Navigating the Fault Lines: Understanding the Seismic Landscape of Taiwan
Related Articles: Navigating the Fault Lines: Understanding the Seismic Landscape of Taiwan
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Fault Lines: Understanding the Seismic Landscape of Taiwan. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Fault Lines: Understanding the Seismic Landscape of Taiwan

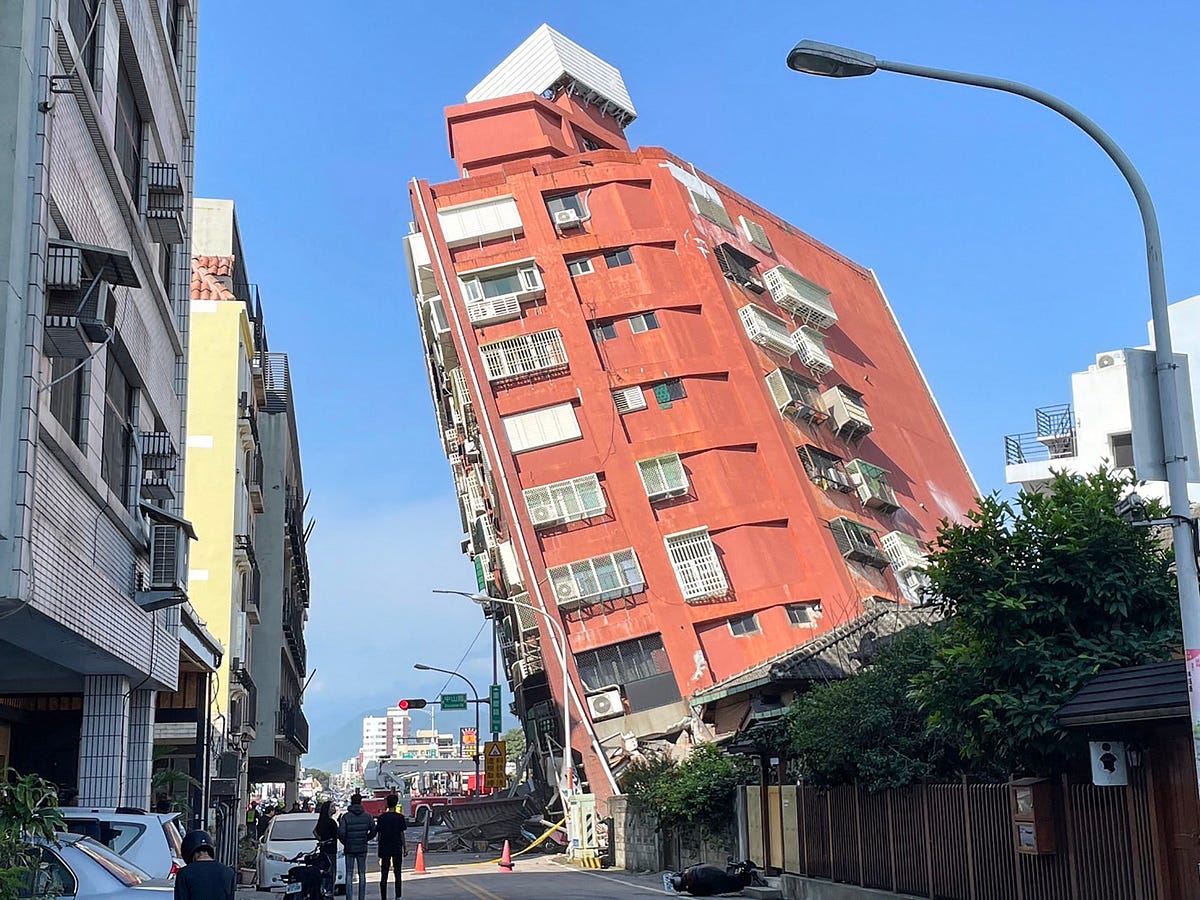
Taiwan, a vibrant island nation nestled amidst the dynamic tectonic forces of the Pacific Rim, exists within a complex and active geological setting. The island’s very existence is a testament to the relentless collision of the Eurasian and Philippine Sea plates, a process that has shaped its rugged mountains, fertile valleys, and the intricate network of fault lines that crisscross its terrain. Understanding this intricate network of faults is crucial for comprehending the island’s seismic vulnerability and for informing strategies to mitigate potential risks.
