The Evolution of MAP Testing: A Comprehensive Look at Its Origins and Significance
Related Articles: The Evolution of MAP Testing: A Comprehensive Look at Its Origins and Significance
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Evolution of MAP Testing: A Comprehensive Look at Its Origins and Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Evolution of MAP Testing: A Comprehensive Look at Its Origins and Significance

The concept of standardized testing has evolved significantly over the years, with various assessments emerging to gauge student learning and progress. One such assessment, the Measures of Academic Progress (MAP) test, has played a pivotal role in shaping educational practices, particularly in the United States. While the exact origins of MAP testing are somewhat complex, understanding its development and impact requires delving into the history of standardized testing and the emergence of computer-adaptive assessments.
Early Roots: Standardized Testing and its Evolution
The roots of standardized testing can be traced back to the late 19th century, when the need for objective measures of student achievement became increasingly apparent. Early attempts at standardized testing focused primarily on measuring basic skills, such as reading and arithmetic, with the goal of identifying students who required additional support. These early tests were often paper-based and relied on a single score to represent a student’s overall performance.
As the 20th century progressed, standardized testing evolved significantly. The development of new psychometric theories and advancements in statistical analysis led to the creation of more sophisticated assessments. These tests incorporated multiple-choice questions, provided more detailed score reports, and offered a wider range of assessments across different subject areas.
The Rise of Computer-Adaptive Testing
A significant breakthrough in standardized testing came with the advent of computer-adaptive testing (CAT) in the 1980s. CAT assessments utilize sophisticated algorithms that adjust the difficulty of questions based on a student’s performance. This adaptive nature allows for more precise measurement of a student’s ability level, as the test dynamically adapts to their individual strengths and weaknesses.
The Birth of MAP Testing: A New Era of Assessment
The MAP test, developed by Northwest Evaluation Association (NWEA), emerged in the late 1990s as a computer-adaptive assessment designed to measure student growth in reading, language usage, and mathematics. The test’s introduction marked a significant shift in educational assessment, offering several key advantages over traditional standardized tests:
- Adaptive Nature: MAP tests utilize CAT technology, allowing them to adjust the difficulty of questions based on a student’s performance. This adaptive nature provides a more accurate measure of a student’s ability level than traditional tests, which often present the same questions to all students.
- Growth-Focused Approach: MAP tests are designed to track student growth over time, providing educators with valuable insights into how students are progressing in their learning. This focus on growth allows educators to tailor instruction to meet individual student needs and identify areas where additional support may be required.
- Frequent Administration: MAP tests can be administered multiple times throughout the year, allowing for more frequent monitoring of student progress and providing educators with real-time data to inform their instruction. This frequent administration contrasts with traditional standardized tests, which are typically administered once or twice a year.
- Comprehensive Reporting: MAP tests generate detailed score reports that provide a comprehensive overview of a student’s performance across different subject areas and skill levels. These reports allow educators to identify specific areas of strength and weakness, enabling them to provide targeted interventions and support.
The Impact of MAP Testing on Educational Practices
The introduction of MAP testing has had a significant impact on educational practices, influencing various aspects of teaching and learning:
- Data-Driven Instruction: MAP test data provides educators with valuable insights into student performance, allowing them to make data-driven decisions about instruction. By analyzing student scores, educators can identify areas where students are struggling and tailor their teaching to address those specific needs.
- Personalized Learning: The adaptive nature of MAP testing allows educators to personalize learning experiences for individual students. By adjusting the difficulty of questions based on a student’s performance, MAP tests can provide a more accurate assessment of their ability level and help educators tailor instruction to meet their individual needs.
- Early Intervention: The frequent administration of MAP tests allows educators to identify students who may be struggling early on and provide them with the necessary support to prevent academic difficulties from escalating. Early intervention programs based on MAP test data can help ensure that all students have the opportunity to succeed.
- Accountability and Progress Monitoring: MAP tests provide a standardized measure of student achievement, allowing educators and policymakers to track student progress over time and hold schools accountable for student learning outcomes. This accountability framework encourages schools to focus on improving student performance and ensuring that all students have access to quality education.
FAQs about MAP Testing
Q: When did MAP testing begin?
