Navigating the Haze: Understanding Thailand’s Air Quality Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Haze: Understanding Thailand’s Air Quality Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Haze: Understanding Thailand’s Air Quality Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Haze: Understanding Thailand’s Air Quality Map

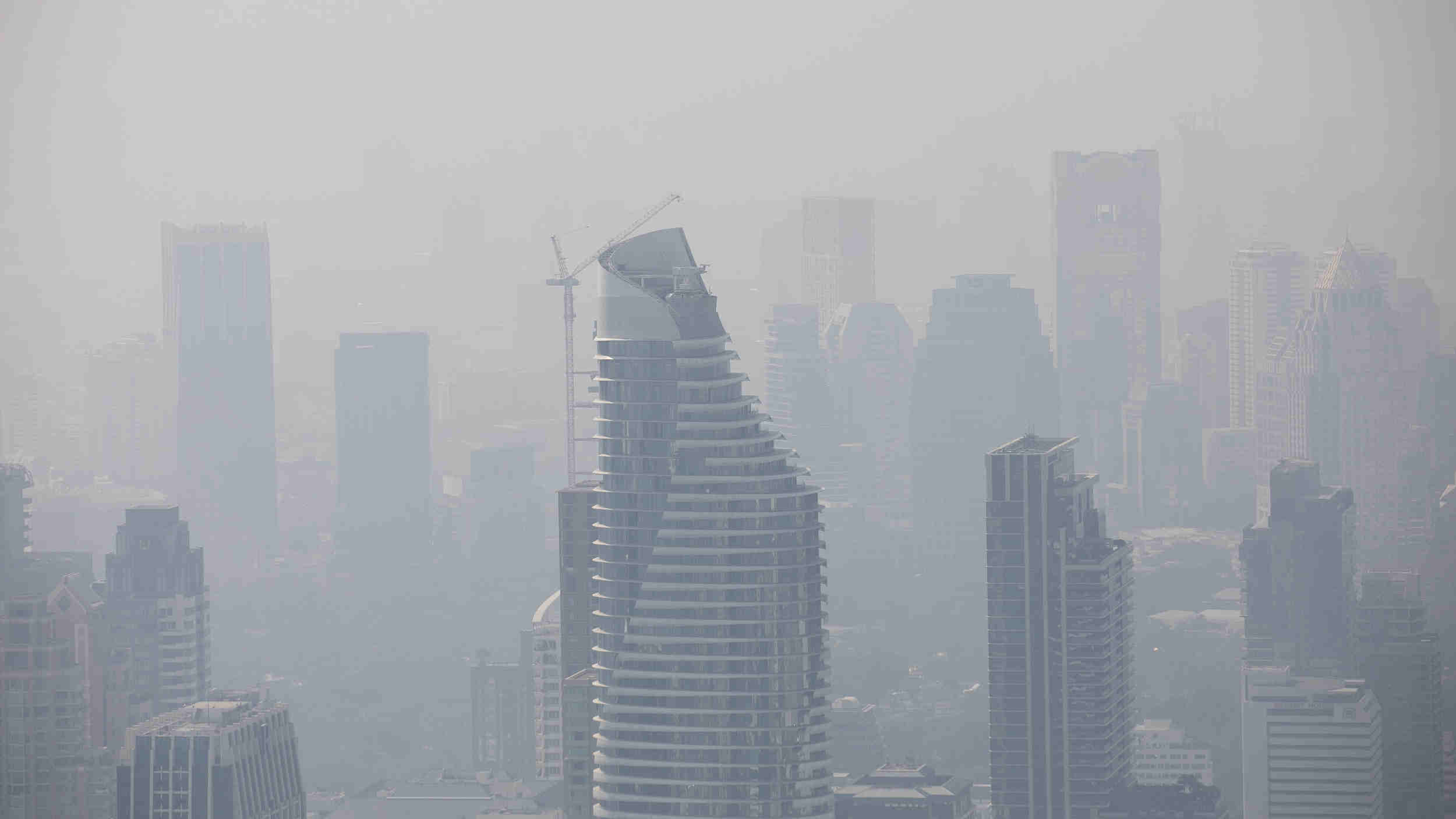
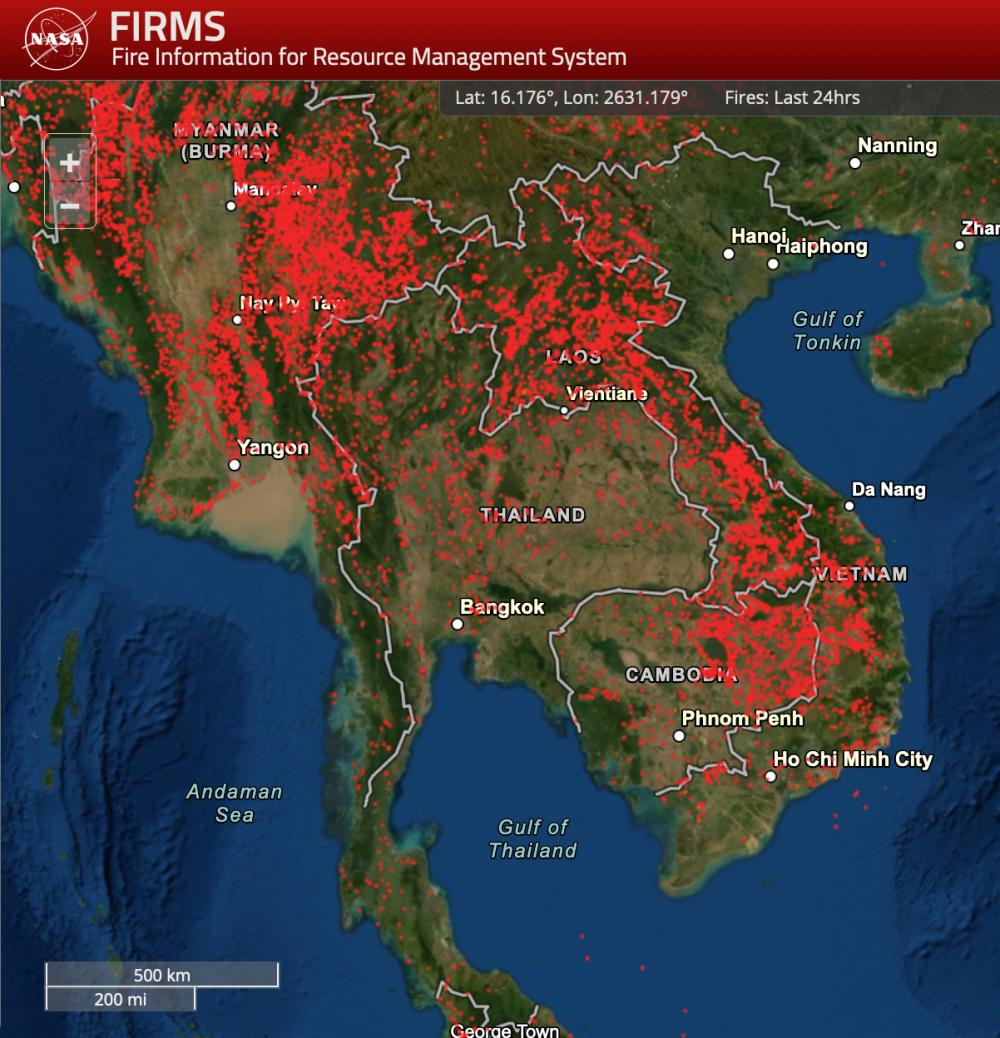
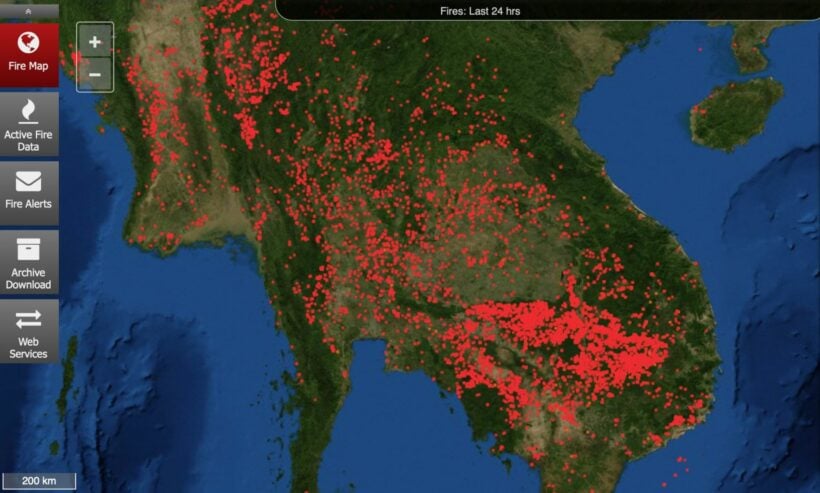
Thailand, a land of vibrant culture, breathtaking landscapes, and bustling cities, faces a growing challenge: air pollution. This invisible threat impacts the health of its citizens, its tourism industry, and its overall economic prosperity. To combat this challenge, the country has developed a comprehensive air quality monitoring system, culminating in the creation of an interactive air quality map. This map, a vital tool for both citizens and policymakers, provides real-time insights into the state of Thailand’s air, enabling informed decisions and effective action.
