Thailand’s Position on the World Map: A Gateway to Southeast Asia
Related Articles: Thailand’s Position on the World Map: A Gateway to Southeast Asia
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Thailand’s Position on the World Map: A Gateway to Southeast Asia. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Thailand’s Position on the World Map: A Gateway to Southeast Asia

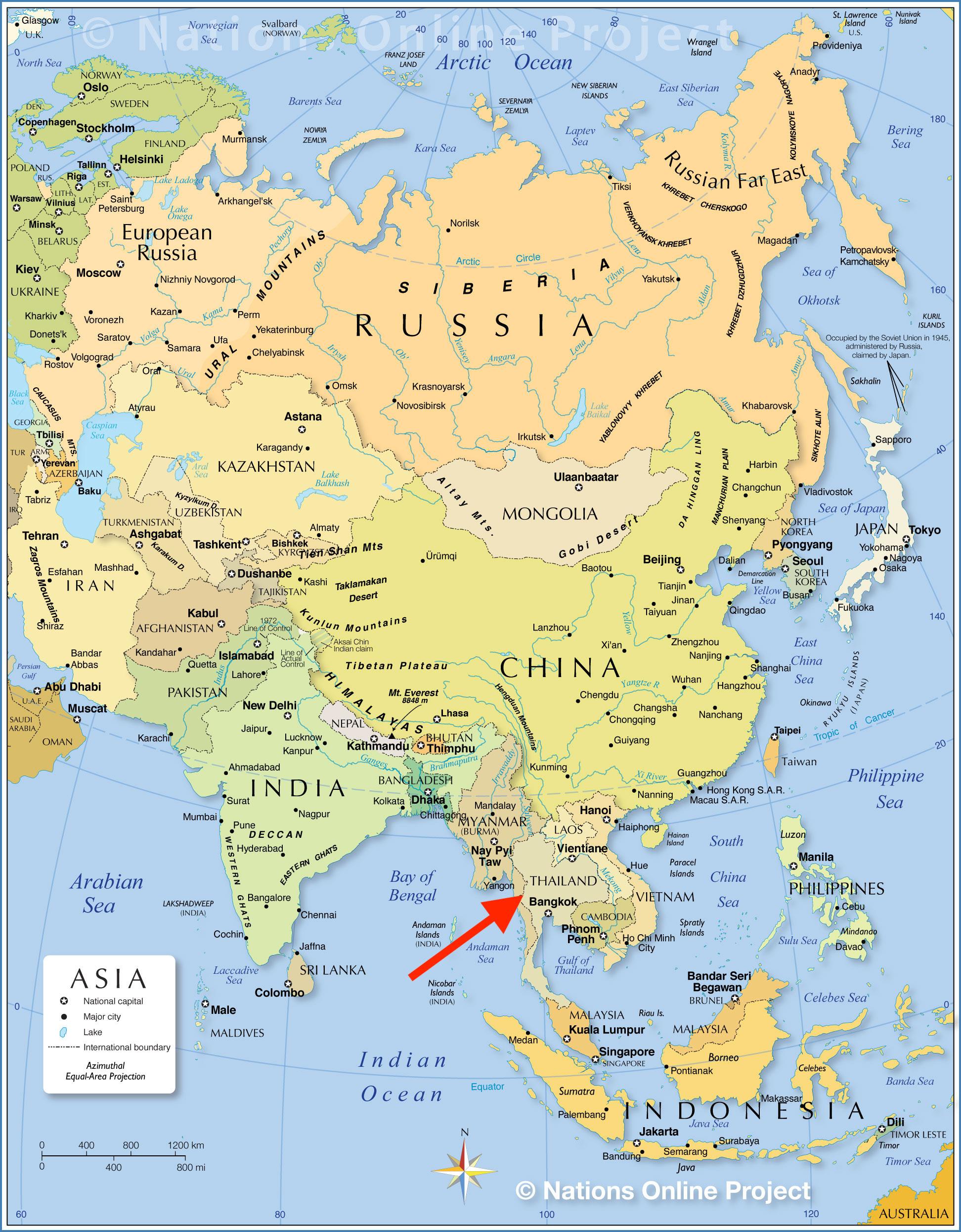
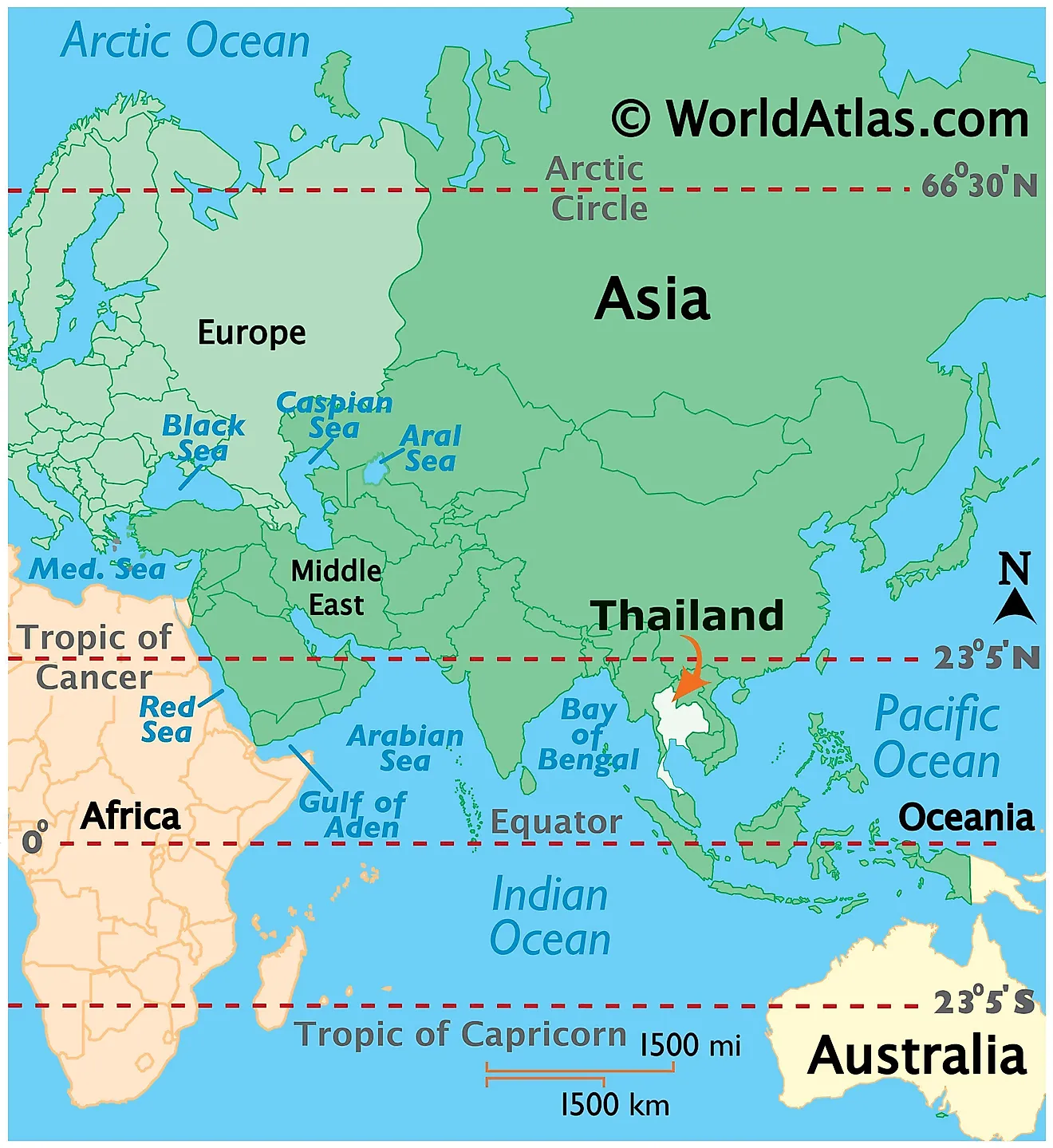
Thailand, a vibrant nation nestled in the heart of Southeast Asia, holds a unique geographical position that has shaped its history, culture, and influence in the region. Understanding Thailand’s location on the world map is crucial for appreciating its geopolitical significance, diverse cultural tapestry, and economic potential.
