The Crucial Role of MAP Sensors in Modern Automotive Systems: A Comprehensive Exploration
Related Articles: The Crucial Role of MAP Sensors in Modern Automotive Systems: A Comprehensive Exploration
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Crucial Role of MAP Sensors in Modern Automotive Systems: A Comprehensive Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Crucial Role of MAP Sensors in Modern Automotive Systems: A Comprehensive Exploration

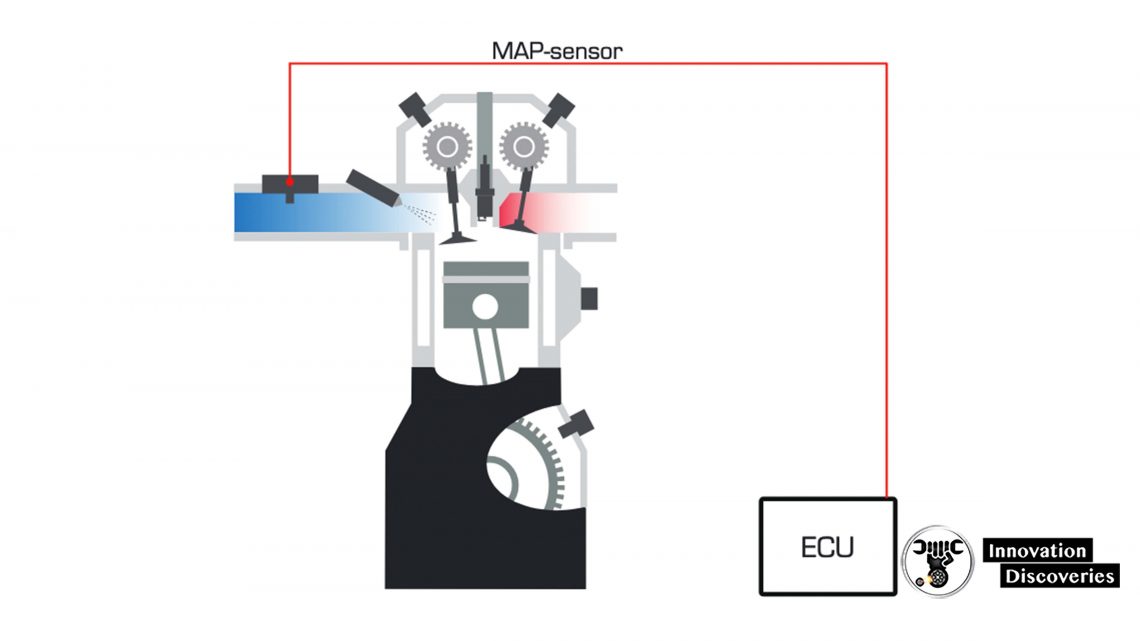
The modern automobile is a marvel of engineering, a complex symphony of interconnected systems working in harmony to deliver safe and efficient transportation. At the heart of this intricate network lie various sensors, each playing a vital role in monitoring and controlling critical engine functions. Among these, the Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor stands out as a crucial component, providing real-time data that directly influences the engine’s performance and fuel efficiency.
Understanding the Function of a MAP Sensor
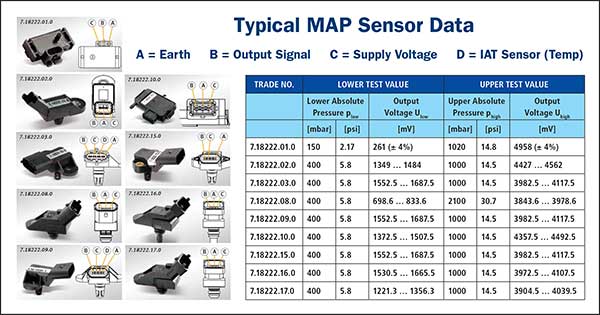
The MAP sensor, a small, robust device typically located in the engine’s intake manifold, is responsible for measuring the absolute pressure within the intake manifold. This pressure, a direct indicator of the air density entering the engine, provides essential information for the engine control unit (ECU).
The Importance of MAP Sensor Data
The data gathered by the MAP sensor is crucial for several key engine functions:
- Fuel Injection Control: The ECU utilizes MAP sensor data to determine the precise amount of fuel to inject into the engine cylinders. This ensures optimal air-fuel mixture for efficient combustion and reduced emissions.
- Ignition Timing Control: The MAP sensor data helps the ECU adjust the ignition timing, ensuring optimal combustion and maximizing engine power output.
