The Crucial Role of the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor in the 2001 Honda Civic
Related Articles: The Crucial Role of the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor in the 2001 Honda Civic
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Crucial Role of the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor in the 2001 Honda Civic. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Crucial Role of the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor in the 2001 Honda Civic

The 2001 Honda Civic, a popular and reliable vehicle, relies on a sophisticated system of sensors and actuators to deliver optimal performance and fuel efficiency. Among these crucial components is the Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor, a small but vital device that plays a significant role in engine control. This article delves into the workings, importance, and potential issues associated with the MAP sensor in the 2001 Honda Civic.
Understanding the MAP Sensor’s Function
The MAP sensor is an integral part of the engine’s Electronic Control Unit (ECU). Its primary function is to measure the absolute pressure within the engine’s intake manifold. This pressure, known as manifold absolute pressure (MAP), provides the ECU with vital information about the engine’s load and air density.
How the MAP Sensor Works
The MAP sensor, typically a small, diaphragm-based device, operates on the principle of pressure sensing. It contains a diaphragm that flexes in response to changes in pressure within the intake manifold. This flexing action is translated into an electrical signal, which is sent to the ECU. The ECU then interprets this signal to determine the engine’s load.
Importance of the MAP Sensor in Engine Control
The MAP sensor’s role in engine control is multifaceted. It provides the ECU with crucial information for:
- Fuel Injection Control: The ECU uses MAP sensor data to determine the optimal amount of fuel to inject into the cylinders. This information is essential for achieving the correct air-fuel ratio, crucial for combustion efficiency and minimizing emissions.
- Ignition Timing Control: The ECU uses MAP sensor data to adjust ignition timing, ensuring optimal spark timing for efficient combustion.
- Throttle Position Control: The ECU utilizes MAP sensor data to fine-tune throttle response and optimize engine performance.
- Emissions Control: The MAP sensor plays a role in the operation of emissions control systems, such as the catalytic converter, by providing the ECU with information necessary for precise control of exhaust gas composition.
Signs of a Faulty MAP Sensor
A malfunctioning MAP sensor can lead to various engine performance issues. Common symptoms include:
- Engine Stalling: A faulty MAP sensor can lead to inaccurate fuel injection, causing the engine to stall, particularly at idle.
- Rough Idle: An inaccurate MAP reading can result in uneven fuel delivery, causing the engine to run rough, especially at idle.
- Poor Acceleration: A malfunctioning MAP sensor can disrupt fuel and ignition timing, leading to sluggish acceleration and reduced power.
- Increased Fuel Consumption: A faulty MAP sensor can cause the engine to run rich, resulting in excessive fuel consumption.
- Check Engine Light: A malfunctioning MAP sensor will often trigger the Check Engine light, indicating a fault in the engine’s control system.
Diagnosing a Faulty MAP Sensor
Diagnosing a faulty MAP sensor typically involves a combination of methods:
- Visual Inspection: A visual inspection of the MAP sensor can reveal signs of damage, such as cracked wiring or a damaged connector.
- Diagnostic Scan Tool: Using a diagnostic scan tool, a mechanic can access the ECU’s fault codes. A code related to the MAP sensor will indicate a potential issue.
- Pressure Testing: A pressure test can be performed to check if the MAP sensor is accurately measuring the manifold pressure.
- Voltage Check: Using a multimeter, a mechanic can measure the voltage output from the MAP sensor to check if it falls within the specified range.
Replacing a Faulty MAP Sensor
Replacing a faulty MAP sensor is a relatively straightforward procedure:
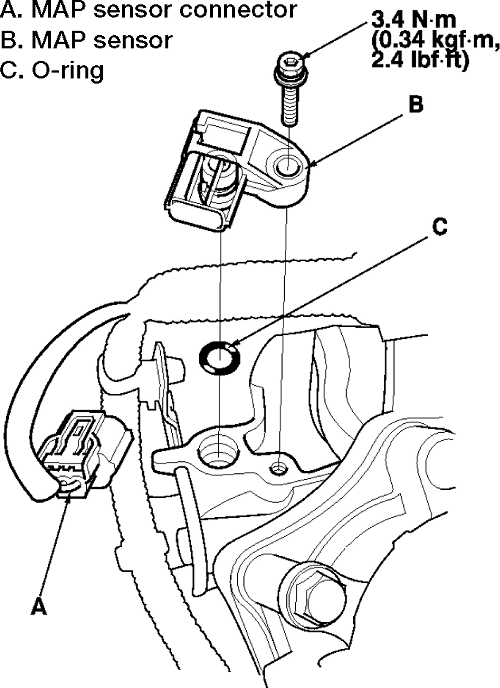
- Locate the MAP Sensor: The MAP sensor is typically located on the intake manifold, close to the throttle body.
- Disconnect the Connector: Disconnect the electrical connector from the MAP sensor.
- Remove the Sensor: Remove the MAP sensor from its mounting location.
- Install the New Sensor: Install the new MAP sensor in the same location and secure it properly.
- Connect the Connector: Connect the electrical connector to the new MAP sensor.
- Clear Fault Codes: Use a diagnostic scan tool to clear any fault codes stored in the ECU.
FAQs Regarding the MAP Sensor in the 2001 Honda Civic
Q: How often should the MAP sensor be replaced?
A: The MAP sensor is generally a durable component and does not typically require frequent replacement. However, regular maintenance and inspection are recommended to ensure optimal performance.
Q: Can a faulty MAP sensor cause a car to fail emissions testing?
A: Yes, a faulty MAP sensor can disrupt fuel and ignition timing, leading to excessive emissions and potentially causing the car to fail emissions testing.
Q: Can I replace the MAP sensor myself?
A: Replacing a MAP sensor is generally a straightforward procedure that can be performed by a DIY enthusiast with basic mechanical skills. However, it’s essential to consult the vehicle’s service manual for specific instructions and precautions.
Q: What are the potential consequences of ignoring a faulty MAP sensor?
A: Ignoring a faulty MAP sensor can lead to various issues, including decreased fuel efficiency, reduced engine performance, increased emissions, and potentially damage to other engine components.
Tips for Maintaining the MAP Sensor
- Regular Inspection: Regularly inspect the MAP sensor for signs of damage, such as cracked wiring or a loose connector.
- Clean the Sensor: Gently clean the MAP sensor with a clean, dry cloth or compressed air to remove any dirt or debris.
- Avoid Harsh Chemicals: Avoid using harsh chemicals or solvents to clean the MAP sensor, as they can damage the sensor’s delicate components.
Conclusion
The MAP sensor plays a vital role in the 2001 Honda Civic’s engine control system. By accurately measuring manifold pressure, it provides the ECU with essential information for optimal fuel injection, ignition timing, throttle response, and emissions control. A faulty MAP sensor can lead to various engine performance issues, so timely diagnosis and repair are crucial for maintaining the vehicle’s performance and fuel efficiency. Regular maintenance and inspection of the MAP sensor can help prevent future problems and ensure the longevity of this crucial component.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Crucial Role of the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor in the 2001 Honda Civic. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
