Taiwan’s Position on the World Map: A Geopolitical and Historical Perspective
Related Articles: Taiwan’s Position on the World Map: A Geopolitical and Historical Perspective
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Taiwan’s Position on the World Map: A Geopolitical and Historical Perspective. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Taiwan’s Position on the World Map: A Geopolitical and Historical Perspective

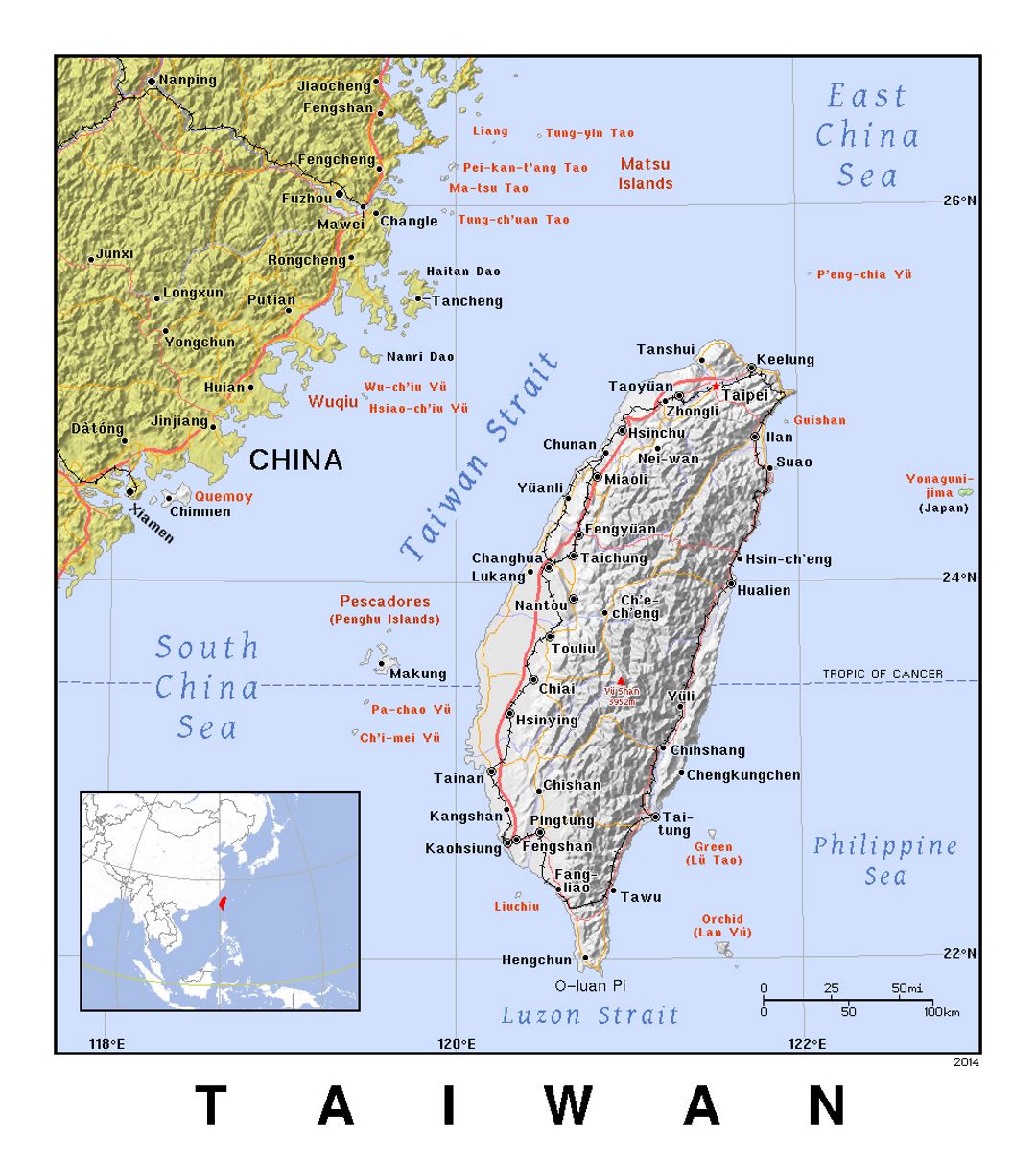
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), occupies a unique and complex position on the world map. Its geographic location, historical development, and political status have all contributed to its intricate relationship with the global community. Understanding Taiwan’s place in the world requires a nuanced perspective that encompasses its physical geography, historical context, and current political realities.
