The Crucial Role of Map Testing in Ensuring Data Accuracy and Reliability
Related Articles: The Crucial Role of Map Testing in Ensuring Data Accuracy and Reliability
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Crucial Role of Map Testing in Ensuring Data Accuracy and Reliability. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Crucial Role of Map Testing in Ensuring Data Accuracy and Reliability

In an increasingly data-driven world, the accuracy and reliability of maps are paramount. Maps serve as foundational tools for a myriad of applications, from navigation and transportation to urban planning and resource management. Ensuring the integrity of these maps is not merely a matter of aesthetic appeal; it is a critical factor in driving efficient decision-making, optimizing resource allocation, and fostering safe and effective operations. This is where the process of map testing comes into play.
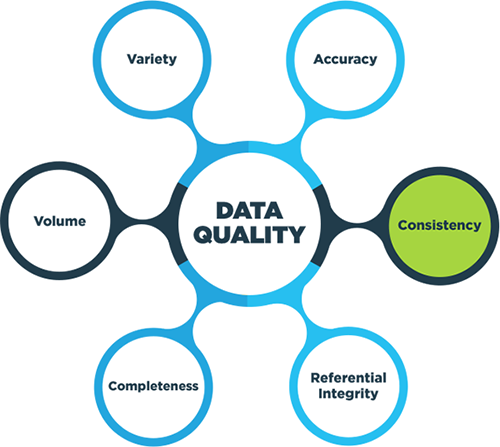
Map testing, also known as map validation or verification, is a systematic process designed to identify and rectify errors in maps. It involves a comprehensive evaluation of various map attributes, including geographic coordinates, feature types, attribute data, and map projections. The goal of this rigorous examination is to ensure that the map accurately reflects the real world and meets the specific requirements of its intended use.
The Importance of Map Testing
The significance of map testing cannot be overstated. It serves as a crucial safeguard against potential inaccuracies that can lead to costly errors, misinterpretations, and even safety hazards. Here are some key reasons why map testing is essential:
- Enhanced Accuracy and Reliability: Map testing helps identify and correct errors, ensuring that the map data is accurate and reliable. This is particularly important for maps used in critical applications, such as emergency response, infrastructure development, and environmental monitoring.
- Improved Decision-Making: Accurate maps provide a solid foundation for informed decision-making. By eliminating potential errors, map testing enhances the trustworthiness of map data, enabling users to make confident decisions based on reliable information.
- Optimized Resource Allocation: Map testing plays a vital role in resource management by ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently. Accurate maps help identify the most suitable locations for infrastructure development, resource extraction, or disaster relief efforts, optimizing resource utilization and minimizing waste.
- Enhanced Safety and Security: In situations involving navigation, emergency response, or security operations, accurate maps are crucial for ensuring safety and security. Map testing helps identify potential hazards, optimize routes, and support effective decision-making in critical situations.
- Increased Public Trust: When users can rely on the accuracy of maps, it fosters trust and confidence in the data provider. This is particularly important for government agencies and organizations that rely on map data for public services and infrastructure development.
Types of Map Testing
Map testing encompasses a range of techniques and methods, tailored to the specific characteristics of the map and its intended use. Here are some common types of map testing:
- Visual Inspection: This involves a visual examination of the map for inconsistencies, errors, and anomalies. Experienced cartographers and map analysts can identify potential problems by scrutinizing the map’s features, labels, and overall presentation.
- Attribute Testing: This type of testing focuses on the accuracy of the map’s attributes, such as names, addresses, elevation data, and other descriptive information. It involves comparing the map data against authoritative sources and databases to ensure consistency and correctness.
- Spatial Testing: This type of testing focuses on the geometric accuracy of the map’s features, including their positions, shapes, and relationships. It involves comparing the map data against ground truth data, such as GPS measurements, aerial imagery, or existing surveys.
- Logical Testing: This type of testing evaluates the logical consistency of the map data. It involves checking for inconsistencies in feature relationships, topological errors, and other logical discrepancies.
- Functional Testing: This type of testing focuses on the usability and functionality of the map. It involves evaluating the map’s performance in specific applications, such as navigation, analysis, or visualization.
