The Engine’s Brain: Unveiling the Role of the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
Related Articles: The Engine’s Brain: Unveiling the Role of the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Engine’s Brain: Unveiling the Role of the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Engine’s Brain: Unveiling the Role of the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor

The intricate dance of combustion within an engine relies on a delicate balance of fuel and air, orchestrated by a sophisticated network of sensors and actuators. Among these crucial components, the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor (MAP Sensor) plays a pivotal role in ensuring optimal engine performance. This article delves into the workings of the MAP sensor, unraveling its significance in the complex symphony of engine operation.
Understanding the Essence of Engine Management
Modern internal combustion engines are marvels of engineering, converting chemical energy into mechanical energy with remarkable efficiency. However, achieving this feat requires meticulous control over the air-fuel mixture entering the cylinders. Too much fuel leads to inefficient combustion and potential damage, while insufficient fuel results in a lean mixture, potentially causing engine knock and reduced power.
The Electronic Control Unit (ECU), the engine’s brain, governs this intricate process. It receives information from various sensors, including the MAP sensor, to determine the optimal air-fuel ratio for different operating conditions. This information allows the ECU to precisely control the fuel injection system, ensuring smooth and efficient engine operation.
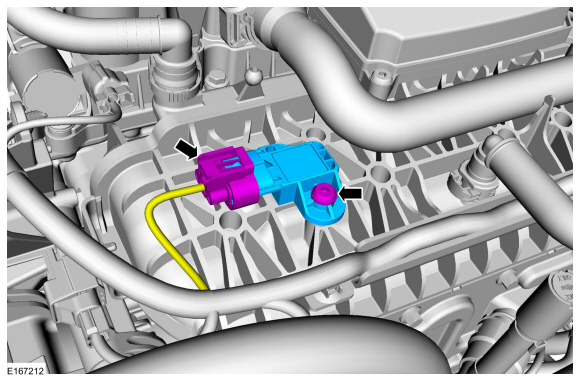
The MAP Sensor: A Window into Engine Conditions
The MAP sensor is strategically positioned in the intake manifold, the conduit that delivers air to the cylinders. Its primary function is to measure the absolute pressure within the manifold, a crucial parameter reflecting the amount of air entering the engine.
The MAP sensor operates on the principle of piezoresistive technology. It contains a small, sensitive diaphragm that deflects under pressure. This deflection alters the resistance of a built-in resistor, generating a voltage signal proportional to the absolute pressure within the manifold. The ECU interprets this voltage signal, translating it into a precise measurement of manifold pressure.
Beyond Airflow: The MAP Sensor’s Diverse Roles
The MAP sensor’s contribution extends beyond simply measuring airflow. Its data plays a crucial role in several critical engine functions:
-
Fuel Injection Control: The ECU uses the manifold pressure reading to calculate the precise amount of fuel required for optimal combustion. This ensures the correct air-fuel mixture is delivered to the cylinders, maximizing efficiency and minimizing emissions.
-
Spark Timing Adjustment: The MAP sensor’s data allows the ECU to adjust the ignition timing, ensuring optimal combustion based on engine load and speed. This fine-tuning contributes to smooth engine operation and improved fuel economy.
-
Boost Pressure Control (Turbocharged Engines): In turbocharged engines, the MAP sensor monitors the boost pressure generated by the turbocharger. This information helps the ECU control the turbocharger’s operation, preventing overboost and ensuring optimal performance.
-
Throttle Position Sensing: Some MAP sensors incorporate a throttle position sensor, providing the ECU with additional information about the engine’s load. This data further refines the ECU’s control over fuel injection and ignition timing.
The Importance of a Healthy MAP Sensor
A malfunctioning MAP sensor can significantly impact engine performance and fuel efficiency. Common symptoms of a faulty MAP sensor include:
-
Rough idling: An inaccurate manifold pressure reading can disrupt the air-fuel mixture, leading to erratic engine operation at idle.
-
Stalling: A faulty sensor may provide incorrect data, causing the ECU to miscalculate fuel delivery, potentially leading to engine stalling.
-
Reduced power: A faulty MAP sensor can result in an incorrect air-fuel mixture, hindering engine power output and acceleration.
-
Increased emissions: A malfunctioning sensor can disrupt the fuel-air ratio, leading to increased emissions and potentially failing emissions tests.
-
Engine knock: Inaccurate manifold pressure readings can lead to improper ignition timing, potentially causing engine knock, a damaging phenomenon characterized by a knocking or rattling sound.
FAQs: Understanding the MAP Sensor
Q: What is the difference between a MAP sensor and a MAF sensor?
A: While both sensors play crucial roles in engine management, they measure different parameters. The MAP sensor measures manifold pressure, reflecting the amount of air entering the engine, while the MAF sensor measures the mass airflow rate, indicating the actual quantity of air flowing into the engine.
Q: Can I test the MAP sensor myself?
A: While basic testing can be performed with a multimeter, a thorough diagnosis requires specialized equipment and expertise. It is recommended to consult a qualified mechanic for proper diagnosis and replacement.
Q: How often should I replace the MAP sensor?
A: MAP sensors are typically designed for long service life. However, factors like environmental conditions and engine wear can affect their longevity. It is recommended to consult your vehicle’s maintenance schedule or a qualified mechanic for replacement recommendations.
Q: Can I drive with a faulty MAP sensor?
A: While driving with a faulty MAP sensor is possible, it can lead to reduced engine performance, increased emissions, and potential engine damage. It is advisable to address any sensor malfunction promptly.
Tips for Maintaining a Healthy MAP Sensor
-
Regular maintenance: Adhering to regular engine maintenance schedules, including air filter replacement, helps prevent debris from contaminating the MAP sensor.
-
Avoiding harsh environments: Excessive dust, dirt, and moisture can damage the sensor. Minimize exposure to these conditions whenever possible.
-
Professional diagnosis: If you suspect a MAP sensor malfunction, consult a qualified mechanic for a proper diagnosis and repair.
Conclusion: The Unsung Hero of Engine Management
The MAP sensor, though often overlooked, plays a vital role in ensuring efficient and reliable engine operation. Its ability to measure manifold pressure provides the ECU with crucial information for controlling fuel injection, spark timing, and other critical functions. By understanding the importance of this sensor and its role in engine management, drivers can maintain optimal performance, fuel efficiency, and longevity for their vehicles.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Engine’s Brain: Unveiling the Role of the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