A Land Bridge Between East and West:
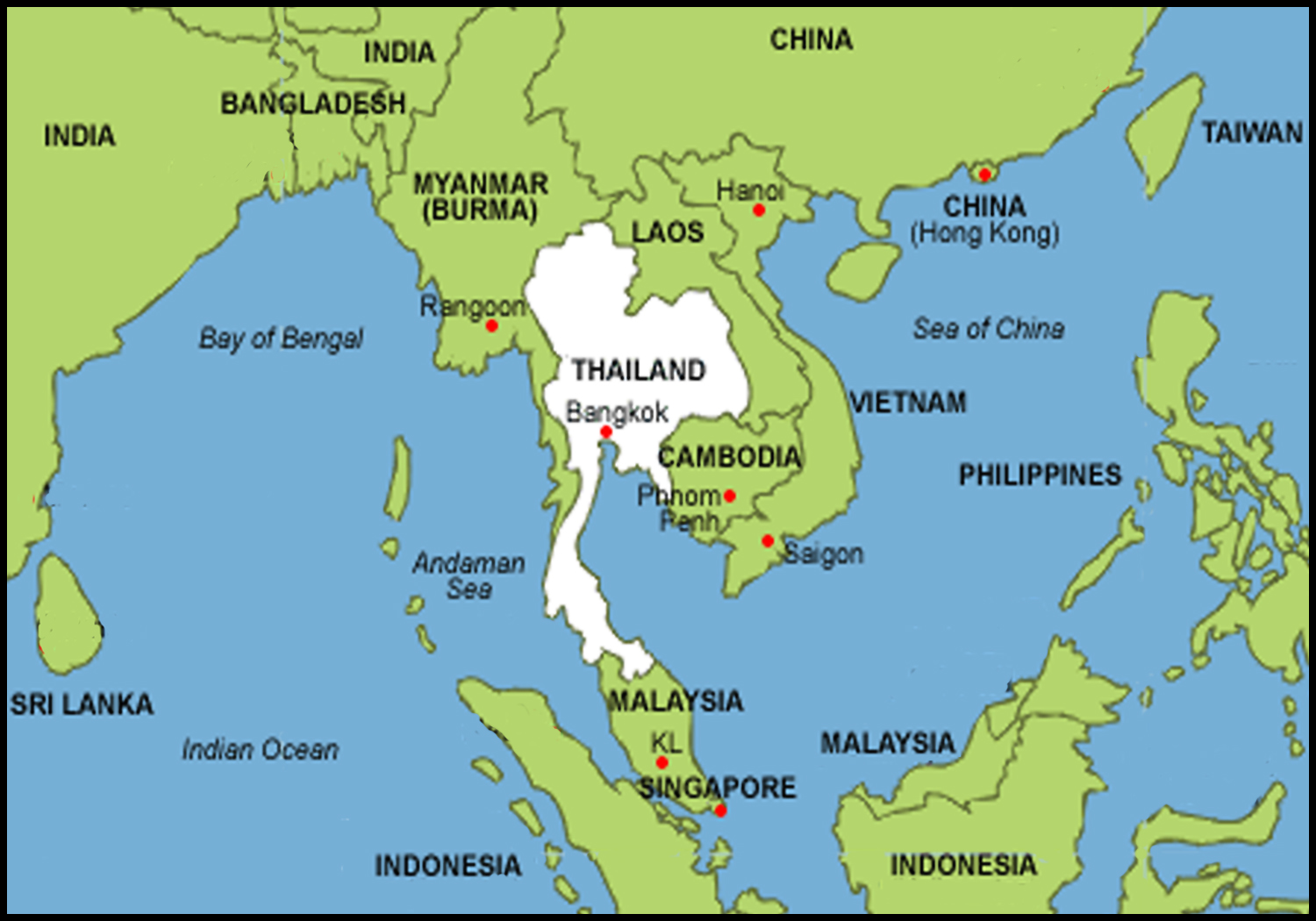
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is situated on the Indochinese Peninsula, bordering Myanmar, Laos, Cambodia, and Malaysia. This strategic location makes Thailand a natural bridge between the East and West, facilitating cultural exchange and trade routes throughout history. Its proximity to major maritime trade routes in the South China Sea and the Indian Ocean has historically positioned Thailand as a hub for commerce, attracting merchants and travelers from across the globe.