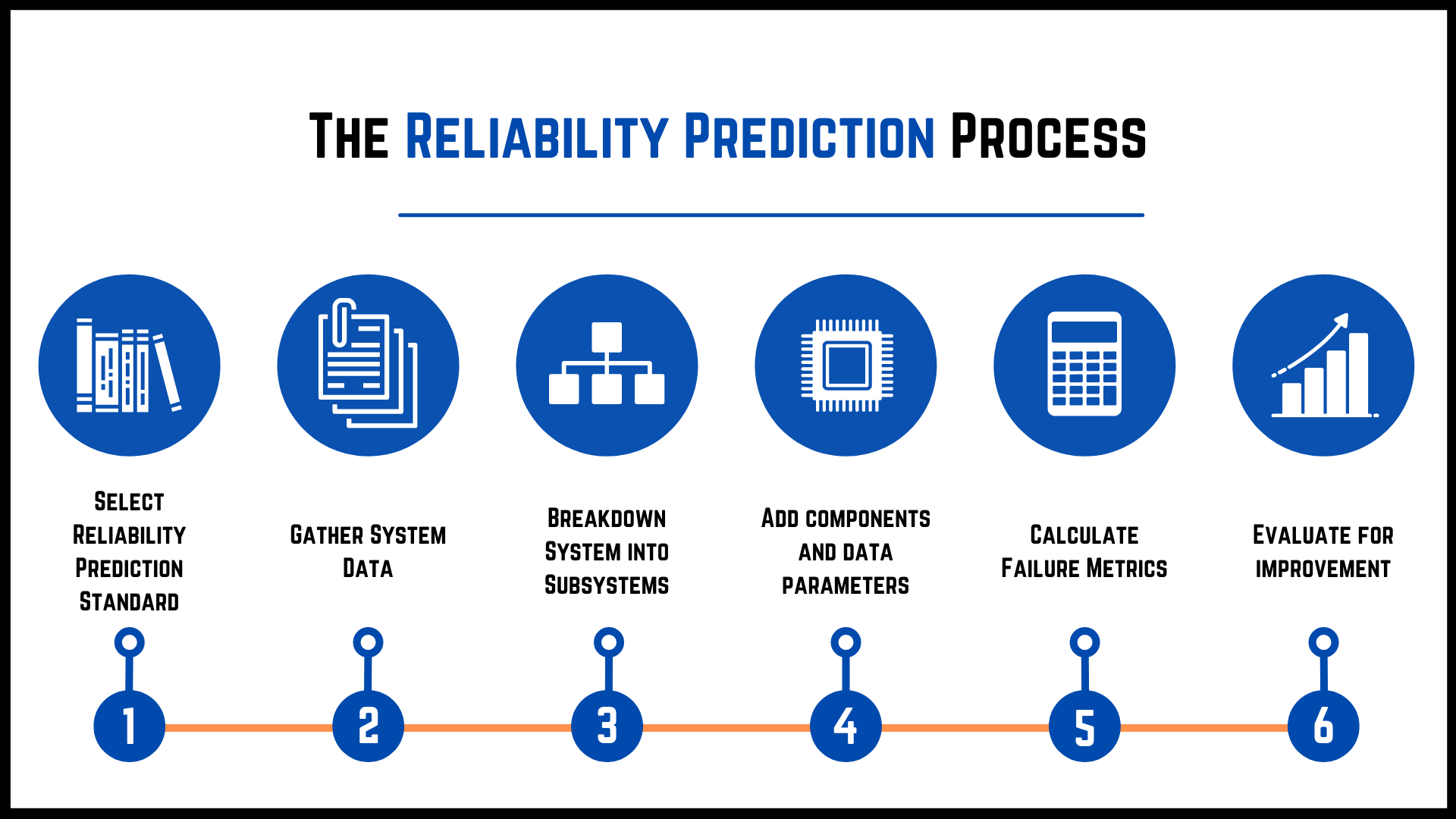
The Map Testing Process
The map testing process typically involves the following steps:
- Planning and Scoping: This stage involves defining the scope of the map testing, identifying the specific map attributes to be tested, and establishing the testing criteria.
- Data Acquisition: This stage involves gathering the necessary data for testing, including the map itself, ground truth data, and any relevant reference materials.
- Testing Execution: This stage involves performing the actual map testing using the chosen methods and techniques.
- Error Reporting and Analysis: This stage involves documenting the identified errors, analyzing their causes, and prioritizing them based on their potential impact.
- Error Correction and Validation: This stage involves correcting the identified errors, updating the map data, and re-testing to ensure the accuracy of the corrections.
Tools and Techniques for Map Testing
A range of tools and techniques are available to facilitate map testing. These include:
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS software provides powerful tools for map analysis, visualization, and testing. It allows users to compare map data against ground truth data, identify inconsistencies, and perform spatial analysis.
