The Crucial Role of MAP and MAF Sensors in Engine Management
Related Articles: The Crucial Role of MAP and MAF Sensors in Engine Management
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Crucial Role of MAP and MAF Sensors in Engine Management. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Crucial Role of MAP and MAF Sensors in Engine Management
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Crucial Role of MAP and MAF Sensors in Engine Management
- 3.1 Understanding the MAP Sensor
- 3.2 Understanding the MAF Sensor
- 3.3 The Interplay Between MAP and MAF Sensors
- 3.4 Benefits of Using MAP and MAF Sensors
- 3.5 FAQs about MAP and MAF Sensors
- 3.6 Tips for Maintaining MAP and MAF Sensors
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
The Crucial Role of MAP and MAF Sensors in Engine Management

Modern internal combustion engines rely on sophisticated electronic control units (ECUs) to optimize performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions. These ECUs rely on a network of sensors to monitor various engine parameters, providing the necessary data for precise fuel and ignition timing adjustments. Two crucial sensors in this network are the Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor and the Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor. While both sensors play a vital role in engine management, their functions and operating principles differ significantly.
Understanding the MAP Sensor
The MAP sensor, as its name suggests, measures the absolute pressure within the engine’s intake manifold. This pressure reflects the amount of air being drawn into the cylinders during the intake stroke. The MAP sensor typically utilizes a piezoresistive element, which changes its electrical resistance in response to pressure fluctuations. This change in resistance is then interpreted by the ECU to determine the manifold pressure.
Key Functions of the MAP Sensor:
- Fuel Delivery Calculation: The MAP sensor provides the ECU with crucial information about the air density in the intake manifold. This information is used to calculate the appropriate amount of fuel to inject for optimal combustion.
- Ignition Timing Adjustment: The MAP sensor also influences ignition timing. By measuring the manifold pressure, the ECU can determine the engine load and adjust the ignition timing accordingly.
- Boost Pressure Monitoring: In turbocharged engines, the MAP sensor plays a vital role in monitoring boost pressure. This information allows the ECU to control the boost pressure within safe operating limits.
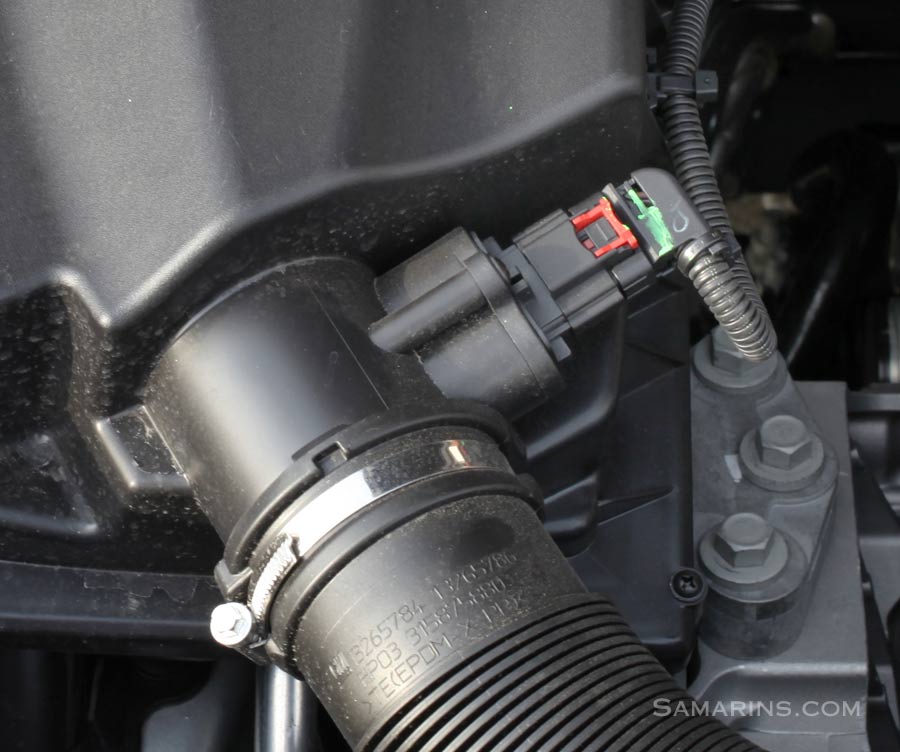
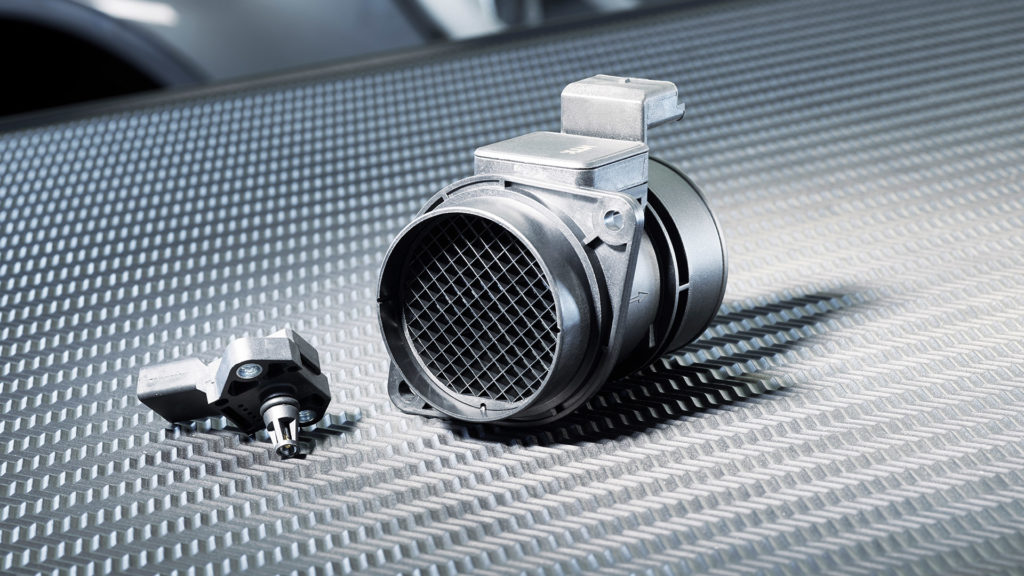
Understanding the MAF Sensor
The MAF sensor, on the other hand, measures the mass of air entering the engine. It does so by measuring the velocity of the air stream passing through a heated element. As air flows over the heated element, it cools it down. The sensor measures the amount of heat required to maintain the element at a constant temperature. This heat loss is directly proportional to the mass of air flowing through the sensor.