Taiwan’s Geographical Context:
Taiwan is an island nation located off the southeastern coast of mainland China, separated by the Taiwan Strait. Its strategic location has historically made it a crossroads of trade and cultural exchange, connecting East Asia with Southeast Asia and the Pacific. The island itself is mountainous and rugged, with the Central Mountain Range running along its length, creating diverse ecosystems and landscapes. This geographical makeup has influenced Taiwan’s history and development, shaping its agriculture, industry, and even its cultural identity.
Taiwan’s Historical Trajectory:
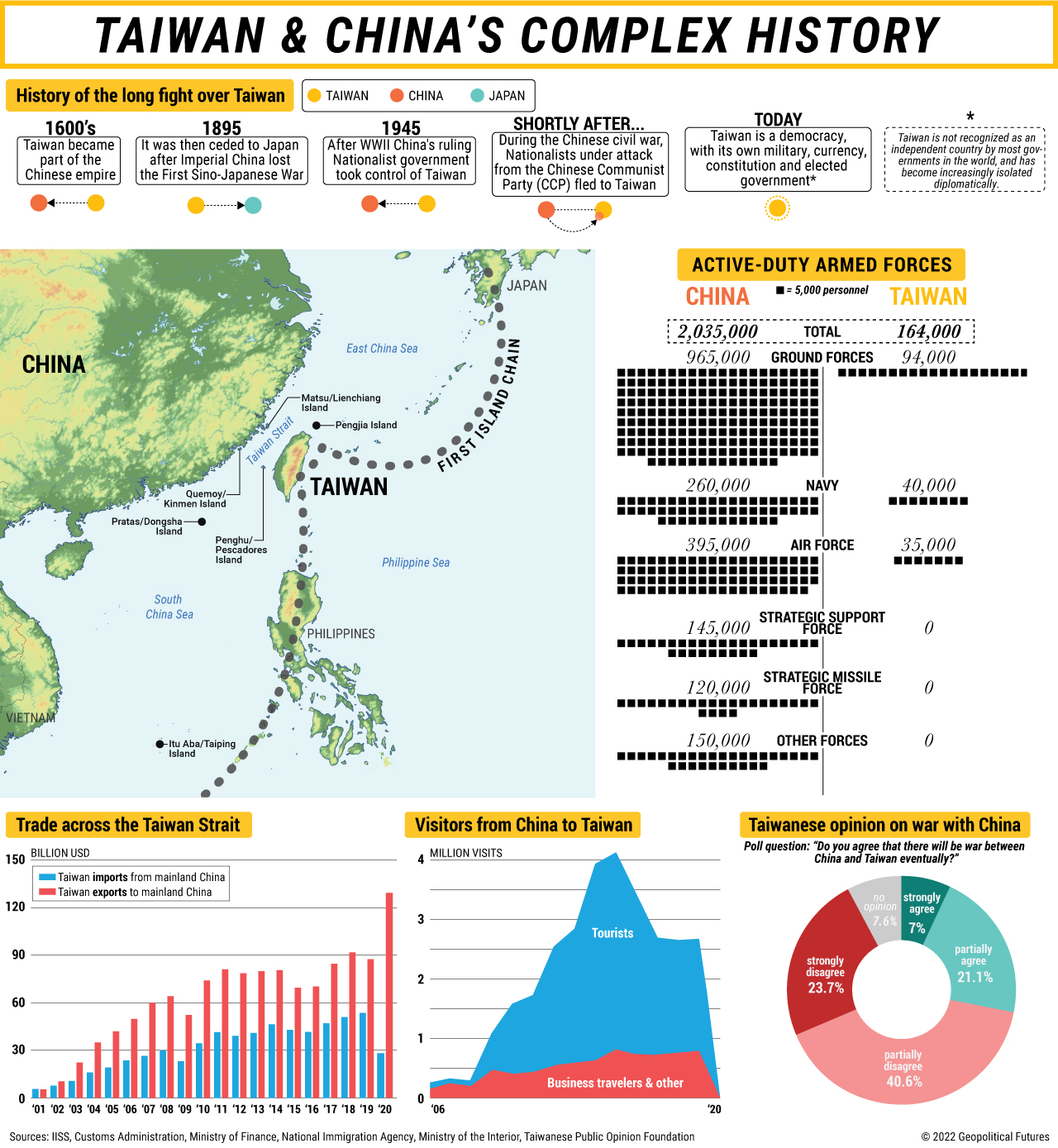
Taiwan’s history is intertwined with that of China. After centuries of indigenous rule, the island was incorporated into the Chinese Empire during the Ming Dynasty. However, the Qing Dynasty ceded Taiwan to Japan in 1895 after the First Sino-Japanese War. This period under Japanese rule (1895-1945) saw significant modernization and economic development.
