The Crucial Role of the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor (MAP) in Mazda Vehicles
Related Articles: The Crucial Role of the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor (MAP) in Mazda Vehicles
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Crucial Role of the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor (MAP) in Mazda Vehicles. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Crucial Role of the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor (MAP) in Mazda Vehicles
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Crucial Role of the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor (MAP) in Mazda Vehicles
- 3.1 Understanding the MAP Sensor’s Function
- 3.2 Common MAP Sensor Problems and Their Symptoms
- 3.3 Diagnosis and Replacement of a Faulty MAP Sensor
- 3.4 FAQs Regarding the MAP Sensor in Mazda Vehicles
- 3.5 Tips for Maintaining the MAP Sensor
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
The Crucial Role of the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor (MAP) in Mazda Vehicles
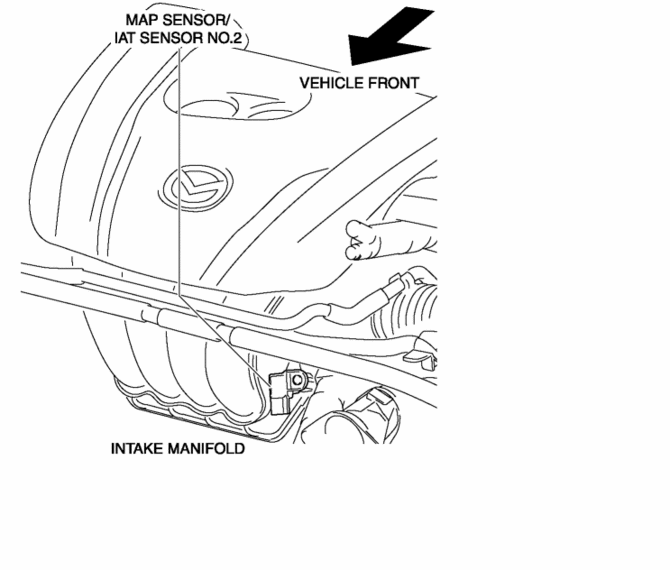
The modern internal combustion engine relies on a delicate balance of fuel and air to achieve optimal performance. This balance is meticulously controlled by a complex system of sensors and actuators, with the manifold absolute pressure sensor (MAP) playing a critical role. This article delves into the workings of the MAP sensor in Mazda vehicles, elucidating its significance in engine management and highlighting its impact on overall vehicle performance.
Understanding the MAP Sensor’s Function
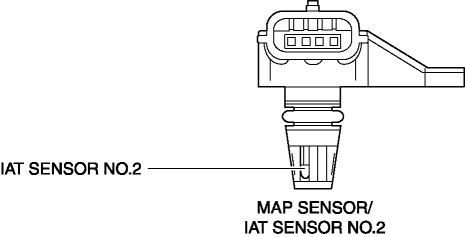
The MAP sensor, a critical component in the engine control unit (ECU), measures the pressure within the intake manifold. This pressure, known as manifold absolute pressure (MAP), is directly proportional to the amount of air entering the engine. The ECU utilizes this information to calculate the precise amount of fuel required for combustion, ensuring an optimal air-fuel mixture.
How it Works:
The MAP sensor is a diaphragm-based device, where a change in pressure within the intake manifold causes the diaphragm to flex. This flexing alters the resistance within a variable resistor, generating a voltage signal that is sent to the ECU. The ECU interprets this voltage signal, translating it into a pressure reading.
The Importance of Accurate MAP Readings:
Accurate MAP readings are crucial for several reasons:
- Fuel Economy: By accurately determining the amount of air entering the engine, the ECU can precisely calculate the fuel injection duration, optimizing fuel consumption and minimizing waste.
- Engine Performance: A precise air-fuel mixture ensures smooth engine operation, preventing misfires, stalling, and other performance issues.
- Emissions Control: Optimal combustion reduces harmful emissions, contributing to cleaner air and environmental sustainability.
- Engine Protection: The MAP sensor helps prevent engine damage caused by excessively rich or lean air-fuel mixtures.
Common MAP Sensor Problems and Their Symptoms
Like any electronic component, the MAP sensor is susceptible to wear and tear, leading to potential malfunctions. These malfunctions can manifest in various ways, affecting vehicle performance and fuel efficiency.
Common MAP Sensor Problems:
- Electrical Failures: Issues within the sensor’s internal circuitry or wiring can disrupt the signal transmission to the ECU.
- Diaphragm Damage: Physical damage to the diaphragm, caused by exposure to extreme temperatures, pressure fluctuations, or debris, can impair its ability to accurately measure pressure.
- Contamination: Dirt, oil, or other contaminants can accumulate on the sensor, obstructing its functionality.
Symptoms of a Faulty MAP Sensor:
- Rough Idle: An inaccurate MAP reading can lead to an uneven air-fuel mixture, resulting in a rough idle.