The Tectonic Tapestry of Taiwan:
The island of Taiwan sits at the juncture of two major tectonic plates: the Eurasian Plate and the Philippine Sea Plate. These plates are constantly in motion, pushing against each other, creating immense pressure that manifests in the form of earthquakes. The Philippine Sea Plate is subducting (sliding) beneath the Eurasian Plate, a process that has led to the formation of the Taiwan orogenic belt, a chain of mountains that dominates the island’s landscape.
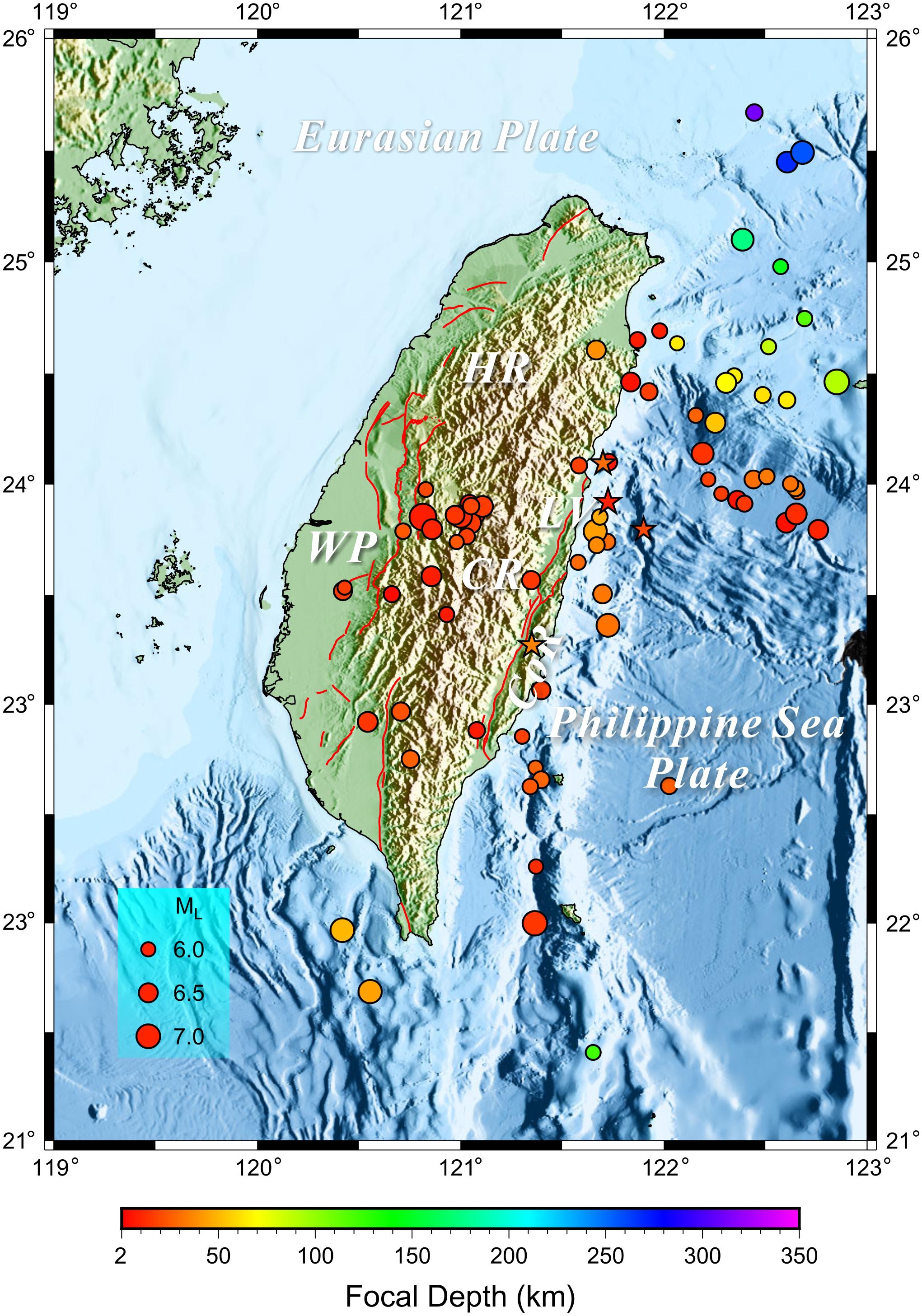
Mapping the Fault Lines:
The Taiwan Fault Lines Map is a crucial tool for understanding the island’s seismic vulnerability. This map, meticulously compiled through years of geological research and analysis, provides a detailed representation of the major fault lines that traverse the island. These fault lines are fractures in the Earth’s crust where tectonic plates move relative to each other. They act as conduits for the release of built-up energy, often resulting in earthquakes.