A Diverse Landscape:
Thailand’s diverse landscape, stretching from the mountainous north to the coastal plains in the south, offers a captivating array of geographical features. The country’s iconic mountainous regions, including the majestic Doi Inthanon, the highest peak in Southeast Asia, offer breathtaking vistas and opportunities for adventure. The fertile plains of the central region, known for their rice paddies and agricultural abundance, have been the heart of Thai civilization for centuries. Thailand’s coastline, encompassing the Gulf of Thailand and the Andaman Sea, boasts stunning beaches, crystal-clear waters, and vibrant marine life, making it a popular destination for tourists and a vital economic sector.
A Hub of Connectivity:
Thailand’s strategic location has fostered a well-developed transportation network, connecting the country to its neighbors and the wider world. A robust road network, extensive rail lines, and numerous international airports facilitate the movement of goods, people, and ideas. The country’s central location within Southeast Asia makes it a crucial node for regional trade and economic integration, contributing to its status as a regional economic powerhouse.
A Tapestry of Cultures:
Thailand’s geographic position has facilitated the interaction of diverse cultures, resulting in a unique and rich cultural heritage. The country’s history is marked by influences from neighboring countries, including India, China, and the Malay Peninsula. This cultural exchange is evident in Thailand’s vibrant traditions, languages, religions, and cuisine. The country’s iconic temples, bustling markets, and lively festivals are testaments to its diverse cultural tapestry.
Geopolitical Significance:
Thailand’s strategic location has also shaped its geopolitical role in Southeast Asia. As a founding member of ASEAN (Association of Southeast Asian Nations), Thailand plays a crucial role in regional cooperation and stability. Its diplomatic efforts have fostered regional integration, promoted economic growth, and addressed common challenges such as terrorism and environmental issues.
Tourism and Economic Growth:
Thailand’s unique blend of natural beauty, cultural heritage, and friendly hospitality has made it one of the world’s most popular tourist destinations. The tourism industry is a significant contributor to the Thai economy, generating substantial revenue and employment opportunities. Thailand’s strategic location, combined with its diverse offerings, continues to attract visitors from all corners of the globe.
Challenges and Opportunities:
While Thailand’s geographic position offers numerous benefits, it also presents certain challenges. The country’s proximity to conflict zones and the potential for natural disasters, such as earthquakes and tsunamis, require robust disaster preparedness and mitigation strategies. Additionally, maintaining regional stability and addressing transboundary issues, such as environmental concerns and illegal migration, are ongoing challenges.
FAQs:
Q: What is Thailand’s geographical location?
A: Thailand is located in Southeast Asia on the Indochinese Peninsula, bordering Myanmar, Laos, Cambodia, and Malaysia.
Q: What are the main geographical features of Thailand?
A: Thailand’s diverse landscape includes mountainous regions, fertile plains, and a coastline along the Gulf of Thailand and the Andaman Sea.
Q: How does Thailand’s location impact its culture?
A: Thailand’s location has facilitated cultural exchange, resulting in a rich tapestry of influences from neighboring countries, including India, China, and the Malay Peninsula.
Q: What is Thailand’s role in Southeast Asian politics?
A: Thailand plays a crucial role in regional cooperation and stability as a founding member of ASEAN.
Q: What are the economic benefits of Thailand’s location?
A: Thailand’s strategic location has fostered a well-developed transportation network, making it a hub for trade and economic growth. The country’s tourism industry is a significant contributor to its economy.
Tips:
- Explore Thailand’s diverse landscapes: From the mountains to the beaches, Thailand offers a wide range of natural beauty to explore.
- Immerse yourself in Thai culture: Visit temples, markets, and festivals to experience the country’s rich traditions.
- Engage with local communities: Interact with locals to gain deeper insights into Thai culture and way of life.
- Respect Thai customs and traditions: Be mindful of cultural sensitivities and dress appropriately when visiting temples and other sacred sites.
- Learn basic Thai phrases: A few words of Thai can go a long way in enhancing your travel experience.
Conclusion:
Thailand’s location on the world map is a testament to its historical significance, cultural diversity, and economic potential. Its strategic position as a bridge between East and West has fostered cultural exchange, trade, and connectivity, shaping the country’s unique identity and its role in Southeast Asia. Understanding Thailand’s geographical context provides a deeper appreciation for its rich history, vibrant culture, and evolving role in the global landscape.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Thailand’s Position on the World Map: A Gateway to Southeast Asia. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
