The Crucial Role of Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor Readings at Idle: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: The Crucial Role of Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor Readings at Idle: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Crucial Role of Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor Readings at Idle: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Crucial Role of Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor Readings at Idle: A Comprehensive Guide

The intricate dance of combustion within an internal combustion engine is a symphony of precisely timed events, orchestrated by a complex web of sensors and actuators. Among these vital components, the Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal engine performance, particularly during idle conditions.
Understanding the MAP Sensor
The MAP sensor, often referred to as a "manifold pressure sensor," is a crucial element in modern engine management systems. Its primary function is to measure the absolute pressure within the engine’s intake manifold, providing the engine control unit (ECU) with real-time data about the amount of air entering the cylinders. This information is vital for calculating the precise amount of fuel required for efficient combustion.
MAP Sensor Operation
The MAP sensor typically employs a piezoresistive element, a semiconductor material whose electrical resistance changes proportionally to the applied pressure. When air enters the intake manifold, it presses against the sensor’s diaphragm, altering the resistance of the piezoresistive element. This change in resistance is then interpreted by the ECU, providing a digital signal that represents the absolute pressure within the manifold.
Idle Conditions and MAP Sensor Readings
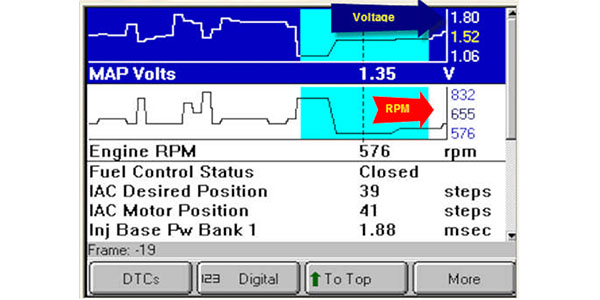
During idle, the engine operates at its lowest RPM, typically around 600-900 RPM. At this point, the throttle plate is nearly closed, restricting airflow into the intake manifold. This results in a relatively low manifold pressure, which is reflected in the MAP sensor readings.
The Significance of Idle MAP Readings
The MAP sensor readings at idle are crucial for several reasons:
- Air/Fuel Ratio Control: The ECU uses the MAP sensor data to determine the appropriate air/fuel ratio for idle conditions. This ratio is essential for smooth engine operation and minimizing emissions.
- Idle Speed Control: The ECU adjusts the engine’s idle speed based on the MAP sensor readings. This ensures that the engine runs smoothly and consistently at idle, preventing stalling or erratic behavior.
- Diagnostic Purposes: Abnormal MAP sensor readings at idle can indicate a variety of engine problems, such as leaks in the intake manifold, faulty vacuum lines, or issues with the sensor itself.
Factors Affecting Idle MAP Readings
Several factors can influence the MAP sensor readings at idle, including:
- Engine Temperature: A cold engine typically has a lower MAP reading at idle compared to a warm engine. This is due to the increased density of cold air.
- Intake Manifold Leaks: Leaks in the intake manifold can cause a decrease in manifold pressure, resulting in lower MAP readings at idle.
- Vacuum Lines: Faulty or disconnected vacuum lines can also affect the MAP sensor readings, leading to inaccurate pressure measurements.
- Sensor Malfunction: A faulty MAP sensor can produce inaccurate readings, affecting engine performance and fuel economy.
Interpreting Idle MAP Readings
Analyzing the MAP sensor readings at idle can provide valuable insights into the health and performance of the engine.
- Normal Idle MAP Readings: Typical idle MAP readings can vary depending on the engine model and specifications. However, a healthy engine typically exhibits a stable MAP reading at idle, within a range specified by the manufacturer.
- Low Idle MAP Readings: Low MAP readings at idle can indicate leaks in the intake manifold, faulty vacuum lines, or a malfunctioning MAP sensor.
- High Idle MAP Readings: High MAP readings at idle can suggest a blockage in the intake manifold, a faulty throttle position sensor, or a vacuum leak.
FAQs Regarding MAP Sensor Readings at Idle
Q: What is the typical range of idle MAP readings?
A: The typical range of idle MAP readings varies significantly depending on the engine model, size, and operating conditions. Consulting the manufacturer’s specifications or a reputable repair manual is recommended for accurate information.
Q: How can I diagnose a faulty MAP sensor?
A: Diagnosing a faulty MAP sensor requires a combination of visual inspection, pressure testing, and utilizing a scan tool. A visual inspection can identify physical damage or corrosion. Pressure testing can verify the sensor’s ability to accurately measure pressure. A scan tool can access the ECU’s data stream and monitor the MAP sensor readings for inconsistencies or erratic behavior.
Q: Can a faulty MAP sensor cause engine stalling?
A: Yes, a faulty MAP sensor can cause engine stalling, particularly at idle. If the sensor is providing inaccurate pressure readings, the ECU may miscalculate the air/fuel ratio, leading to an unstable idle and potential stalling.
Q: How often should the MAP sensor be replaced?
A: MAP sensors are generally quite durable and can last for many years. However, like any other sensor, they can eventually wear out or become faulty. Regular maintenance and monitoring of the sensor’s readings are essential for identifying potential issues.
Tips for Maintaining MAP Sensor Performance
- Regular Inspections: Visually inspect the MAP sensor for signs of damage, corrosion, or debris.
- Cleanliness: Keep the intake manifold and surrounding areas clean to prevent dirt and debris from contaminating the sensor.
- Vacuum Lines: Regularly check the vacuum lines for leaks, cracks, or disconnections.
- Pressure Testing: Periodically test the sensor’s pressure readings to ensure accuracy.
- Professional Service: If you suspect a problem with the MAP sensor, consult a qualified automotive technician for diagnosis and repair.
Conclusion
The MAP sensor plays a vital role in ensuring optimal engine performance, particularly during idle conditions. By accurately measuring the manifold pressure, the sensor provides the ECU with crucial information for precise air/fuel ratio control, idle speed regulation, and diagnostic purposes. Understanding the significance of MAP sensor readings at idle, the factors that can influence them, and the potential consequences of sensor malfunction is essential for maintaining a healthy and efficient engine. Regular inspections, maintenance, and professional attention to any potential issues can help ensure the longevity and optimal performance of the MAP sensor and the engine as a whole.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Crucial Role of Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor Readings at Idle: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
