Navigating the Landscape of Mathematical Proficiency: Understanding Standardized Testing Scores
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape of Mathematical Proficiency: Understanding Standardized Testing Scores
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape of Mathematical Proficiency: Understanding Standardized Testing Scores. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Landscape of Mathematical Proficiency: Understanding Standardized Testing Scores
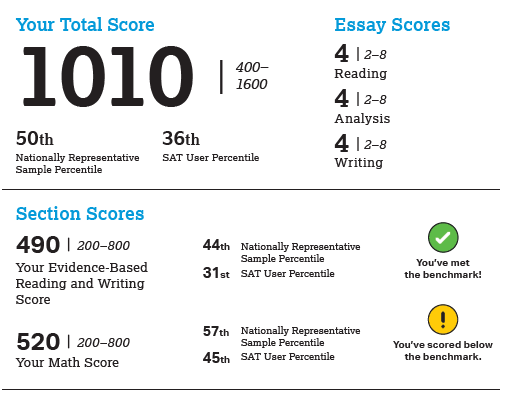
Standardized mathematics testing plays a crucial role in education, providing a common framework for evaluating student progress and gauging the effectiveness of educational programs. While the specific structure and scoring of these tests may vary, a fundamental question arises: what constitutes the highest achievable score? This article delves into the intricacies of standardized mathematics testing, exploring the significance of achieving the highest possible score and offering insights into effective test preparation strategies.
The Essence of Standardized Mathematics Testing
Standardized mathematics tests are designed to assess an individual’s understanding of mathematical concepts, skills, and problem-solving abilities. These tests are typically administered at various educational levels, from elementary school to college, and serve multiple purposes:
- Measuring Individual Progress: Standardized tests provide a snapshot of a student’s mathematical knowledge and skills at a specific point in time, allowing educators to track individual growth and identify areas needing further development.
- Evaluating Curriculum Effectiveness: By analyzing the performance of a group of students on standardized tests, educators and policymakers can assess the effectiveness of existing curricula and identify potential areas for improvement.
- Benchmarking and Comparison: Standardized tests facilitate comparisons between students within a school, across schools, or even at the national level, providing valuable data for educational decision-making.
- College Admissions and Placement: For high school students, standardized mathematics tests often serve as a crucial component of college applications, influencing admissions decisions and potential placement in college-level mathematics courses.
Deciphering the Score Structure
The highest achievable score on standardized mathematics tests varies depending on the specific test being administered. However, most tests employ a standardized scoring system with a defined range of possible scores, typically ranging from a minimum of 0 to a maximum that can vary depending on the test.
Understanding the Significance of Achieving the Highest Score
While achieving the highest possible score is not the sole indicator of a student’s mathematical understanding, it does carry significant weight:
- Academic Recognition and Validation: A high score on a standardized mathematics test demonstrates a strong foundation in mathematical concepts and problem-solving skills, often earning recognition and validation for the student’s academic achievements.
- Enhanced College Admissions Prospects: For high school students, a high score on standardized mathematics tests can significantly enhance their college admissions prospects, showcasing their preparedness for rigorous academic programs.
- Increased Confidence and Motivation: Achieving a high score can boost a student’s confidence in their mathematical abilities, fostering a positive learning environment and encouraging further exploration of mathematical concepts.
- Potential for Advanced Placement and Enrichment: High scores on standardized mathematics tests can qualify students for advanced placement courses or specialized enrichment programs, providing opportunities to delve deeper into their mathematical interests.
Navigating the Path to Success: Effective Test Preparation Strategies
While inherent mathematical ability plays a role in achieving a high score, effective test preparation is crucial. Here are some key strategies to consider:
- Thorough Understanding of Test Content: Familiarity with the specific topics covered in the test is paramount. Students should review their curriculum, identify areas of weakness, and seek clarification from teachers or tutors.
- Practice, Practice, Practice: The more students practice solving problems similar to those found on the test, the more comfortable they will become with the format and the types of questions asked.
- Time Management Skills: Standardized mathematics tests often have strict time limits. Students should practice working efficiently, allocating their time wisely, and avoiding spending too much time on any single problem.
- Strategic Test-Taking Techniques: Learning effective test-taking strategies, such as eliminating unlikely answer choices, working backward from the answer choices, and carefully reading each question, can significantly improve performance.
