The Crucial Role of the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor in Dodge Durango Performance
Related Articles: The Crucial Role of the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor in Dodge Durango Performance
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Crucial Role of the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor in Dodge Durango Performance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Crucial Role of the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor in Dodge Durango Performance
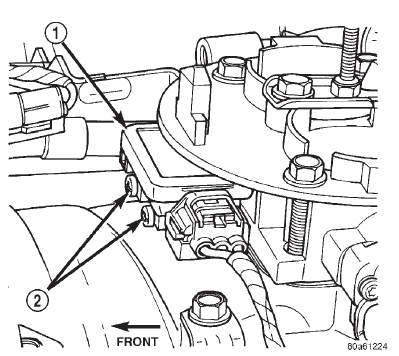
The Dodge Durango, a popular SUV known for its ruggedness and versatility, relies on a complex network of sensors and actuators to ensure optimal performance. Among these, the Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor plays a critical role in managing engine functions, directly influencing fuel efficiency, power output, and overall drivability. This article delves into the intricacies of the MAP sensor in Dodge Durango models, explaining its function, common issues, and troubleshooting strategies.
Understanding the MAP Sensor’s Function
The MAP sensor acts as a vital link between the engine’s intake manifold and the engine control unit (ECU). Its primary task is to measure the absolute pressure within the intake manifold, providing the ECU with crucial data about the engine’s load and air density. This information is then used to determine the optimal amount of fuel and air required for combustion.
How the MAP Sensor Works
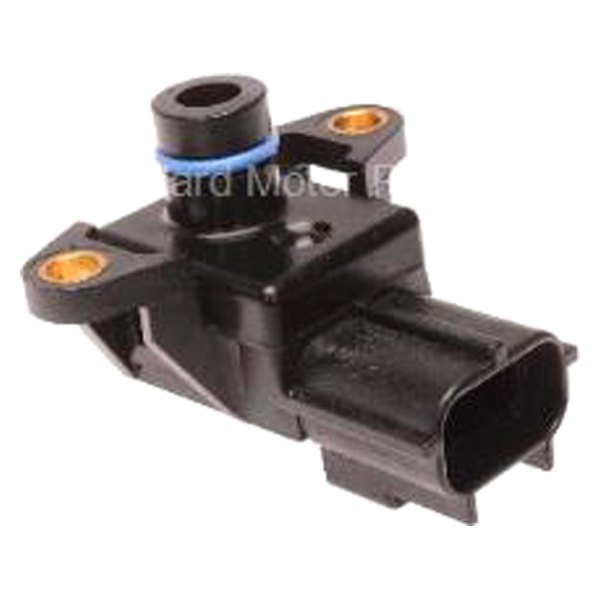
