Navigating the Landscape: Understanding and Implementing Accommodations in Standardized Testing
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape: Understanding and Implementing Accommodations in Standardized Testing
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape: Understanding and Implementing Accommodations in Standardized Testing. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Landscape: Understanding and Implementing Accommodations in Standardized Testing
Standardized testing plays a significant role in the educational landscape, serving as a tool for measuring student progress, evaluating programs, and informing policy decisions. However, the very nature of these assessments can present challenges for students with diverse learning needs. Recognizing this, the concept of testing accommodations has emerged as a crucial mechanism to ensure equitable participation and accurate measurement of student abilities.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of testing accommodations, exploring their purpose, types, and implementation. It delves into the rationale behind their use, highlighting the benefits for both students and the educational system as a whole.
Defining the Terrain: What are Testing Accommodations?
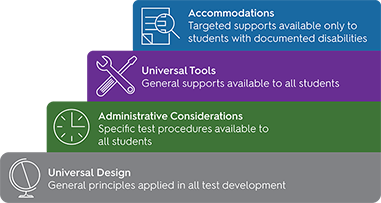
Testing accommodations are adjustments made to the standard testing procedures, environment, or format to provide students with disabilities or specific learning differences an equal opportunity to demonstrate their knowledge and skills. These adjustments are not intended to change the content or difficulty of the assessment but rather to remove barriers that might hinder a student’s ability to access and perform on the test.
The Foundation of Fairness: Rationale for Accommodations
The rationale for implementing testing accommodations rests on the fundamental principle of fairness and inclusivity. Students with disabilities or learning differences often face unique challenges that can impact their test performance, despite possessing the knowledge and skills being assessed. These challenges can stem from:
- Cognitive impairments: Difficulty with processing information, memory, attention, or executive functioning.
- Sensory impairments: Visual or auditory processing difficulties that hinder comprehension or engagement with test materials.
- Physical limitations: Motor skills impairments that make it challenging to complete the test, such as writing or manipulating test materials.
- Language differences: Limited proficiency in the language of the test, leading to comprehension issues.
By providing appropriate accommodations, testing environments become more accessible and equitable, allowing students to demonstrate their true abilities without being disadvantaged by their disability or learning difference.
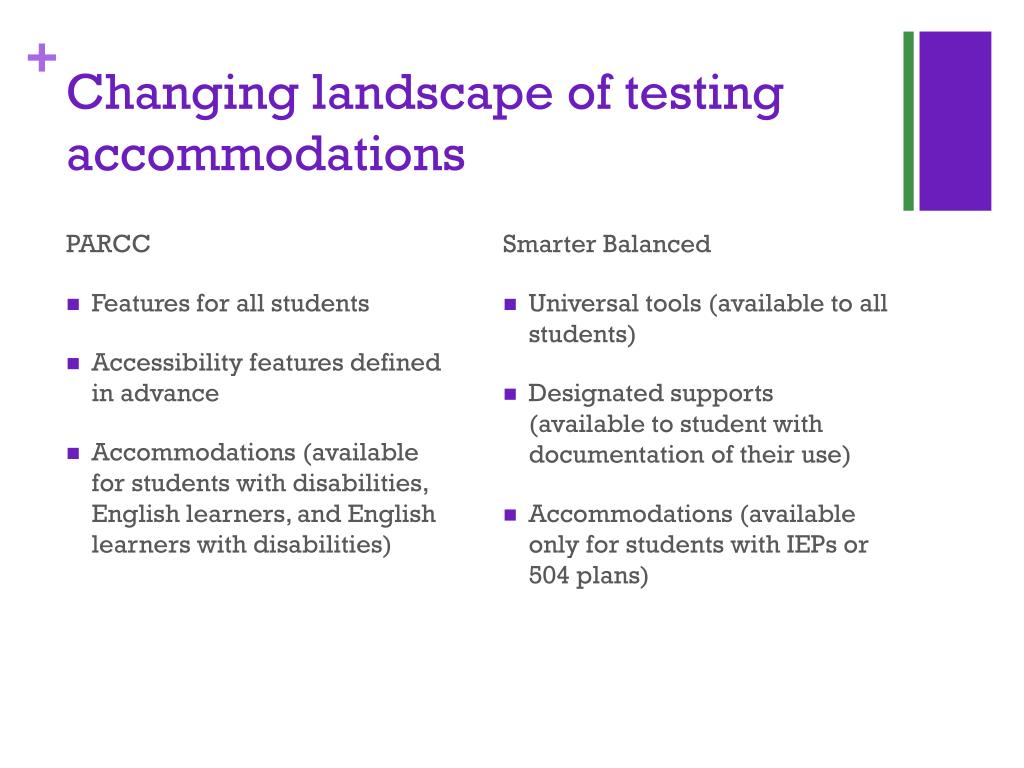
Types of Testing Accommodations: A Diverse Toolkit
The types of accommodations offered can vary greatly depending on the student’s specific needs and the nature of the assessment. Common categories include:
-
Presentation Accommodations: These adjustments modify how the test is presented to the student, facilitating easier access to the information. Examples include:
- Large print or braille versions: For students with visual impairments.