Understanding the Map’s Design and Data:
The air quality map, typically presented as a digital interface, visually represents the air quality across Thailand. It utilizes a color-coded system, with different shades indicating varying levels of air pollution. The most common pollutants monitored include:
- Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10): These tiny particles, invisible to the naked eye, penetrate deep into the lungs and can cause serious respiratory and cardiovascular problems.
- Ozone (O3): A highly reactive gas that can damage lung tissue and contribute to smog formation.
- Carbon Monoxide (CO): A colorless, odorless gas produced by incomplete combustion, which can reduce oxygen-carrying capacity in the blood.
- Sulfur Dioxide (SO2): A pungent gas that can irritate the respiratory system and contribute to acid rain.
- Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2): A reddish-brown gas that contributes to smog and respiratory problems.
The map typically displays data collected from a network of monitoring stations strategically placed across the country. These stations continuously measure air quality parameters, transmitting the data in real-time to a central database. This data is then processed and visualized on the map, providing a comprehensive overview of the current air quality situation.
Beyond the Colors: Interpreting the Data:
While the color-coded system offers a quick visual assessment, understanding the specific data points is crucial for informed decision-making. The map usually provides details such as:
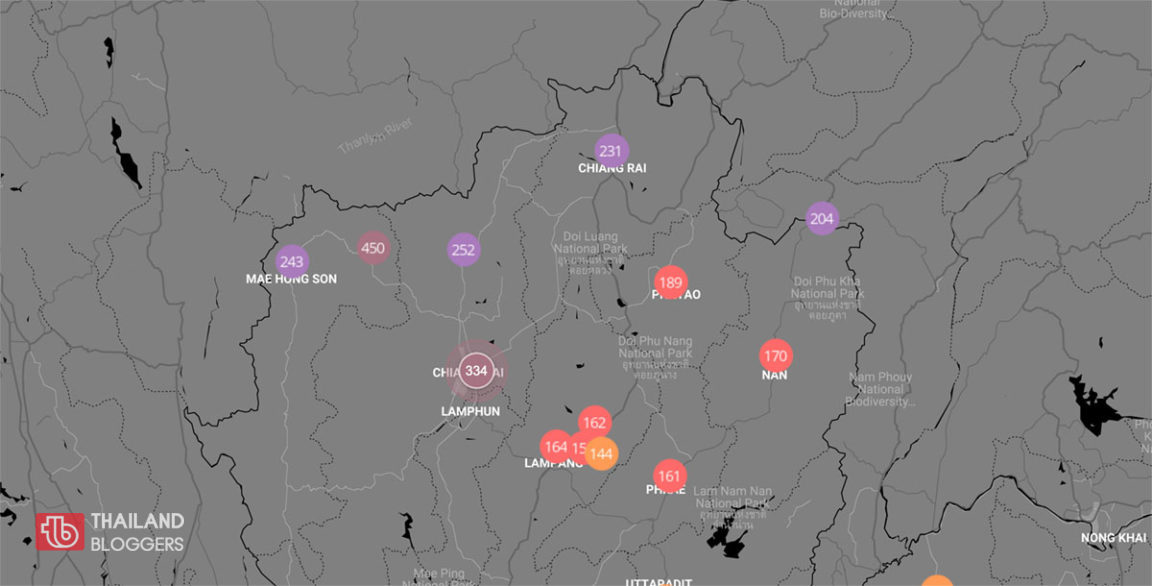
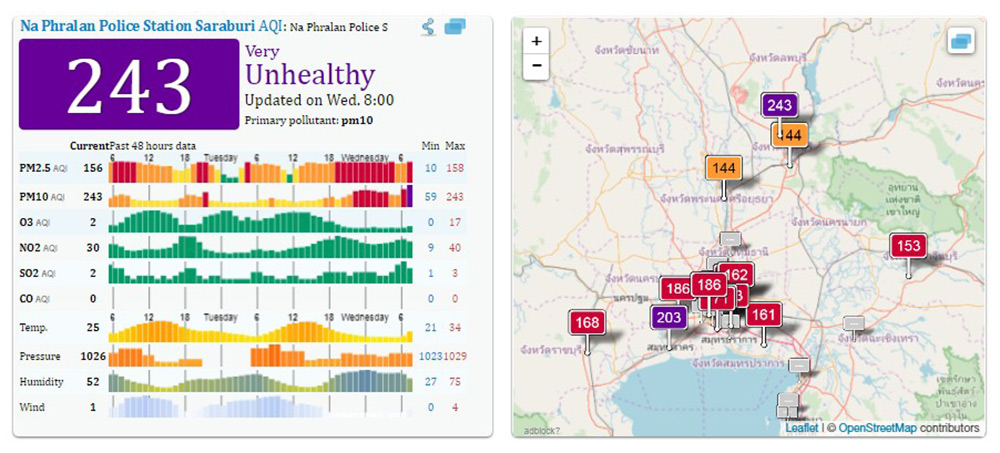
- Air Quality Index (AQI): A numerical value representing the overall air quality at a specific location, categorized into different levels (e.g., good, moderate, unhealthy, very unhealthy, hazardous).