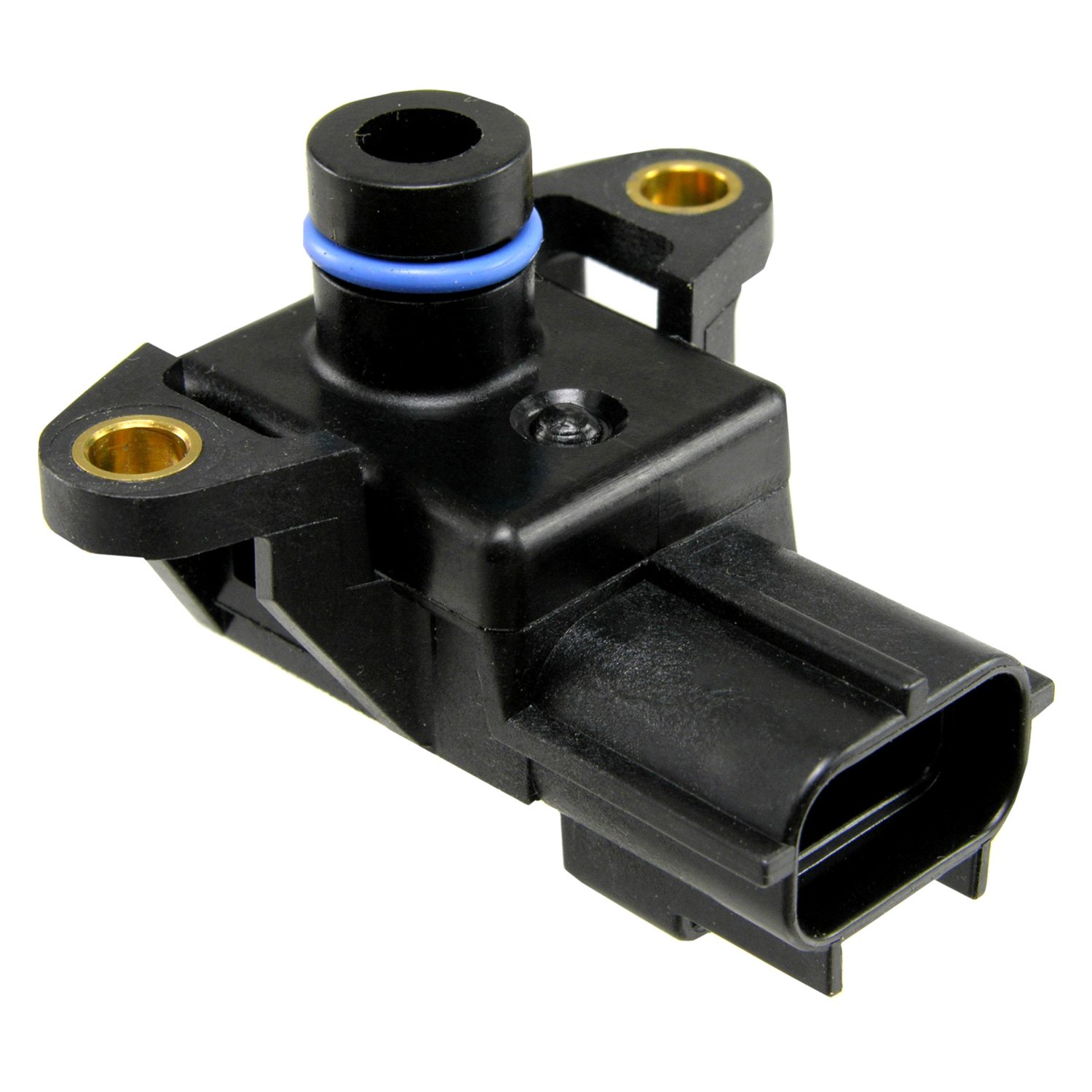
The MAP sensor, typically located on the intake manifold, employs a pressure-sensitive element, often a diaphragm, to detect pressure fluctuations. This diaphragm is connected to a strain gauge or a variable resistor, which converts the pressure changes into electrical signals. These signals are transmitted to the ECU, providing real-time information about the engine’s intake manifold pressure.
The Impact of a Faulty MAP Sensor
A malfunctioning MAP sensor can lead to a cascade of problems, significantly impacting the vehicle’s performance. Some common symptoms of a failing MAP sensor include:
- Engine Stalling: A faulty MAP sensor may provide inaccurate pressure readings to the ECU, leading to incorrect fuel delivery and potentially causing the engine to stall, especially during acceleration or idling.
- Rough Idle: A malfunctioning MAP sensor can lead to an erratic idle, characterized by engine vibrations and inconsistent RPM fluctuations.
- Reduced Power: The ECU relies on the MAP sensor’s data to determine fuel injection timing and duration. A faulty sensor can result in an insufficient fuel-air mixture, leading to reduced power output and sluggish acceleration.
- Increased Fuel Consumption: Inaccurate pressure readings can cause the ECU to overcompensate for fuel delivery, leading to excessive fuel consumption and decreased fuel efficiency.
- Check Engine Light: A faulty MAP sensor will trigger the Check Engine Light, indicating a problem within the engine’s control system.