A: While the exact date of the first MAP test administration is not readily available, NWEA began developing the MAP test in the late 1990s, with the first versions of the test being introduced in the early 2000s.
Q: What are the different types of MAP tests?
A: NWEA offers several different MAP tests, including:
- MAP Reading: Measures reading comprehension and fluency.
- MAP Language Usage: Measures language skills, such as grammar, vocabulary, and writing mechanics.
- MAP Math: Measures mathematical reasoning and problem-solving skills.
Q: How often are MAP tests administered?
A: MAP tests can be administered multiple times throughout the year, typically three to four times per year, allowing for frequent monitoring of student progress.
Q: How are MAP test scores interpreted?
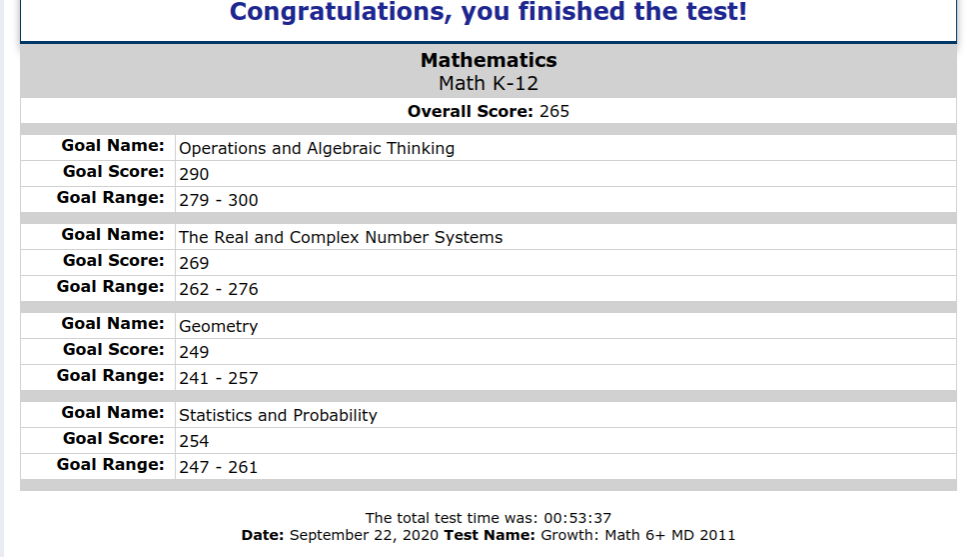
A: MAP test scores are reported on a scale called the RIT scale, which is a percentile-based system that allows for comparisons across different grade levels. The scale provides a measure of a student’s relative performance compared to other students in their grade level.
Q: What are the benefits of using MAP testing?
A: MAP testing offers several benefits, including:
- Adaptive assessment: Provides a more accurate measure of a student’s ability level.
- Growth-focused approach: Tracks student growth over time, allowing educators to identify areas where students need additional support.
- Frequent administration: Allows for more frequent monitoring of student progress and provides educators with real-time data to inform their instruction.
- Comprehensive reporting: Generates detailed score reports that provide a comprehensive overview of a student’s performance.
Tips for Using MAP Testing Effectively
- Utilize the data: Analyze MAP test data to identify student strengths and weaknesses and tailor instruction accordingly.
- Focus on growth: Use MAP testing to track student progress over time and celebrate their achievements.
- Incorporate MAP testing into a comprehensive assessment plan: Don’t rely solely on MAP testing; use it in conjunction with other assessments to gain a holistic understanding of student learning.
- Communicate with parents: Share MAP test results with parents and explain how the data can be used to support their child’s learning.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of MAP Testing
The introduction of MAP testing marked a significant shift in educational assessment, ushering in a new era of computer-adaptive assessments that prioritize student growth and personalized learning. The test’s adaptive nature, frequent administration, and comprehensive reporting have provided educators with valuable tools to monitor student progress, identify areas of need, and tailor instruction to meet individual student requirements. As educational practices continue to evolve, MAP testing remains a valuable tool for supporting student learning and promoting educational equity.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Evolution of MAP Testing: A Comprehensive Look at Its Origins and Significance. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