Key Functions of the MAF Sensor:
- Precise Fuel Delivery: The MAF sensor provides the ECU with a precise measurement of the air mass entering the engine. This allows for highly accurate fuel injection calculations, optimizing fuel efficiency and minimizing emissions.
- Engine Load Calculation: The MAF sensor data is used to determine the engine load, which is crucial for adjusting engine parameters like ignition timing and fuel injection duration.
- Airflow Monitoring: The MAF sensor provides real-time information about airflow, enabling the ECU to monitor and adjust engine parameters based on changing driving conditions.
The Interplay Between MAP and MAF Sensors
While both MAP and MAF sensors contribute to engine management, they are often used in different engine configurations:
- Naturally Aspirated Engines: Naturally aspirated engines typically rely on a MAP sensor. The pressure within the intake manifold is directly related to the amount of air drawn in. This allows the MAP sensor to provide sufficient information for fuel and ignition timing calculations.
- Turbocharged Engines: Turbocharged engines, on the other hand, often utilize a MAF sensor. The presence of a turbocharger significantly alters the pressure within the intake manifold, making it less reliable for determining air mass. The MAF sensor provides a more accurate measurement of the air mass entering the engine, regardless of the boost pressure.
- Hybrid Systems: Some engines employ both MAP and MAF sensors, utilizing the strengths of each sensor. The MAP sensor can provide information about manifold pressure, while the MAF sensor offers precise airflow measurements. This combined approach allows for more accurate engine management under various operating conditions.
Benefits of Using MAP and MAF Sensors
The use of MAP and MAF sensors offers numerous advantages for engine performance and efficiency:
- Optimized Fuel Consumption: By providing accurate information about air mass and engine load, these sensors enable the ECU to adjust fuel injection precisely, leading to reduced fuel consumption.
- Reduced Emissions: Precise fuel delivery and optimized ignition timing contribute to cleaner combustion, minimizing harmful emissions.
- Enhanced Performance: Accurate engine management ensures optimal combustion, leading to improved power delivery and overall performance.
- Improved Driveability: The ability to adjust engine parameters based on real-time sensor data results in smoother engine operation and improved driveability.
FAQs about MAP and MAF Sensors
1. What are the symptoms of a faulty MAP or MAF sensor?
A faulty MAP or MAF sensor can lead to various symptoms, including:
- Engine Stalling: A faulty sensor can cause inaccurate fuel delivery, leading to stalling, especially at idle or during acceleration.
- Rough Idle: A faulty sensor can lead to erratic fuel injection, resulting in a rough idle.
- Reduced Power: An inaccurate air mass measurement can hinder engine performance, leading to reduced power.
- Increased Fuel Consumption: Faulty sensors can cause over-fueling, resulting in increased fuel consumption.
- Check Engine Light: A faulty sensor will often trigger a check engine light, indicating a problem with the engine management system.
2. How can I test a MAP or MAF sensor?
Testing a MAP or MAF sensor typically requires specialized tools and knowledge. It’s recommended to consult a qualified mechanic for diagnosis and replacement.
3. Can I replace a MAP or MAF sensor myself?
Replacing a MAP or MAF sensor is generally a straightforward process. However, it requires some basic mechanical knowledge and tools. Consult your vehicle’s owner manual or a repair guide for specific instructions.
4. How often should I replace a MAP or MAF sensor?
MAP and MAF sensors typically have a long lifespan and rarely need replacement unless they become faulty. However, it’s important to inspect them regularly for signs of wear or damage.
5. What is the cost of replacing a MAP or MAF sensor?
The cost of replacing a MAP or MAF sensor varies depending on the vehicle make and model. It’s best to consult a local auto parts store or mechanic for pricing information.
Tips for Maintaining MAP and MAF Sensors
- Regular Inspections: Regularly inspect the sensors for signs of damage, dirt, or debris.
- Cleaning: Clean the sensors with a specialized cleaner or compressed air to remove any accumulated dirt or debris.
- Avoid Oil Sprays: Avoid using oil sprays near the sensors, as oil can contaminate the sensitive elements.
- Proper Installation: Ensure the sensors are properly installed and secured to prevent damage.
Conclusion
The MAP and MAF sensors play a crucial role in modern engine management systems, ensuring optimal fuel delivery, ignition timing, and overall engine performance. Understanding the functions and differences between these sensors is essential for diagnosing and resolving engine problems. By maintaining these sensors and addressing any issues promptly, drivers can ensure optimal engine performance, fuel efficiency, and reduced emissions.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Crucial Role of MAP and MAF Sensors in Engine Management. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
