Navigating the Landscape: Understanding and Utilizing Mathematical Mapping
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape: Understanding and Utilizing Mathematical Mapping
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape: Understanding and Utilizing Mathematical Mapping. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Landscape: Understanding and Utilizing Mathematical Mapping
The field of mathematics is vast and intricate, encompassing a diverse array of concepts, theories, and applications. As educators and researchers strive to effectively assess student understanding and progress in this multifaceted domain, the need for robust and comprehensive assessment tools becomes paramount. This is where the concept of "map testing" in mathematics emerges, offering a powerful framework for navigating the complex terrain of mathematical knowledge and skill acquisition.
Defining the Terrain: What is Map Testing in Mathematics?
Map testing in mathematics, often referred to as "mathematical mapping," is a systematic approach to assessment that visualizes and analyzes the interconnectedness of mathematical concepts and skills. It transcends traditional standardized tests, focusing on a holistic understanding of the student’s mathematical journey rather than simply measuring isolated knowledge points.
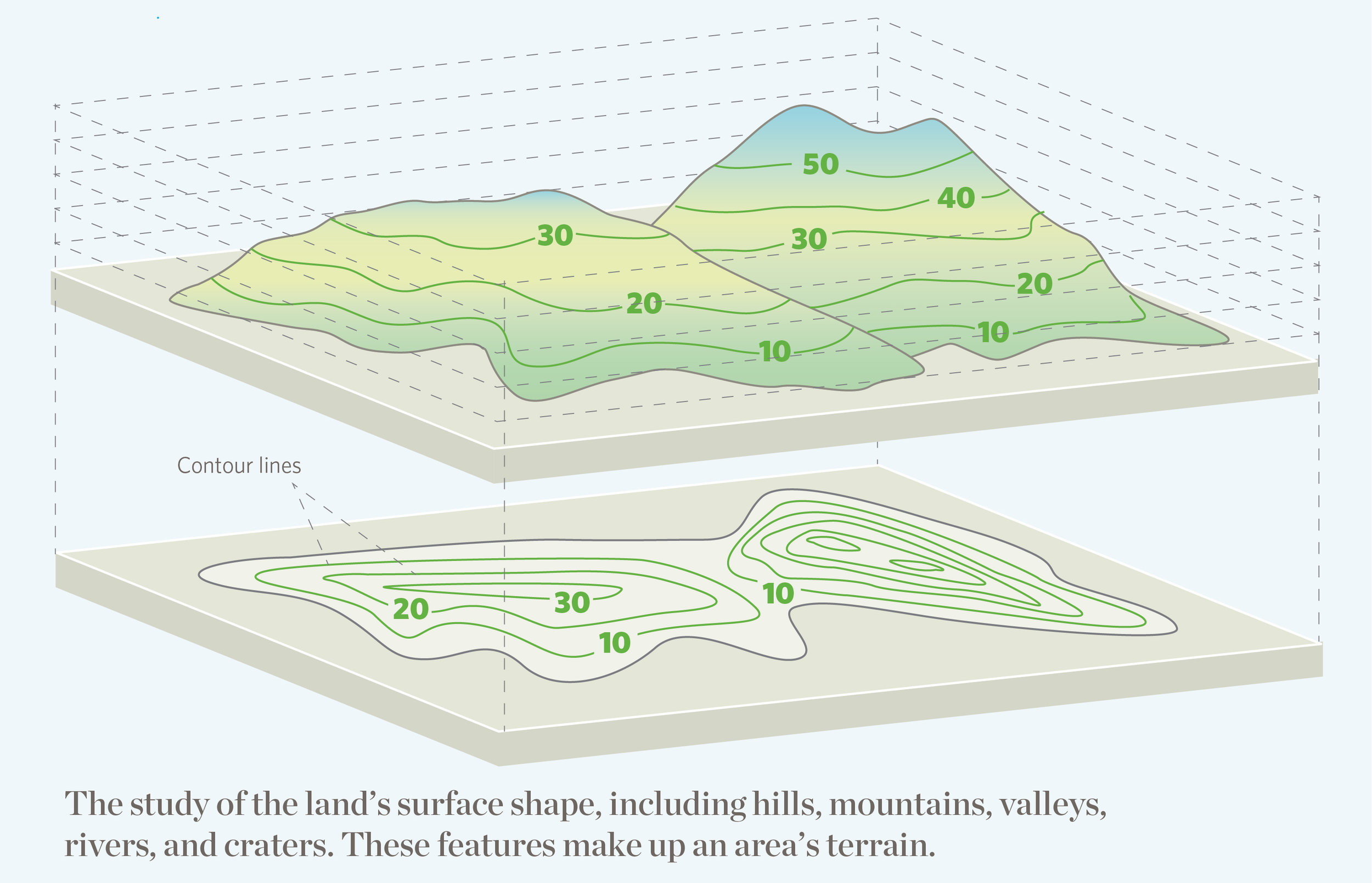
This approach employs a visual representation, akin to a map, to illustrate the relationships between different mathematical concepts, their prerequisite skills, and the progression of learning. The map serves as a guide for both educators and learners, offering a clear picture of the mathematical landscape and the pathways leading to mastery.