Key Fault Lines:
The map highlights several major fault lines, each with its unique characteristics and potential for seismic activity:
- The Longitudinal Valley Fault: This fault runs along the eastern edge of the island, stretching for over 200 kilometers. It is considered one of the most active fault lines in Taiwan and is responsible for numerous significant earthquakes throughout history.
- The Chaochou Fault: Located in the western part of the island, this fault is another major contributor to seismic activity in Taiwan. It has been linked to several powerful earthquakes, including the 1999 Chi-Chi earthquake, one of the most devastating earthquakes in Taiwan’s history.
- The Chelungpu Fault: This fault, which runs through the central part of the island, was the epicenter of the 1999 Chi-Chi earthquake. The earthquake caused widespread damage and destruction, highlighting the immense potential of this fault to generate powerful earthquakes.
- The Hsuehshan Range Fault: This fault runs along the eastern edge of the Hsuehshan Range, a mountain range that dominates central Taiwan. It is known for its potential to generate significant earthquakes, posing a threat to the surrounding areas.
The Importance of the Fault Lines Map:
The Taiwan Fault Lines Map serves as a vital tool for a multitude of purposes:
- Seismic Hazard Assessment: The map is crucial for assessing the seismic hazard in different regions of Taiwan. By understanding the location and characteristics of fault lines, scientists can estimate the likelihood of earthquakes and their potential impacts.
- Infrastructure Design and Construction: The map informs the design and construction of critical infrastructure, such as buildings, bridges, and dams. By considering the location of fault lines, engineers can design structures that are more resilient to seismic forces.
- Earthquake Preparedness and Response: The map plays a crucial role in earthquake preparedness and response. It helps authorities identify areas at higher risk of earthquakes and develop effective emergency plans for evacuation and rescue operations.
- Land Use Planning: The map informs land use planning by identifying areas prone to seismic activity. This information can help prevent development in high-risk areas and ensure the safety of communities.
FAQs on the Taiwan Fault Lines Map:
1. What is the significance of the Taiwan Fault Lines Map?
The Taiwan Fault Lines Map is essential for understanding the island’s seismic vulnerability and informing strategies for earthquake mitigation. It provides a detailed representation of the major fault lines, allowing scientists, engineers, and policymakers to assess seismic hazards, design resilient infrastructure, and plan for earthquake preparedness.
2. How is the Taiwan Fault Lines Map created?
The map is created through a combination of geological research, field surveys, and analysis of seismic data. Geologists map out the location of fault lines by studying rock formations, identifying geological structures, and analyzing the history of earthquakes in the region.
3. How often is the Taiwan Fault Lines Map updated?
The map is continuously updated as new geological data becomes available. Regular updates ensure that the map reflects the latest understanding of fault lines and their potential for seismic activity.
4. Are there any areas in Taiwan that are considered particularly vulnerable to earthquakes?
Yes, the areas along the major fault lines, including the Longitudinal Valley Fault, the Chaochou Fault, and the Chelungpu Fault, are considered particularly vulnerable to earthquakes. These areas are characterized by a high frequency of seismic events and the potential for strong earthquakes.
5. What are some of the challenges associated with mapping fault lines in Taiwan?
Mapping fault lines in Taiwan presents several challenges due to the island’s complex geology, dense population, and rugged terrain. Access to remote areas can be difficult, and the presence of vegetation and human settlements can obscure geological features.
Tips for Using the Taiwan Fault Lines Map:
- Familiarize yourself with the location of major fault lines in your area.
- Understand the potential hazards associated with each fault line.
- Develop a plan for earthquake preparedness and response.
- Ensure that your home and workplace are earthquake-resistant.
- Stay informed about earthquake warnings and advisories.
Conclusion:
The Taiwan Fault Lines Map serves as a vital tool for understanding the island’s seismic vulnerability and informing strategies for earthquake mitigation. By carefully studying the map and implementing the necessary precautions, Taiwan can enhance its resilience to earthquakes and safeguard its people and infrastructure. The map serves as a constant reminder of the dynamic nature of the Earth’s crust and the importance of preparedness in a region where seismic activity is an integral part of the landscape.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Fault Lines: Understanding the Seismic Landscape of Taiwan. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