- Managing Test Anxiety: Test anxiety can negatively impact performance. Students should develop relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or visualization, to manage their anxiety levels on test day.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Standardized Mathematics Testing
Q1: What are some of the most common standardized mathematics tests?
A1: Some of the most common standardized mathematics tests include:
- SAT Math: A standardized test widely used for college admissions in the United States.
- ACT Math: Another standardized test used for college admissions in the United States.
- GRE Math: A standardized test required for admission to graduate programs in the United States.
- GMAT Math: A standardized test required for admission to business schools.
- PSAT/NMSQT Math: A standardized test taken by high school students to prepare for the SAT.
- NAEP Math: A national assessment used to monitor student progress in mathematics across the United States.
Q2: How are scores on standardized mathematics tests used?
A2: Scores on standardized mathematics tests are used for a variety of purposes, including:
- College admissions and placement: High scores can enhance college admissions prospects and influence placement in college-level mathematics courses.
- Evaluating student progress: Teachers use test scores to track student growth and identify areas needing improvement.
- Benchmarking and comparison: Test scores can be used to compare student performance within a school, across schools, or at the national level.
- Curriculum development: Scores can help educators and policymakers assess the effectiveness of curricula and identify areas for improvement.
Q3: What are some common misconceptions about standardized mathematics testing?
A3: Some common misconceptions about standardized mathematics testing include:
- A single test score accurately reflects a student’s overall mathematical ability: Standardized tests are just one measure of a student’s mathematical understanding and should not be the sole indicator of their abilities.