- Audio recordings: For students with reading difficulties or visual impairments.
- Sign language interpreters: For students who are deaf or hard of hearing.
- Assistive technology: Software or hardware designed to assist with reading, writing, or other tasks.
-
Response Accommodations: These modifications address how the student interacts with the test and provides their responses. Examples include:
- Oral responses: For students who have difficulty writing or typing.
- Scribe: A person who writes down the student’s responses.
- Assistive technology: Speech-to-text software or other tools to aid in response input.
- Extended time: Additional time to complete the test, particularly beneficial for students with processing or attention challenges.
-
Setting Accommodations: These adjustments modify the physical environment of the testing situation to create a more supportive and conducive setting. Examples include:
- Quiet testing room: For students who are easily distracted.
- Individualized testing: Testing in a separate, quiet location with a designated proctor.
- Break opportunities: Scheduled breaks to allow for rest and refocusing.
Implementing Accommodations: A Collaborative Approach
Implementing testing accommodations effectively requires a collaborative approach involving multiple stakeholders:
- Educators: Teachers and school administrators are responsible for identifying students who may benefit from accommodations and developing Individualized Education Programs (IEPs) or 504 plans that outline specific accommodations.
- Parents/Guardians: Parents and guardians play a crucial role in providing information about their child’s needs and working with educators to ensure appropriate accommodations are in place.
- Testing Agencies: Organizations responsible for developing and administering standardized tests must provide guidance on acceptable accommodations and ensure that testing procedures are flexible enough to accommodate diverse needs.
- Assessment Specialists: Professionals with expertise in assessment and accommodations can provide guidance on selecting and implementing appropriate accommodations.
Benefits of Testing Accommodations: A Ripple Effect
Implementing testing accommodations offers a multitude of benefits, not only for students but also for the educational system as a whole:
- Accurate Assessment of Student Abilities: Accommodations allow students to demonstrate their true abilities, providing a more accurate reflection of their knowledge and skills. This leads to more reliable and meaningful assessment data.
- Increased Student Engagement and Motivation: When students feel supported and empowered to participate in testing, they are more likely to engage with the process and demonstrate their best work.
- Reduced Testing Anxiety: Accommodations can help reduce anxiety and stress associated with testing, creating a more positive and productive environment for students.
- Improved Access to Education: Accommodations help ensure that students with disabilities or learning differences have equal access to educational opportunities and resources.
- Enhanced Equity and Inclusion: Implementing accommodations promotes a more inclusive and equitable educational system, ensuring that all students have the chance to succeed.
Navigating the FAQs: Addressing Common Concerns
1. Are accommodations a form of cheating?
No. Accommodations are not intended to give students an unfair advantage. They simply remove barriers that might otherwise hinder their ability to demonstrate their true abilities.
2. How do I know if my child needs accommodations?
If your child has a disability or a learning difference that may impact their ability to participate in standardized testing, it is important to discuss their needs with their teacher or school administrator. They can help determine if accommodations are appropriate and develop an individualized plan.
3. What if my child doesn’t want to use accommodations?
It is essential to respect the student’s preferences. However, it is also important to explain the purpose of accommodations and how they can help them perform their best. If the student still refuses accommodations, it is important to document their decision and ensure they understand the potential consequences.
4. How can I advocate for my child to receive appropriate accommodations?
Stay informed about your child’s needs and the available accommodations. Collaborate with teachers, administrators, and assessment specialists to develop an individualized plan that meets your child’s unique requirements. Be prepared to provide documentation of your child’s disability or learning difference and advocate for their right to receive appropriate support.
5. Are there any limitations or restrictions on accommodations?
While accommodations are designed to provide equitable access, there are some limitations. Accommodations should not change the content or difficulty of the assessment. They should also be reasonable and practical, taking into consideration the resources available and the testing environment.
Tips for Effective Accommodation Implementation:
- Early Identification: Identify students who may benefit from accommodations early in their educational journey to ensure timely support and planning.
- Individualized Plans: Develop individualized education programs (IEPs) or 504 plans that outline specific accommodations based on each student’s unique needs.
- Collaboration: Foster collaboration between educators, parents, and assessment specialists to ensure effective implementation and ongoing monitoring of accommodations.
- Training and Professional Development: Provide teachers and other staff with training on implementing accommodations effectively and understanding the needs of students with disabilities and learning differences.
- Open Communication: Maintain open communication with parents, students, and other stakeholders to address concerns, provide updates, and ensure that accommodations are meeting the student’s needs.
Conclusion: Embracing Equity and Inclusivity in Assessment
Testing accommodations represent a crucial step towards creating a more equitable and inclusive educational system. By removing barriers and providing appropriate support, these adjustments empower students with disabilities and learning differences to demonstrate their true abilities and achieve their full potential. Implementing accommodations effectively requires a collaborative effort, informed decision-making, and a commitment to ensuring that all students have the opportunity to succeed. As we continue to navigate the evolving landscape of education, embracing the principles of fairness and inclusivity in assessment is essential for fostering a truly equitable and supportive learning environment for all students.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape: Understanding and Implementing Accommodations in Standardized Testing. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