- Boost Pressure Control: In turbocharged engines, the MAP sensor monitors boost pressure, allowing the ECU to regulate the turbocharger’s performance and prevent overboosting.
- Altitude Compensation: The MAP sensor data helps the ECU compensate for changes in atmospheric pressure at different altitudes, ensuring consistent engine performance regardless of location.
- Emissions Control: By optimizing fuel injection and ignition timing, the MAP sensor contributes to reducing harmful emissions from the engine.
The Impact of a Faulty MAP Sensor
A malfunctioning MAP sensor can have significant consequences on engine performance and overall vehicle operation:
- Poor Fuel Economy: Inaccurate MAP sensor readings can lead to an overly rich or lean fuel mixture, resulting in decreased fuel efficiency and increased fuel consumption.
- Reduced Engine Power: Incorrect fuel injection and ignition timing due to a faulty MAP sensor can cause engine misfires, reduced power output, and sluggish acceleration.
- Rough Idling: A faulty MAP sensor can cause the engine to idle erratically, potentially leading to stalling or difficulty starting.
- Increased Emissions: Incorrect fuel-air ratios due to a faulty MAP sensor can result in increased emissions of harmful pollutants.
- Check Engine Light: A faulty MAP sensor will trigger the Check Engine Light, indicating the need for diagnostics and repairs.
Common MAP Sensor Issues and Solutions
While MAP sensors are generally reliable, they can experience issues over time. Common problems include:
- Contamination: Dust, dirt, or oil buildup can affect the sensor’s accuracy. Regular cleaning or replacement may be necessary.
- Electrical Problems: Damaged wiring or a faulty electrical connection can disrupt the sensor’s communication with the ECU.
- Sensor Failure: The sensor itself can fail due to wear and tear, requiring replacement.
Diagnosing and Replacing a Faulty MAP Sensor
Diagnosing a faulty MAP sensor typically involves:
- Visual Inspection: Inspect the sensor for signs of damage, contamination, or loose connections.
- Diagnostic Scan Tool: Using a scan tool, the ECU can be interrogated for any fault codes related to the MAP sensor.
- Pressure Testing: A pressure test can verify the accuracy of the sensor’s readings.
Replacing a faulty MAP sensor is a relatively straightforward process:
- Locate the Sensor: The MAP sensor is typically located in the intake manifold, easily accessible for replacement.
- Disconnect Electrical Connections: Disconnect the electrical connector leading to the sensor.
- Remove the Sensor: Remove the sensor from its mounting location.
- Install the New Sensor: Install the new sensor in the same location, ensuring a secure fit.
- Reconnect Electrical Connections: Reconnect the electrical connector to the new sensor.
- Clear Fault Codes: Using a scan tool, clear any fault codes related to the MAP sensor.
FAQs on MAP Sensors
Q: How often should a MAP sensor be replaced?
A: MAP sensors are generally quite durable and can last for many years. However, they can be affected by wear and tear, contamination, or electrical issues. It is recommended to inspect the sensor for signs of damage or contamination during routine maintenance checks. If any issues are detected, replacement may be necessary.
Q: What are the symptoms of a faulty MAP sensor?
A: Common symptoms include poor fuel economy, reduced engine power, rough idling, increased emissions, and a Check Engine Light.
Q: Can I drive with a faulty MAP sensor?
A: While it is possible to drive with a faulty MAP sensor, it is not recommended. A faulty sensor can lead to decreased fuel efficiency, reduced engine performance, and increased emissions. It is best to have the sensor diagnosed and replaced as soon as possible.
Q: How much does it cost to replace a MAP sensor?
A: The cost of replacing a MAP sensor can vary depending on the vehicle make and model. However, the replacement cost is typically affordable, ranging from a few tens of dollars to a few hundred dollars.
Tips for Maintaining Your MAP Sensor
- Regular Inspections: Inspect the MAP sensor for signs of damage, contamination, or loose connections during routine maintenance checks.
- Clean the Sensor: If the sensor is contaminated, clean it with a non-abrasive cleaner or compressed air.
- Check Wiring: Ensure the electrical wiring leading to the sensor is intact and securely connected.
- Replace as Needed: If the sensor is damaged or fails, replace it promptly.
Conclusion
The MAP sensor is an essential component in modern automotive systems, providing critical data for optimal engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions control. Understanding its function and potential issues is crucial for maintaining vehicle health and ensuring a smooth driving experience. Regular inspections, proper maintenance, and prompt replacement when necessary can help prolong the life of your MAP sensor and prevent costly repairs down the line.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Crucial Role of MAP Sensors in Modern Automotive Systems: A Comprehensive Exploration. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