- Test scores are solely a reflection of a student’s innate talent: While innate talent plays a role, a student’s effort, preparation, and learning environment also significantly impact their performance.
- Standardized tests are designed to be difficult and trick students: Standardized tests are designed to assess a wide range of mathematical skills and concepts, and they are not intended to be intentionally difficult or misleading.
Tips for Success on Standardized Mathematics Tests
- Start Early: Begin preparing for standardized mathematics tests well in advance, allowing ample time to review concepts, practice problems, and develop effective test-taking strategies.
- Understand the Test Format: Familiarize yourself with the specific format of the test, including the types of questions, time limits, and scoring system.
- Seek Professional Guidance: Consider seeking assistance from tutors, teachers, or test preparation programs to address specific areas of weakness and develop effective study habits.
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: Ensure adequate sleep, proper nutrition, and regular exercise to maintain focus and reduce stress during the test preparation period.
Conclusion
Achieving the highest possible score on standardized mathematics tests is a testament to a student’s dedication, effort, and understanding of mathematical concepts. While the test score itself is not the sole measure of a student’s mathematical proficiency, it serves as a valuable indicator of their preparedness and ability to apply their knowledge in a standardized setting. By understanding the significance of standardized mathematics testing, engaging in effective preparation strategies, and embracing a growth mindset, students can navigate the landscape of mathematics with confidence and achieve their full potential.


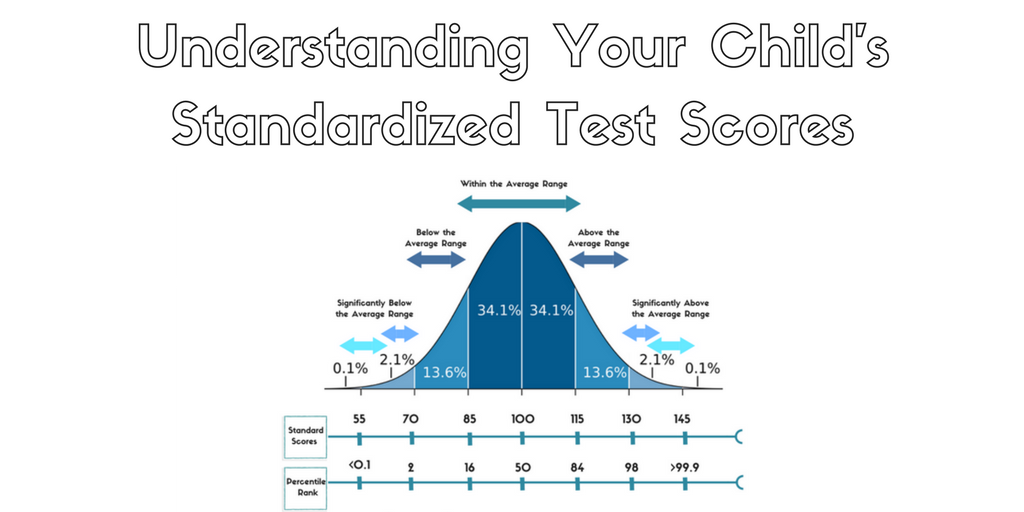



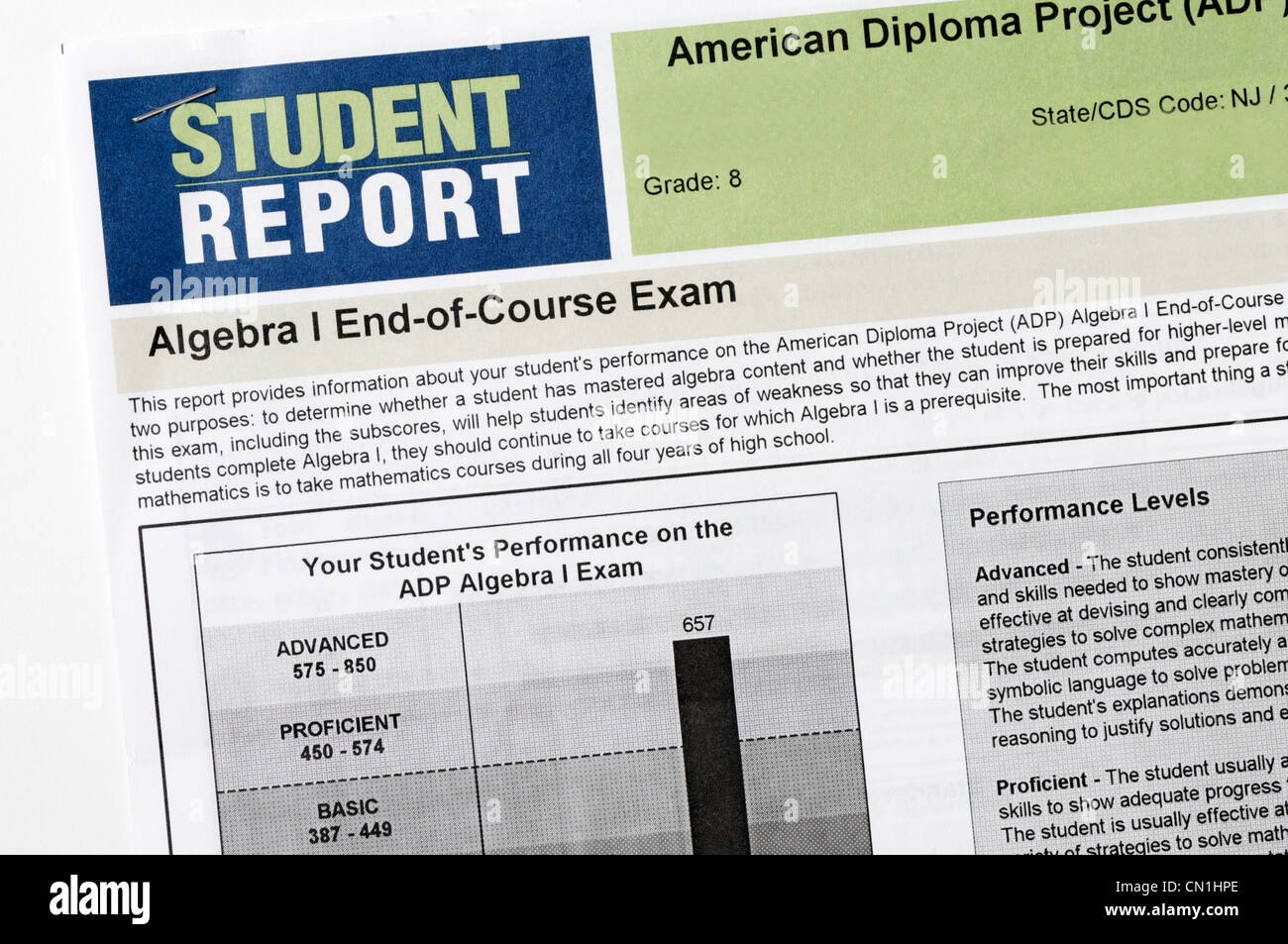

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape of Mathematical Proficiency: Understanding Standardized Testing Scores. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
