The Geography of Taiwan and Japan: Island Nations in East Asia
Related Articles: The Geography of Taiwan and Japan: Island Nations in East Asia
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Geography of Taiwan and Japan: Island Nations in East Asia. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Geography of Taiwan and Japan: Island Nations in East Asia
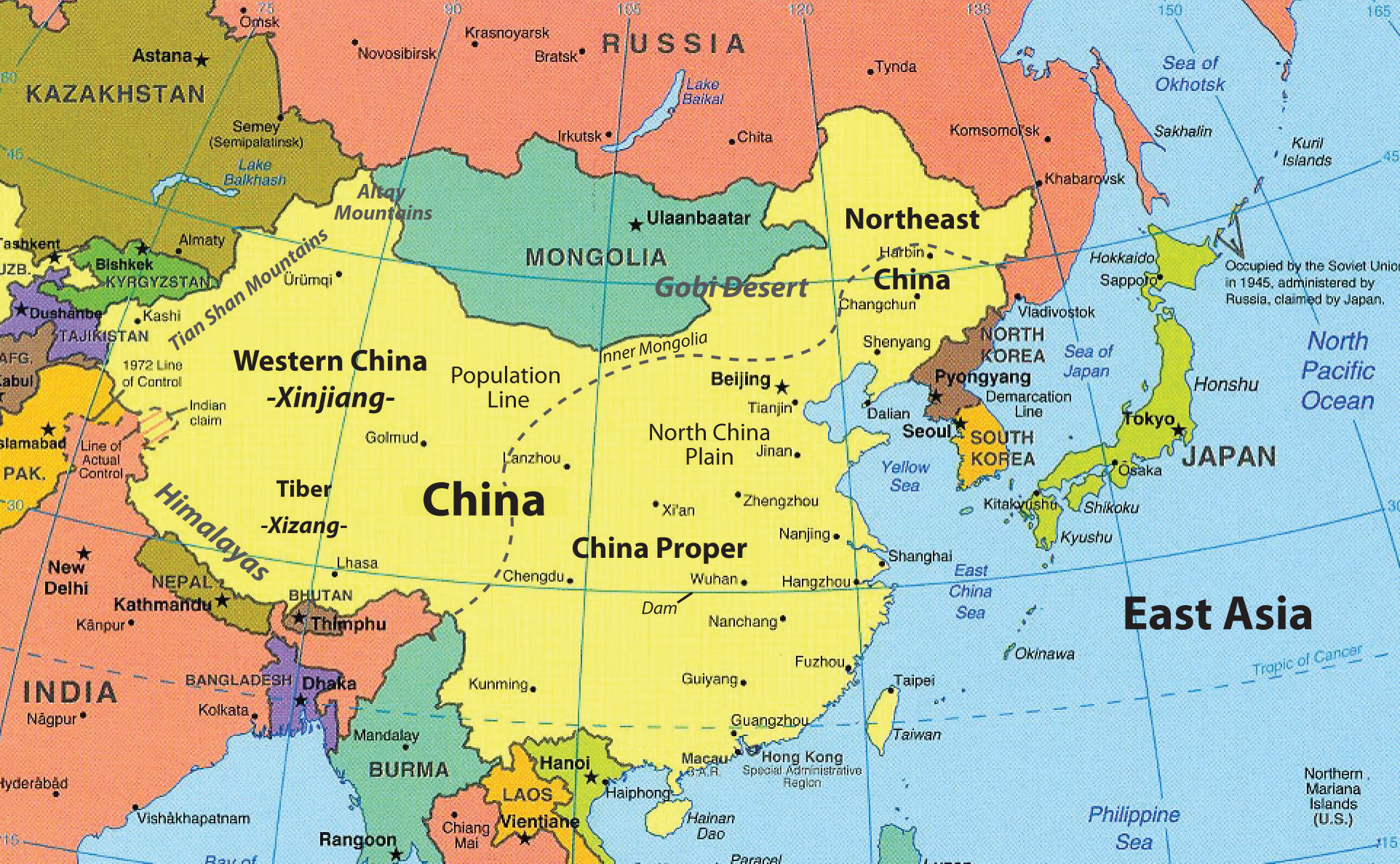
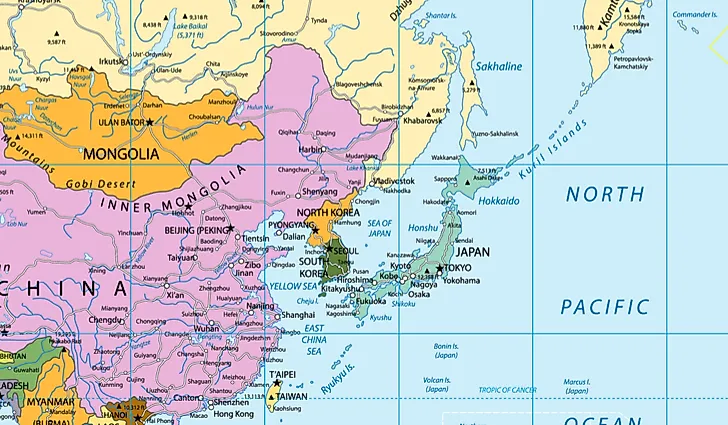
Taiwan and Japan, two island nations in East Asia, share a complex and fascinating geographical history. Despite their proximity and shared maritime influence, their landscapes and geological formations exhibit distinct characteristics, each contributing to their unique cultural and societal development.
