Navigating the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Low Map Testing
Related Articles: Navigating the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Low Map Testing
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Low Map Testing. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Low Map Testing

In the realm of software development, ensuring the quality and functionality of a product is paramount. This pursuit often involves meticulous testing, where various aspects of the software are rigorously evaluated to identify and rectify any flaws. Among the diverse testing methodologies, map testing stands out as a valuable technique for assessing the performance and accuracy of mapping systems.
Map testing, as the name suggests, involves subjecting a map or geographic data to a series of tests to evaluate its accuracy, completeness, and usability. This process is crucial for various applications, ranging from navigation systems and mapping services to geographical information systems (GIS) and spatial analysis tools.
The Essence of Low Map Testing:
While map testing encompasses a broad spectrum of evaluations, "low map testing" specifically refers to the process of examining the underlying data and processes that drive the map’s functionality. This focus on the "low-level" aspects of the map system allows for a deeper understanding of its potential weaknesses and vulnerabilities.
Benefits of Low Map Testing:
The significance of low map testing stems from its ability to uncover critical issues that might otherwise go undetected. By scrutinizing the fundamental components of the map, this methodology offers several distinct advantages:
- Early Detection of Errors: Low map testing helps identify errors in the source data, processing algorithms, and data structures that might lead to inaccuracies in the final map output. This early detection allows for timely correction, preventing the propagation of errors to subsequent stages of development.
- Enhanced Accuracy and Reliability: Through rigorous testing, low map testing ensures the accuracy and reliability of the map data, fostering confidence in the system’s output. This is particularly crucial in applications where precise spatial information is essential, such as navigation, resource management, and emergency response.
- Improved Data Integrity: By examining the data handling processes, low map testing promotes data integrity, ensuring that information is consistent, complete, and free from inconsistencies. This leads to a more robust and reliable map system.
- Enhanced User Experience: A well-tested map system translates to a superior user experience. Low map testing ensures that the map functions smoothly, accurately displays information, and provides a seamless user interface, enhancing user satisfaction and confidence.
Key Components of Low Map Testing:
Low map testing involves a systematic approach to evaluating the underlying aspects of a map system. This typically encompasses the following key components:
- Data Validation: This involves verifying the accuracy, completeness, and consistency of the source data used to generate the map. This includes checking for missing values, duplicate entries, and inconsistencies in data formats.
- Algorithm Verification: Low map testing evaluates the algorithms used to process and transform the data into a map. This involves ensuring that the algorithms are correctly implemented and produce accurate results.
- Data Structure Analysis: The process examines the data structures used to store and manage the map data. This involves assessing the efficiency and effectiveness of the chosen data structures in terms of storage, retrieval, and manipulation.
- Performance Evaluation: Low map testing measures the performance of the map system, including its speed, responsiveness, and resource utilization. This helps identify potential bottlenecks and optimize the system for efficient operation.
- Security Assessment: In cases where the map system handles sensitive information, low map testing includes a security assessment to identify potential vulnerabilities and ensure data privacy and integrity.
Real-World Applications of Low Map Testing:
Low map testing finds practical applications in a wide range of industries and domains, including:
- Navigation Systems: Low map testing ensures the accuracy and reliability of navigation systems, guaranteeing safe and efficient routes for drivers and pedestrians.
- Mapping Services: Online mapping services rely heavily on low map testing to maintain the accuracy and completeness of their maps, providing users with reliable spatial information.
- Geographical Information Systems (GIS): Low map testing is crucial for GIS applications, ensuring the integrity and accuracy of geospatial data used for various purposes, such as urban planning, environmental monitoring, and resource management.
- Spatial Analysis Tools: Tools for spatial analysis, such as crime mapping and disease surveillance, rely on low map testing to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the underlying data, leading to more robust and informed decision-making.
FAQs on Low Map Testing:
1. What are the challenges associated with low map testing?
Low map testing can be challenging due to the complexity of map systems and the vast amount of data involved. Additionally, identifying and simulating real-world scenarios for testing can be complex and time-consuming.
2. How can I ensure effective low map testing?
Effective low map testing requires a well-defined testing plan, a thorough understanding of the system’s architecture, and the use of appropriate testing tools and techniques. Collaboration between developers, testers, and domain experts is also crucial.
3. What are some common testing tools for low map testing?
Various tools are available for low map testing, including data validation tools, geospatial analysis software, and performance testing platforms. The choice of tools depends on the specific needs of the project.
4. What is the role of automation in low map testing?
Automation plays a significant role in enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of low map testing. Automated testing tools can streamline the testing process, reduce manual effort, and ensure consistent test execution.
Tips for Effective Low Map Testing:
- Define Clear Testing Objectives: Before commencing testing, clearly define the specific goals and objectives of the testing process. This will ensure that the testing is focused and comprehensive.
- Develop a Comprehensive Test Plan: A well-structured test plan outlining the testing scope, methodologies, and expected outcomes is essential for effective low map testing.
- Utilize Real-World Data: Employ real-world data sets to simulate realistic scenarios and ensure that the map system performs accurately under real-world conditions.
