grade 6 standardized testing, exploring its purpose, structure, and implications for students, educators, and the educational system as a whole.
Understanding the Purpose and Structure of Grade 6 Standardized Testing
Grade 6 standardized tests, often referred to as "MAP" tests (Measures of Academic Progress), serve as a comprehensive evaluation tool designed to assess student proficiency in core subject areas, primarily reading, mathematics, and language arts. These tests are typically administered nationwide, providing a standardized benchmark against which student performance can be compared. The primary objectives of these assessments are:
- Measuring Academic Progress: Grade 6 standardized tests provide a snapshot of a student’s academic standing, highlighting areas of strength and identifying potential areas for improvement. This data enables educators to tailor instruction and support to individual student needs.
- Monitoring Curriculum Effectiveness: These tests serve as valuable indicators of the effectiveness of curriculum implementation and instructional practices. By analyzing student performance trends, educators can identify areas where adjustments may be necessary to enhance learning outcomes.
- Informing Educational Policy: Data collected from standardized tests informs policy decisions at the district, state, and national levels. This information helps policymakers allocate resources, prioritize educational initiatives, and track overall educational progress.
The structure of Grade 6 standardized tests varies depending on the specific assessment tool employed. However, most tests share common characteristics:
- Multiple-Choice Format: The majority of questions are presented in a multiple-choice format, requiring students to select the best answer from a set of options.
- Subject-Specific Sections: Tests are typically divided into sections dedicated to specific subject areas, such as reading comprehension, mathematics, and language arts.
- Computer-Based Administration: Many standardized tests are now administered online, allowing for efficient scoring and immediate feedback.
- Adaptive Testing: Some tests utilize adaptive technology, adjusting the difficulty of questions based on a student’s performance, providing a more personalized assessment experience.
Benefits and Challenges of Grade 6 Standardized Testing
While standardized tests offer valuable insights into student learning and the effectiveness of educational practices, they also present certain challenges and limitations.
Benefits:
- Objective Measurement: Standardized tests provide an objective measure of student proficiency, minimizing subjective biases that may arise in traditional assessments.
- Data-Driven Instruction: The data generated by standardized tests allows educators to identify specific areas where students struggle and tailor instruction accordingly.
- Accountability and Transparency: Standardized tests promote accountability by providing a consistent measure of student performance, fostering transparency in educational outcomes.
- Early Intervention: Identifying potential academic difficulties through standardized tests enables early intervention strategies, supporting students in overcoming challenges before they escalate.
Challenges:
- Test Anxiety and Stress: The high-stakes nature of standardized testing can induce anxiety and stress in students, potentially impacting their performance.
- Narrow Focus on Specific Skills: Standardized tests often focus on a limited range of skills, potentially overlooking other important aspects of learning, such as creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving.
- Cultural and Socioeconomic Bias: Standardized tests may inadvertently perpetuate cultural and socioeconomic biases, potentially disadvantaging students from marginalized backgrounds.
- Teaching to the Test: The emphasis on standardized test scores can lead to a narrow focus on test preparation, potentially neglecting other essential aspects of the curriculum.
Addressing Concerns and Ensuring Equity in Standardized Testing
Recognizing the limitations of standardized testing, educational leaders and policymakers are continuously striving to mitigate potential biases and ensure equitable assessment practices. Key strategies include:
- Addressing Test Anxiety: Schools are implementing strategies to reduce test anxiety, such as providing students with practice opportunities, familiarizing them with the test format, and fostering a supportive learning environment.
- Expanding Assessment Methods: Incorporating a wider range of assessment tools, including performance-based tasks, projects, and portfolios, can provide a more holistic picture of student learning.
- Promoting Inclusive Practices: Ensuring that standardized tests are accessible to all students, regardless of their background or learning needs, is crucial. This includes providing accommodations and modifications for students with disabilities and those who are English language learners.
- Developing Comprehensive Assessment Systems: Moving beyond a sole reliance on standardized tests by incorporating multiple data points, such as teacher observations, student portfolios, and classroom assessments, can provide a more nuanced understanding of student progress.
Frequently Asked Questions about Grade 6 Standardized Testing
1. How often are Grade 6 standardized tests administered?
The frequency of standardized testing varies depending on the specific test and the state or district regulations. However, most students take standardized tests annually in Grade 6.
2. What are the consequences of failing a Grade 6 standardized test?
Failing a Grade 6 standardized test does not typically result in grade retention or other punitive measures. However, low scores may trigger interventions such as tutoring, summer school, or additional academic support.
3. How can parents support their children in preparing for Grade 6 standardized tests?
Parents can support their children by encouraging regular study habits, providing a quiet and supportive learning environment, and familiarizing them with the test format. They can also work with teachers to identify areas where their child may need additional support.
4. What are the best resources for preparing for Grade 6 standardized tests?
A variety of online resources, practice tests, and study guides are available to help students prepare for standardized tests. Additionally, teachers and school administrators can provide guidance and support.
5. How can schools ensure that standardized tests are administered fairly and equitably?
Schools can ensure fairness and equity by providing all students with access to the necessary resources, accommodations, and modifications. They can also implement culturally responsive practices and ensure that test materials are free from bias.
Tips for Success in Grade 6 Standardized Testing
- Practice Regularly: Encourage students to engage in regular practice sessions using sample tests and study materials.
- Focus on Foundational Skills: Emphasize the development of foundational skills in reading, mathematics, and language arts, as these form the basis for success on standardized tests.
- Build Test-Taking Strategies: Teach students effective test-taking strategies, such as time management, pacing, and eliminating incorrect answers.
- Reduce Test Anxiety: Create a supportive and encouraging environment to minimize test anxiety. Provide students with opportunities to practice and familiarize themselves with the test format.
- Address Individual Needs: Identify students who may require additional support and provide individualized instruction or accommodations.
Conclusion
Grade 6 standardized testing serves as a critical milestone in a student’s educational journey, providing valuable insights into academic progress and informing educational decisions. While these tests offer benefits in terms of objective measurement and data-driven instruction, it is essential to acknowledge their limitations and strive for equitable assessment practices. By fostering a balanced approach that incorporates a variety of assessment methods, reduces test anxiety, and addresses individual needs, educators can ensure that standardized tests serve as a valuable tool for supporting student learning and promoting educational excellence.




![The Educational Assessment Landscape [INFOGRAPHIC] - Online Education Blog of Touro University](https://i2.wp.com/blogs.onlineeducation.touro.edu/wp-content/uploads/2013/08/educational-assessment-landscape-infographic.png?fit=966%2C787u0026ssl=1)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Educational Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Grade 6 Standardized Testing. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
