The Ford Fusion’s Unsung Hero: Understanding the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
Related Articles: The Ford Fusion’s Unsung Hero: Understanding the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Ford Fusion’s Unsung Hero: Understanding the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Ford Fusion’s Unsung Hero: Understanding the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
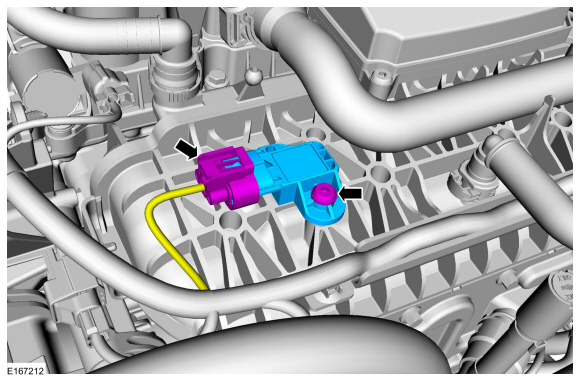
The Ford Fusion, a popular mid-size sedan known for its reliability and comfort, relies on a complex network of sensors and systems to ensure optimal performance. One critical component within this intricate web is the Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor. While often overlooked, the MAP sensor plays a crucial role in the Fusion’s engine management system, impacting fuel efficiency, power output, and emissions control.
The Role of the MAP Sensor
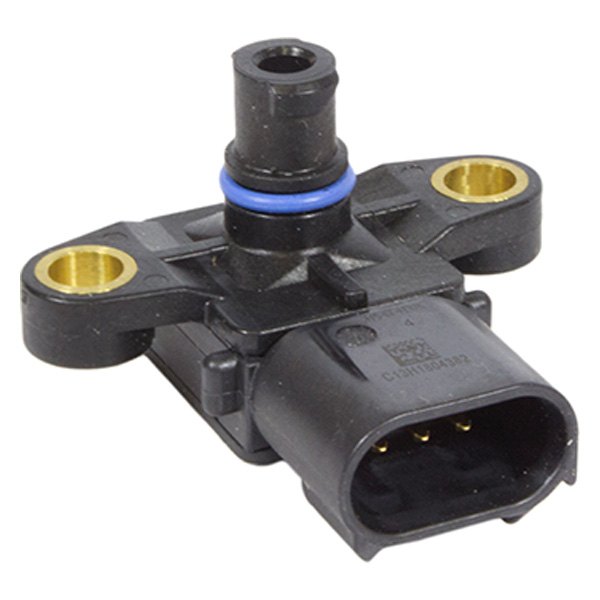
The MAP sensor, located on the intake manifold, is responsible for measuring the pressure inside the engine’s intake manifold. This pressure, known as manifold absolute pressure, is a direct indicator of the amount of air entering the engine during each intake stroke.
How the MAP Sensor Works
The MAP sensor utilizes a piezoresistive element, a material whose electrical resistance changes with pressure. As air pressure in the intake manifold increases, the piezoresistive element compresses, altering its resistance. This change in resistance is then translated into an electrical signal by the sensor, which is sent to the engine control unit (ECU).
The MAP Sensor’s Impact on Engine Performance
The ECU utilizes the information provided by the MAP sensor to perform several critical functions:
- Fuel Injection Control: The ECU determines the precise amount of fuel to inject into the engine cylinders based on the air pressure measured by the MAP sensor. This ensures an optimal air-fuel mixture, maximizing combustion efficiency and minimizing emissions.
- Ignition Timing: The ECU adjusts the timing of the spark plugs based on the air pressure in the intake manifold. Precise ignition timing contributes to smoother engine operation and optimal power output.
- Emissions Control: The MAP sensor data is used to regulate the operation of the catalytic converter, a crucial component in reducing harmful emissions from the exhaust.
Recognizing MAP Sensor Problems
A malfunctioning MAP sensor can lead to a range of symptoms, including:
- Reduced Fuel Efficiency: An inaccurate air pressure reading can cause the ECU to inject too much or too little fuel, impacting fuel consumption.
- Engine Stalling or Hesitation: Erratic fuel injection and ignition timing due to a faulty MAP sensor can cause the engine to stall or hesitate during acceleration.
- Check Engine Light: A malfunctioning MAP sensor will trigger the check engine light, indicating a fault in the engine management system.
- Rough Idle: An inaccurate air pressure reading can lead to an irregular engine idle, causing vibrations and noise.
- Poor Acceleration: The engine may struggle to accelerate smoothly due to improper fuel injection and ignition timing.
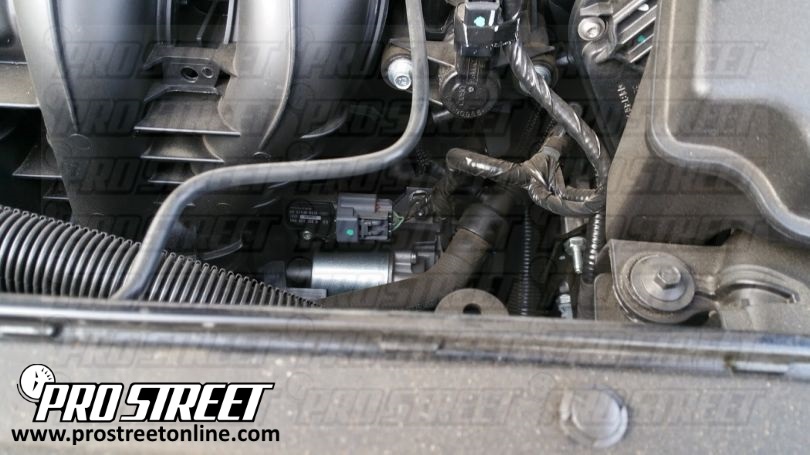
Diagnosing and Replacing a Faulty MAP Sensor
Diagnosing a faulty MAP sensor typically involves a combination of visual inspection, code reading, and pressure testing.
- Visual Inspection: Inspect the MAP sensor for any visible damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Code Reading: Using an OBD-II scanner, retrieve any diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to the MAP sensor.
- Pressure Testing: Use a specialized tool to measure the actual air pressure in the intake manifold and compare it to the readings provided by the MAP sensor.
If the MAP sensor is found to be faulty, it should be replaced with a genuine Ford part or a high-quality aftermarket equivalent.
Tips for Maintaining the MAP Sensor
- Regular Maintenance: Ensure regular engine maintenance, including air filter replacement and intake manifold cleaning, to prevent dirt and debris from accumulating on the MAP sensor.
- Avoid Harsh Chemicals: Do not use harsh chemicals or cleaners near the MAP sensor, as they can damage the delicate sensor elements.
- Protect from Moisture: Ensure the MAP sensor is properly sealed and protected from moisture, which can lead to corrosion and malfunction.
Conclusion
The MAP sensor is a vital component in the Ford Fusion’s engine management system, playing a critical role in fuel efficiency, power output, and emissions control. Understanding its function and potential problems can help owners identify and address issues promptly, ensuring optimal performance and longevity for their Fusion. By addressing any issues related to the MAP sensor, drivers can maintain their Fusion’s efficiency, power, and overall driving experience.








Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Ford Fusion’s Unsung Hero: Understanding the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