- Stalling: A faulty sensor can cause the engine to stall, particularly at low speeds or during acceleration.
- Reduced Power: An incorrect air-fuel mixture can lead to a loss of engine power and sluggish acceleration.
- Increased Fuel Consumption: A faulty MAP sensor can disrupt the fuel injection system, leading to increased fuel consumption.
- Check Engine Light: The ECU will typically illuminate the check engine light if it detects a problem with the MAP sensor.
Diagnosis and Replacement of a Faulty MAP Sensor
Diagnosing a faulty MAP sensor requires a combination of observation, diagnostic tools, and testing procedures.
Diagnostic Steps:
- Visual Inspection: Check for any visible damage to the sensor, wiring, or surrounding components.
- Diagnostic Scan Tool: Utilize an OBD-II scanner to retrieve any fault codes related to the MAP sensor.
- Pressure Testing: Use a pressure gauge to measure the actual manifold pressure and compare it to the sensor’s readings.
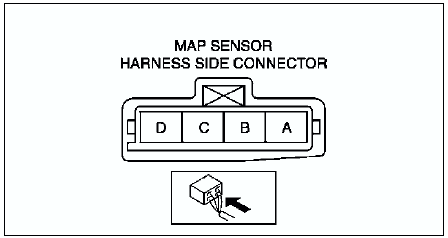
- Voltage Testing: Use a multimeter to check the voltage signal output by the sensor and compare it to the manufacturer’s specifications.
Replacement Procedure:
Once a faulty MAP sensor is identified, it must be replaced. This procedure typically involves:
- Disconnecting the Battery: Disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to prevent electrical hazards.
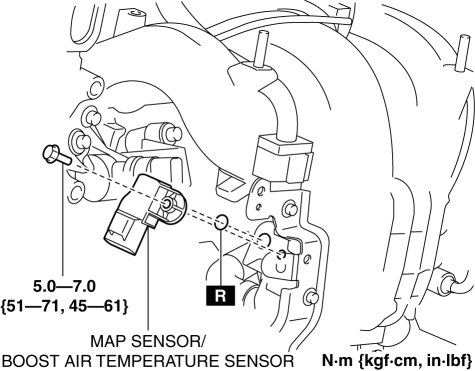
- Locating the Sensor: Identify the MAP sensor, usually located on the intake manifold, near the throttle body.
- Unplugging the Connector: Carefully disconnect the electrical connector from the sensor.
- Removing the Sensor: Use a wrench or socket to loosen and remove the sensor from its mounting location.
- Installing the New Sensor: Install the new sensor in the same location, ensuring a secure connection.
- Reconnecting the Connector: Reconnect the electrical connector to the new sensor.
- Reconnecting the Battery: Reconnect the negative terminal of the battery.
- Clearing Fault Codes: Use a diagnostic scan tool to clear any stored fault codes related to the MAP sensor.
FAQs Regarding the MAP Sensor in Mazda Vehicles
Q1: What are the common signs of a faulty MAP sensor in Mazda vehicles?
A: Common signs include rough idling, stalling, reduced engine power, increased fuel consumption, and the illumination of the check engine light.
Q2: How often should the MAP sensor be replaced?
A: The MAP sensor typically has a lifespan of 100,000 miles or more, but it can fail prematurely due to environmental factors or damage. Regular maintenance and inspection can help identify potential issues.
Q3: Can I drive with a faulty MAP sensor?
A: Driving with a faulty MAP sensor can lead to reduced performance, increased fuel consumption, and potential engine damage. It is recommended to address the issue promptly.
Q4: How much does it cost to replace a MAP sensor in a Mazda vehicle?
A: The cost of replacing a MAP sensor varies depending on the vehicle model, labor costs, and the specific sensor. Prices typically range from $50 to $200.
Q5: Is it possible to clean a MAP sensor?
A: While cleaning a MAP sensor may be possible in some cases, it is generally not recommended. The sensor’s internal components are delicate, and attempting to clean them can potentially damage the sensor.
Tips for Maintaining the MAP Sensor
- Regular Inspections: Visually inspect the sensor for any signs of damage, dirt, or oil accumulation.
- Clean Air Filter: A clean air filter ensures that only clean air enters the intake manifold, preventing contamination of the MAP sensor.
- Avoid Harsh Chemicals: Avoid using harsh chemicals or solvents near the MAP sensor, as they can damage its delicate components.
- Professional Maintenance: Schedule regular maintenance appointments with a qualified mechanic for comprehensive inspections and repairs.
Conclusion
The MAP sensor plays a crucial role in the smooth and efficient operation of Mazda engines. By accurately measuring the air pressure within the intake manifold, it enables the ECU to precisely control the air-fuel mixture, optimizing fuel economy, engine performance, and emissions control. Understanding the function, common problems, and maintenance tips related to the MAP sensor can help Mazda owners maintain their vehicles’ peak performance and reliability.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Crucial Role of the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor (MAP) in Mazda Vehicles. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