- Automate Repetitive Tests: Leverage automation tools to streamline repetitive tests, freeing up resources for more complex and exploratory testing.
- Collaborate with Domain Experts: Involve domain experts in the testing process to ensure that the testing scenarios and criteria are relevant and accurate.
Conclusion:
Low map testing plays a vital role in ensuring the accuracy, reliability, and usability of map systems. By focusing on the underlying data, algorithms, and data structures, this methodology helps identify and rectify potential issues early in the development process. Through rigorous testing, low map testing fosters confidence in the map system, leading to a superior user experience and informed decision-making. The comprehensive understanding and utilization of low map testing are essential for any project that relies on accurate and reliable spatial information.
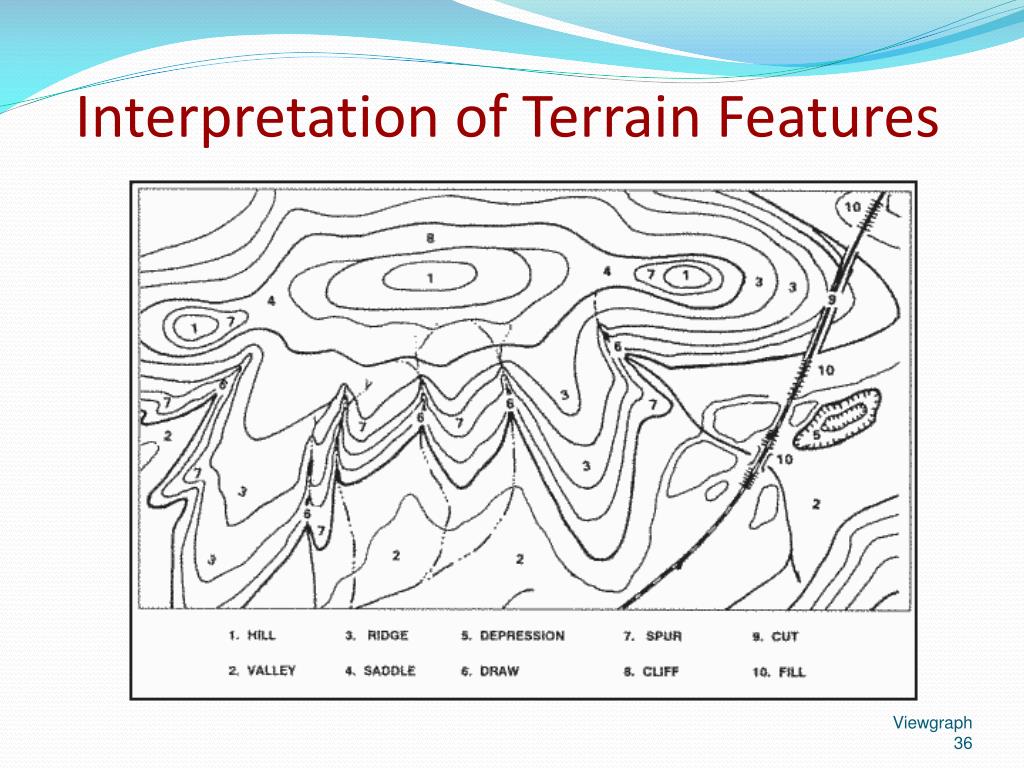

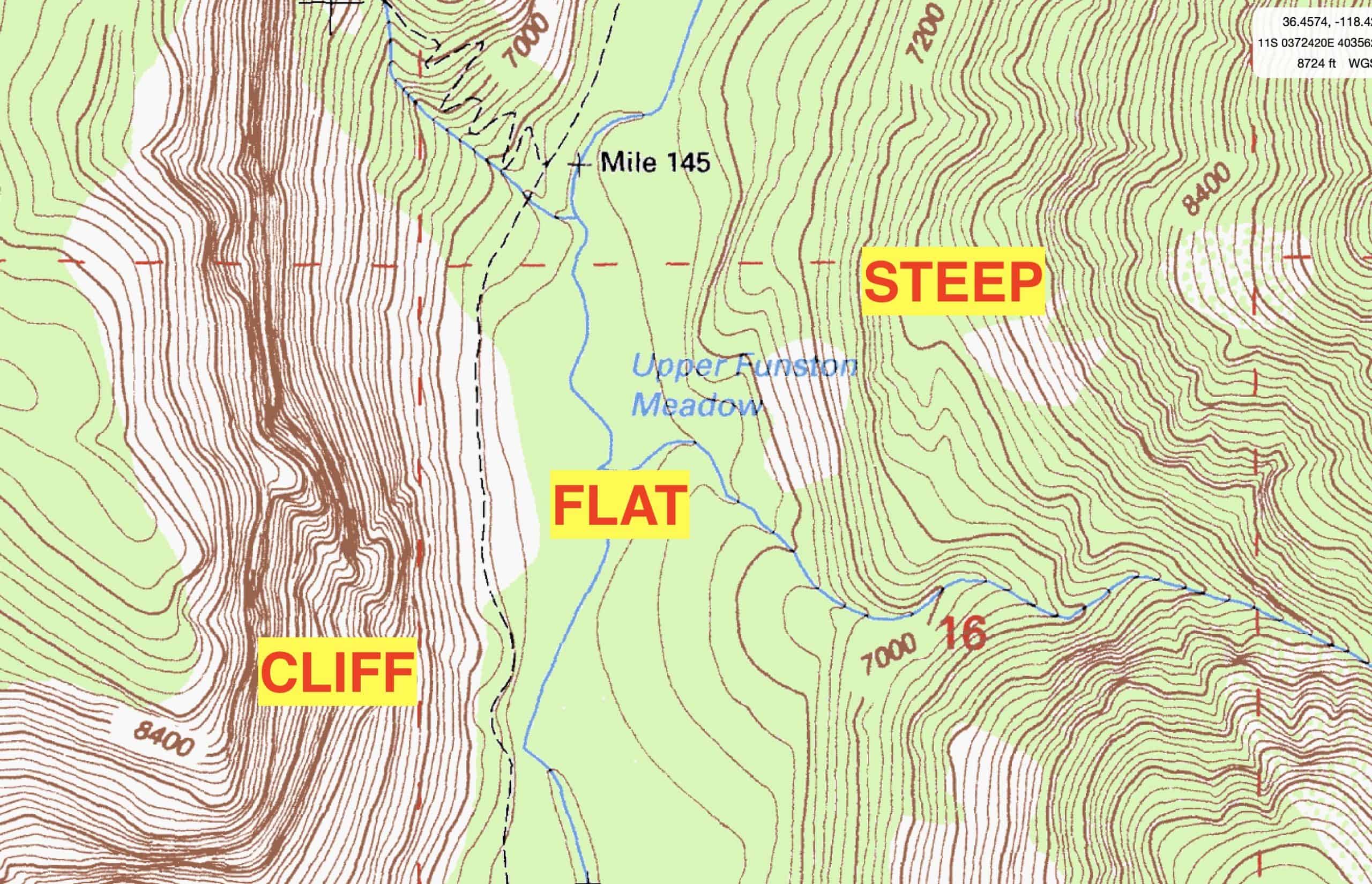
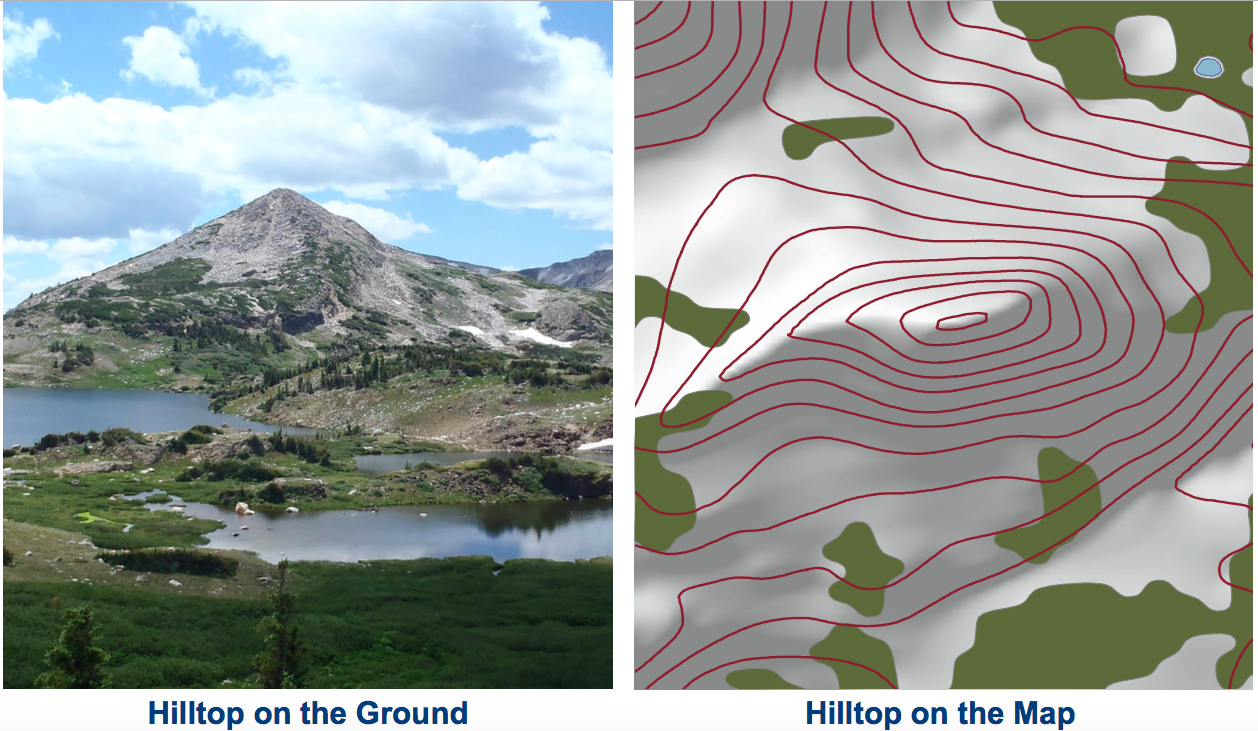


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Low Map Testing. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
