The Crucial Role of the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor in the Mazda 3: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: The Crucial Role of the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor in the Mazda 3: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Crucial Role of the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor in the Mazda 3: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Crucial Role of the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor in the Mazda 3: A Comprehensive Guide
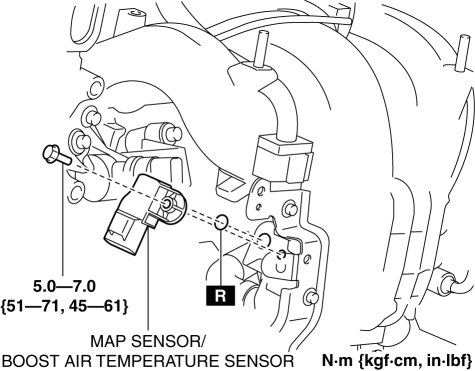
The Mazda 3, a popular compact car known for its reliability and performance, relies on a sophisticated network of sensors to ensure optimal engine operation. Among these, the Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor plays a critical role in regulating fuel injection and ignition timing, directly impacting the vehicle’s power, fuel efficiency, and emissions.
Understanding the MAP Sensor’s Function
The MAP sensor, typically located in the engine’s intake manifold, measures the pressure within the intake manifold. This pressure, known as manifold absolute pressure, is directly related to the amount of air being drawn into the engine. The sensor converts this pressure reading into an electrical signal that is sent to the engine control unit (ECU).
The ECU’s Role in Utilizing MAP Sensor Data
The ECU uses the MAP sensor data to determine various parameters, including:
- Fuel Injection Timing: The ECU calculates the precise amount of fuel to inject into the cylinders based on the intake manifold pressure. A higher pressure indicates a greater demand for air, requiring more fuel to maintain the proper air-fuel ratio.
- Ignition Timing: The ECU adjusts the ignition timing based on the MAP sensor readings. This ensures optimal combustion and maximizes engine performance.
- Airflow Calculation: The MAP sensor data, in conjunction with other sensor readings like the throttle position sensor, helps the ECU calculate the amount of air flowing into the engine.
- Emissions Control: The ECU uses MAP sensor data to optimize the operation of emissions control systems, such as the catalytic converter, to reduce harmful pollutants.
The Importance of a Functional MAP Sensor
A properly functioning MAP sensor is crucial for maintaining optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency. Here’s why:
- Power and Acceleration: An inaccurate MAP sensor reading can lead to incorrect fuel injection, resulting in a lean or rich air-fuel mixture. This can cause a loss of power, poor acceleration, and a rough idle.
- Fuel Consumption: A malfunctioning MAP sensor can cause the engine to run inefficiently, leading to increased fuel consumption.
- Emissions: An inaccurate MAP sensor reading can disrupt the engine’s emissions control system, resulting in higher emissions levels.
- Check Engine Light: A faulty MAP sensor will often trigger the check engine light, indicating a potential problem that needs attention.
Signs of a Failing MAP Sensor
Several symptoms can indicate a failing MAP sensor:
- Engine Stalling: A faulty MAP sensor can cause the engine to stall, especially at idle or during acceleration.
- Rough Idle: The engine may run rough, exhibiting vibrations or shaking, particularly at idle.
- Hesitation or Stuttering: The engine may hesitate or stutter during acceleration, as the ECU struggles to adjust the fuel mixture.
- Reduced Power: The vehicle may experience a noticeable loss of power, making acceleration sluggish.
- Increased Fuel Consumption: The vehicle may consume more fuel than usual, as the engine runs inefficiently.
- Check Engine Light: A check engine light illuminating, accompanied by a code related to the MAP sensor, indicates a problem with the sensor.
Troubleshooting and Repair
If you suspect a failing MAP sensor, it’s crucial to diagnose the issue correctly. This can be done by:
- Checking for Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve any error codes related to the MAP sensor.