- Pollutant Concentration: The actual concentration levels of each monitored pollutant, measured in units like micrograms per cubic meter (µg/m3).
- Historical Data: Trends and patterns over time, allowing for analysis of seasonal variations, long-term changes, and the effectiveness of pollution control measures.
Benefits and Applications of the Air Quality Map:
The air quality map serves as a valuable tool for various stakeholders, empowering them to:
- Individuals: Monitor air quality in their immediate surroundings, making informed decisions about outdoor activities, exercise routines, and the use of air purifiers.
- Health Professionals: Identify areas with high pollution levels, enabling them to advise patients on health risks and preventative measures.
- Schools and Universities: Utilize the map for educational purposes, raising awareness about air pollution and its impact on health and the environment.
- Businesses: Assess air quality in areas where they operate, optimizing operations and ensuring employee safety.
- Government Agencies: Monitor air quality trends, identify pollution hotspots, and develop targeted pollution control strategies.
- Researchers: Analyze air quality data for scientific research, contributing to a deeper understanding of pollution sources, impacts, and effective mitigation strategies.
Beyond the Map: Contributing to Cleaner Air:
The air quality map is not merely a passive tool; it serves as a powerful catalyst for action. By providing transparent and accessible information, it fosters public awareness, encourages individual responsibility, and motivates policymakers to implement effective pollution control measures.
FAQs Regarding Thailand’s Air Quality Map:
1. How often is the air quality data updated?
The frequency of updates varies depending on the specific monitoring station and the map provider. However, most maps strive to provide real-time or near real-time data, typically updated every hour or even more frequently.
2. What are the sources of air pollution in Thailand?
Thailand’s air pollution stems from a combination of factors, including:
- Vehicle Emissions: Traffic congestion in urban areas contributes significantly to air pollution, particularly from exhaust gases.
- Industrial Activities: Factories and manufacturing plants release pollutants into the atmosphere, especially in industrial zones.
- Construction and Demolition: Dust and particulate matter are released during construction and demolition activities, contributing to air pollution.
- Agricultural Burning: The practice of burning agricultural waste, often during the dry season, releases large amounts of smoke and pollutants.
- Wildfires: Forest fires, both natural and human-induced, contribute to air pollution, particularly in rural areas.
3. How can I use the air quality map to protect my health?
- Avoid Outdoor Activities During Peak Pollution Hours: Check the map for areas with high pollution levels and adjust your outdoor activities accordingly.
- Wear a Mask: Consider wearing a mask, especially during periods of high pollution, to reduce your exposure to harmful pollutants.
- Stay Indoors: When air quality is poor, limit your time outdoors and stay indoors with windows closed.
- Use Air Purifiers: Consider using air purifiers indoors to improve indoor air quality.
- Consult a Doctor: If you experience respiratory symptoms, consult a doctor to assess any potential link to air pollution.
4. What steps is the Thai government taking to improve air quality?
The Thai government has implemented various measures to address air pollution, including:
- Vehicle Emission Standards: Implementing stricter emission standards for vehicles and promoting the use of cleaner fuels.
- Industrial Pollution Control: Enforcing regulations to reduce industrial emissions and promoting cleaner production technologies.
- Urban Planning: Promoting public transportation, reducing traffic congestion, and creating green spaces to improve air quality in urban areas.
- Agricultural Practices: Encouraging sustainable agricultural practices to reduce agricultural burning and promoting alternatives to open burning.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Raising public awareness about air pollution and its health impacts, encouraging individual responsibility.
Tips for Using the Air Quality Map Effectively:
- Familiarize Yourself with the Map: Understand the color-coded system, the pollutants monitored, and the data displayed.
- Check the Map Regularly: Monitor air quality in your area and adjust your activities accordingly.
- Share the Map with Others: Encourage family, friends, and colleagues to use the map to stay informed about air quality.
- Report Pollution Incidents: If you witness any pollution incidents, report them to the relevant authorities.
- Support Pollution Control Efforts: Advocate for policies and initiatives aimed at reducing air pollution.
Conclusion:
Thailand’s air quality map stands as a testament to the country’s commitment to addressing air pollution and ensuring the health and well-being of its citizens. This powerful tool provides real-time information, empowering individuals, businesses, and policymakers to make informed decisions and take effective action. By fostering public awareness, promoting responsible behavior, and driving innovative solutions, the air quality map serves as a beacon of hope for a cleaner and healthier future for Thailand.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Haze: Understanding Thailand’s Air Quality Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