Following World War II, Taiwan became a base for the retreating Nationalist government of China after its defeat in the Chinese Civil War. The Communist Party established the People’s Republic of China (PRC) on the mainland, while the ROC government maintained control of Taiwan. This political division, known as the "Taiwan Strait Crisis," continues to this day.
Taiwan’s Political Landscape:
The political situation between Taiwan and China remains one of the most sensitive issues in East Asian geopolitics. The PRC claims sovereignty over Taiwan, viewing it as a renegade province. Conversely, Taiwan maintains its own democratic government and has developed a distinct national identity. This unresolved status quo has led to a complex web of international relations, with varying degrees of recognition and diplomatic ties from different countries.
Taiwan’s Importance on the Global Stage:
Taiwan’s significance on the world map extends beyond its geopolitical complexities. It is a major economic powerhouse, a technological innovator, and a vibrant democracy. Its economic success, particularly in manufacturing and technology, has made it a vital player in global supply chains. Taiwan’s commitment to democratic principles and human rights also serves as an inspiration for other countries in the region and beyond.
FAQs about Taiwan’s Position on the World Map:
1. What is the current political status of Taiwan?
Taiwan is a self-governing democracy with its own constitution, government, and military. However, the PRC claims sovereignty over the island, leading to a complex and unresolved political situation.
2. Why is Taiwan important to the world?
Taiwan is a significant economic power, a technological innovator, and a vibrant democracy. Its contributions to global trade, technological advancement, and democratic values make it an influential player on the world stage.
3. What are the major challenges facing Taiwan?
The primary challenge facing Taiwan is the unresolved political status with China. This tension impacts Taiwan’s international relations, security, and economic stability. Additionally, Taiwan faces challenges related to its aging population, environmental sustainability, and social inequality.
4. What is the future of Taiwan?
The future of Taiwan remains uncertain. The political situation with China is volatile, and the island’s future hinges on the outcome of this complex relationship. However, Taiwan’s economic strength, democratic values, and resilience suggest a future that holds both challenges and opportunities.
Tips for Understanding Taiwan’s Position on the World Map:
- Explore the historical context: Understanding Taiwan’s history, particularly its relationship with China, is crucial for grasping its current situation.
- Engage with different perspectives: Acknowledge the diverse viewpoints on Taiwan’s political status and the complex geopolitical dynamics involved.
- Focus on Taiwan’s strengths: Recognize Taiwan’s contributions to the global community in terms of its economy, technology, and democratic values.
- Stay informed about current events: The situation surrounding Taiwan is constantly evolving, so staying informed about recent developments is essential.
Conclusion:
Taiwan’s position on the world map is a reflection of its unique history, geography, and political realities. The island’s strategic location, economic prowess, and commitment to democracy make it a vital player in the global community. Understanding Taiwan’s complex relationship with China and its aspirations for self-determination is essential for navigating the intricate geopolitical landscape of East Asia and the world.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Taiwan’s Position on the World Map: A Geopolitical and Historical Perspective. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