- Visual Inspection: Inspect the MAP sensor for any physical damage, cracks, or loose connections.
- Pressure Testing: Use a pressure gauge to test the actual manifold pressure against the sensor’s readings.
- Replacement: If the MAP sensor is found to be faulty, it should be replaced with a new, genuine part.
FAQs Regarding the MAP Sensor in the Mazda 3
Q: How often should the MAP sensor be replaced?
A: The MAP sensor typically has a long lifespan, lasting for several years or tens of thousands of miles. However, environmental factors and driving conditions can affect its longevity. If you notice any symptoms of a failing MAP sensor, it’s best to have it inspected and potentially replaced.
Q: Can I clean a faulty MAP sensor?
A: While cleaning a MAP sensor might seem tempting, it’s generally not recommended. The sensor is a delicate electronic component, and cleaning it could potentially damage it further. It’s best to replace a faulty sensor with a new one.
Q: What is the cost of replacing a MAP sensor?
A: The cost of replacing a MAP sensor varies depending on the specific model year and the chosen replacement part. However, the cost is typically relatively affordable, ranging from a few tens to a few hundred dollars.
Q: Can I drive my Mazda 3 with a faulty MAP sensor?
A: Driving with a faulty MAP sensor can lead to various issues, including reduced performance, increased fuel consumption, and potential damage to other engine components. It’s best to address a faulty MAP sensor promptly to avoid further complications.
Tips for Maintaining the MAP Sensor
- Regular Maintenance: Ensure regular engine maintenance, including oil changes and air filter replacements, to minimize dust and debris accumulation that can affect the MAP sensor.
- Avoid Extreme Conditions: Expose the engine to extreme temperatures and harsh environments can damage the MAP sensor.
- Professional Inspection: Have the MAP sensor inspected during routine car maintenance checks.
Conclusion
The MAP sensor is a crucial component in the Mazda 3’s engine management system, playing a vital role in optimizing fuel injection, ignition timing, and emissions control. A properly functioning MAP sensor ensures optimal engine performance, fuel efficiency, and reduced emissions. If you experience any symptoms of a failing MAP sensor, it’s essential to have it inspected and repaired promptly to avoid further complications and maintain the reliability of your Mazda 3.
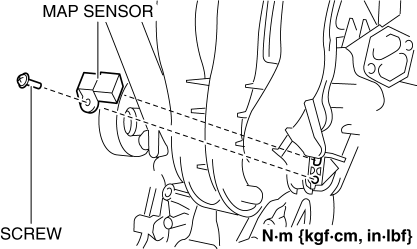

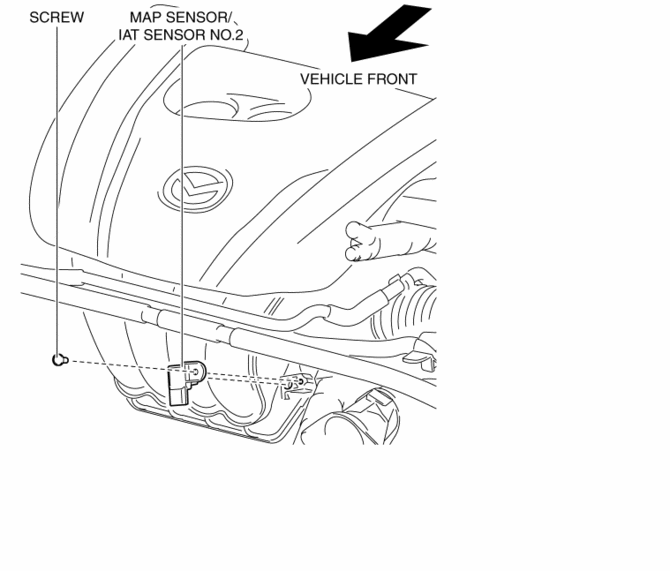





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Crucial Role of the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor in the Mazda 3: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