- Remote Sensing Data: Aerial imagery, satellite imagery, and other remote sensing data can be used as ground truth data for map testing. This data provides a comprehensive view of the real world, enabling accurate comparison with map data.
- GPS Measurements: GPS measurements can be used to verify the accuracy of geographic coordinates on maps. This data provides precise location information, which can be compared against the map’s coordinates.
- Field Surveys: Field surveys can be used to collect ground truth data for specific areas or features. This involves physically visiting the locations and collecting measurements, photographs, or other relevant data.
- Statistical Analysis: Statistical analysis can be used to assess the overall accuracy and reliability of map data. This involves analyzing the distribution of errors, identifying potential biases, and quantifying the level of uncertainty.
Map Testing in Different Applications
Map testing is essential in a wide range of applications, each with its own unique requirements and challenges. Here are some examples:
- Navigation and Transportation: In navigation systems, accurate maps are critical for ensuring safe and efficient travel. Map testing helps identify and correct errors in road networks, traffic data, and point-of-interest information.
- Urban Planning and Development: Accurate maps are essential for urban planning and development, enabling planners to identify suitable locations for infrastructure, housing, and other projects. Map testing helps ensure the accuracy of land use data, zoning information, and other relevant data.
- Environmental Monitoring and Management: Accurate maps are crucial for environmental monitoring and management, allowing researchers and policymakers to track changes in land cover, biodiversity, and pollution levels. Map testing helps ensure the accuracy of environmental data, such as vegetation maps, pollution maps, and wildlife habitat maps.
- Emergency Response and Disaster Relief: Accurate maps are essential for emergency response and disaster relief efforts, enabling first responders to navigate affected areas, locate victims, and distribute resources effectively. Map testing helps ensure the accuracy of infrastructure data, population density maps, and other critical information.
- Resource Management and Extraction: Accurate maps are essential for resource management and extraction, enabling companies to identify and access resources efficiently while minimizing environmental impact. Map testing helps ensure the accuracy of geological data, resource distribution maps, and other relevant information.
FAQs on Map Testing
Q: What are the common types of errors found in maps?
A: Common errors in maps include:
- Geometric errors: Incorrect coordinates, distorted shapes, and inaccurate distances.
- Attribute errors: Incorrect names, addresses, elevations, and other descriptive information.
- Topological errors: Incorrect connections between features, overlapping features, and missing features.
- Logical errors: Inconsistent data, conflicting information, and illogical relationships between features.
Q: How often should maps be tested?
A: The frequency of map testing depends on factors such as the map’s purpose, the rate of change in the real world, and the level of accuracy required. Maps used in critical applications, such as navigation and emergency response, may require more frequent testing than maps used for general information purposes.
Q: Who is responsible for map testing?
A: The responsibility for map testing typically lies with the organization or individual responsible for creating and maintaining the map. However, map users also play a role in identifying and reporting errors.
Q: What are the benefits of using a third-party map testing service?
A: Using a third-party map testing service can provide several benefits, including:
- Objectivity and impartiality: Third-party testers are not biased towards the map’s creator, ensuring a more objective assessment.
- Expertise and experience: Third-party testers have specialized expertise in map testing and can identify errors that may be overlooked by the map’s creator.
- Standardized testing procedures: Third-party testers often use standardized testing procedures, ensuring consistency and comparability across different maps.
Tips for Effective Map Testing
- Define clear testing objectives: Determine the specific goals of the map testing and establish the criteria for success.
- Use a variety of testing methods: Employ a range of testing techniques to ensure a comprehensive evaluation of the map’s accuracy.
- Prioritize error correction: Focus on correcting errors that have the greatest potential impact on the map’s intended use.
- Document all errors and corrections: Maintain a detailed record of identified errors, their causes, and the implemented corrections.
- Continuously monitor and improve the testing process: Regularly review and refine the map testing process to ensure its effectiveness and efficiency.
Conclusion
Map testing is an essential process for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of maps, which are foundational tools for a wide range of applications. By systematically identifying and rectifying errors, map testing enhances decision-making, optimizes resource allocation, and promotes safety and security. As the world becomes increasingly data-driven, the importance of map testing will continue to grow, ensuring that maps remain reliable sources of information and crucial tools for navigating the complexities of the real world.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Crucial Role of Map Testing in Ensuring Data Accuracy and Reliability. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