The Benefits of Navigating with a Map:
The utility of map testing in mathematics lies in its ability to provide a comprehensive and insightful assessment experience, offering numerous benefits:
- Identifying Gaps and Strengthening Foundations: By mapping the interconnectedness of concepts, map testing can pinpoint areas where students may have gaps in their understanding. This allows educators to tailor instruction to address specific weaknesses and ensure a solid foundation for future learning.
- Promoting Deeper Understanding: The process of constructing and analyzing maps encourages students to engage with the interconnectedness of mathematical concepts. This active engagement fosters a deeper understanding of the subject matter, going beyond rote memorization and promoting meaningful learning.
- Tailoring Instruction and Assessment: Map testing provides educators with valuable data that can inform instructional decisions. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of individual students and the class as a whole, educators can personalize learning experiences and tailor assessments to accurately reflect student progress.
- Enhancing Collaboration and Communication: The visual nature of map testing facilitates communication between educators, students, and parents. The shared understanding of the mathematical landscape promotes collaboration and fosters a supportive learning environment.
Types of Map Testing:
The implementation of map testing in mathematics can take various forms, each tailored to specific needs and objectives:
- Concept Maps: These maps focus on visualizing the relationships between different mathematical concepts. They can be used to explore the hierarchical structure of knowledge, identify key connections, and reveal potential areas of confusion.
- Skill Maps: These maps emphasize the progression of skills required to master a particular concept or area of mathematics. They highlight the building blocks of learning, allowing educators to identify areas where students may need additional practice or support.
- Curriculum Maps: These maps provide a comprehensive overview of the curriculum, outlining the sequence of topics and the expected learning outcomes. They serve as a guide for educators, ensuring a coherent and progressive learning experience for students.
Implementing Map Testing in the Classroom:
The successful implementation of map testing in mathematics requires a systematic approach and careful consideration of the following factors:
- Defining the Scope and Objectives: Clearly define the specific mathematical concepts or skills to be assessed. This will help in determining the appropriate level of detail for the map and the relevant learning outcomes.
- Constructing the Map: The map should be designed in a clear and concise manner, using appropriate symbols and visual representations to effectively illustrate the relationships between concepts and skills.
- Using the Map for Assessment: The map can be used for various assessment purposes, including pre-tests to identify prior knowledge, formative assessments to monitor student progress, and summative assessments to evaluate overall understanding.
- Integrating the Map into Instruction: The map should not be a standalone assessment tool but rather an integral part of the instructional process. It can be used to guide lesson planning, facilitate student discussions, and support differentiated instruction.
FAQs on Map Testing in Mathematics:
Q: What are the limitations of map testing?
A: While map testing offers numerous benefits, it is essential to acknowledge its limitations. The effectiveness of map testing is contingent on the quality of the map itself and the ability of educators to interpret and utilize the data effectively. Additionally, map testing may not be suitable for assessing all aspects of mathematical understanding, such as problem-solving skills or creative thinking.
Q: How can I create effective concept maps for my students?
A: Creating effective concept maps involves a collaborative process. Encourage students to participate in the construction of the map, allowing them to express their understanding and identify key connections. Utilize visual representations, such as diagrams, symbols, and colors, to enhance comprehension and engagement.
Q: What are some strategies for using map testing to support struggling learners?
A: Map testing can be a powerful tool for identifying and addressing learning difficulties. By analyzing the map, educators can identify specific areas where students are struggling and provide targeted interventions. This may involve providing additional practice, offering alternative explanations, or utilizing different teaching strategies.
Q: How can map testing be used to promote higher-order thinking skills?
A: Map testing can encourage higher-order thinking by prompting students to make connections between concepts, analyze patterns, and apply their knowledge to new situations. By engaging in the process of mapping, students develop critical thinking skills and enhance their ability to solve complex problems.
Tips for Effective Map Testing in Mathematics:
- Keep it Simple: The map should be clear, concise, and easy to understand. Avoid overloading it with too much information.
- Use Visual Representations: Utilize diagrams, symbols, and colors to enhance comprehension and engagement.
- Promote Collaboration: Encourage students to work together to construct and analyze maps.
- Integrate it into Instruction: Make map testing an integral part of the learning process, not just a standalone assessment tool.
- Reflect and Revise: Regularly review and revise the maps to ensure they are accurate and aligned with the curriculum.
Conclusion: Charting the Course to Mathematical Proficiency
Map testing in mathematics offers a valuable tool for educators and researchers seeking to navigate the complex terrain of mathematical knowledge and skill acquisition. By providing a visual representation of the interconnectedness of concepts and skills, map testing empowers students to develop a deeper understanding of the subject matter, while providing educators with insightful data to inform instruction and assessment. As we continue to explore and refine this powerful assessment approach, map testing promises to play an increasingly significant role in charting the course to mathematical proficiency for learners of all levels.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape: Understanding and Utilizing Mathematical Mapping. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