Troubleshooting a Faulty MAP Sensor
Diagnosing a faulty MAP sensor involves a combination of visual inspection, diagnostic tools, and understanding common failure patterns.
- Visual Inspection: A visual inspection can reveal signs of damage, corrosion, or leaks in the MAP sensor itself or its wiring harness.
- Diagnostic Tools: Using an OBD-II scanner to read fault codes can pinpoint potential issues with the MAP sensor. Specific codes related to MAP sensor malfunction will provide valuable insights.
- Pressure Testing: A pressure test can verify the accuracy of the MAP sensor by applying known pressure values and comparing the output readings to the manufacturer’s specifications.
Replacing a Faulty MAP Sensor
If a faulty MAP sensor is diagnosed, replacing it with a genuine OEM part is crucial to ensure optimal performance and reliability. The replacement process typically involves:
- Disconnecting the Battery: Disconnect the battery terminal to prevent electrical shocks and potential damage to the electrical system.
- Locating the MAP Sensor: The MAP sensor is usually located on the intake manifold, easily accessible with a visual inspection.
- Unplugging the Connector: Disconnect the electrical connector from the MAP sensor, ensuring a secure release.
- Removing the Sensor: Depending on the sensor’s mounting type, it can be unscrewed or unclipped from its location.
- Installing the New Sensor: Insert the new MAP sensor into its mounting location, ensuring a secure fit and proper alignment.
- Connecting the Connector: Reconnect the electrical connector to the new MAP sensor, ensuring a secure connection.
- Reconnecting the Battery: Reconnect the battery terminal and start the engine to verify proper functionality.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: How often should the MAP sensor be replaced?
A: The MAP sensor is generally a reliable component and does not require regular replacement. However, its lifespan can be influenced by environmental factors, such as extreme temperatures, dirt, and vibration. If you suspect a faulty sensor, it’s best to consult a qualified mechanic for diagnosis and replacement.
Q: Can a faulty MAP sensor cause engine damage?
A: While a faulty MAP sensor won’t directly cause mechanical damage, it can lead to incorrect fuel-air mixtures, potentially resulting in engine misfires or excessive wear on components like spark plugs and catalytic converters.
Q: Can I clean the MAP sensor?
A: While cleaning a MAP sensor may seem tempting, it’s not recommended. The sensor’s internal workings are sensitive and can be easily damaged by cleaning attempts. Replacing a faulty sensor with a new one is the most reliable solution.
Q: How can I improve the longevity of the MAP sensor?
A: Regular maintenance, such as ensuring clean air filters and proper engine vacuum, can help prolong the lifespan of the MAP sensor. Avoid exposure to extreme temperatures and ensure the sensor is securely mounted to prevent damage.
Tips for Maintaining MAP Sensor Health
- Regular Engine Maintenance: Adhering to a regular engine maintenance schedule, including oil changes, air filter replacements, and spark plug inspections, can prevent excessive wear on the engine and minimize strain on the MAP sensor.
- Clean Air Intake: A clogged air filter restricts airflow, affecting the MAP sensor’s readings. Ensure the air filter is clean and replaced as recommended by the manufacturer.
- Avoid Extreme Temperatures: Excessive heat or cold can negatively impact the MAP sensor’s functionality. Avoid parking in extreme environments and ensure proper engine cooling.
- Prevent Moisture Exposure: Moisture can corrode the sensor’s electrical components. Protect the MAP sensor from direct exposure to water or excessive humidity.
Conclusion
The MAP sensor plays a crucial role in optimizing engine performance in Dodge Durango models. Understanding its function, recognizing common failure symptoms, and implementing proper troubleshooting strategies are essential for maintaining optimal vehicle performance. Regular maintenance, a clean air intake, and avoiding extreme temperatures contribute to the longevity of the MAP sensor, ensuring a smooth and reliable driving experience.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Crucial Role of the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor in Dodge Durango Performance. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