Taiwan: A Mountainous Island with Diverse Landscapes
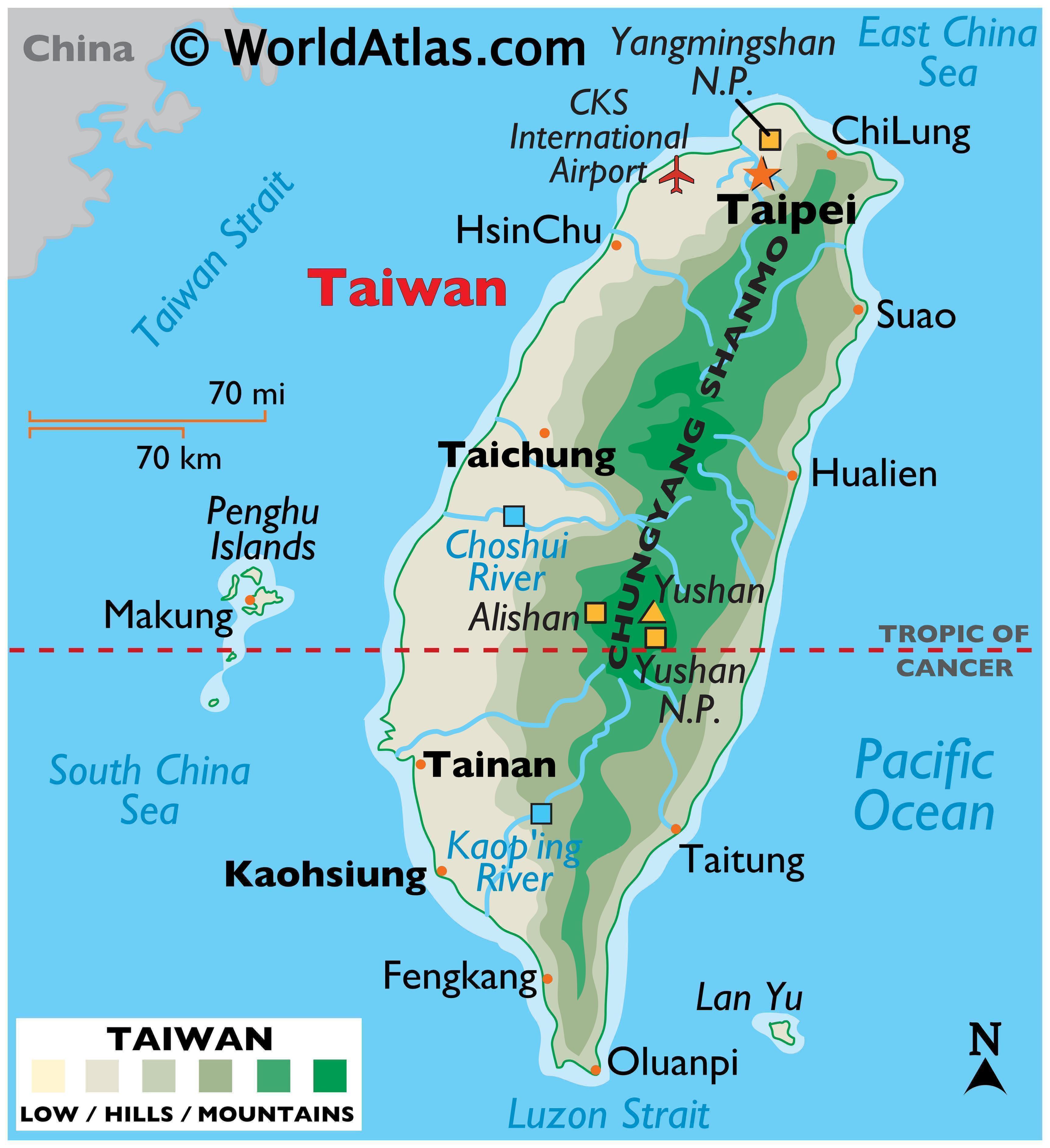
Taiwan, formally the Republic of China, is an island located off the southeastern coast of mainland China. It is often referred to as "Formosa," a Portuguese word meaning "beautiful," reflecting its diverse and captivating natural beauty.
- Mountainous Terrain: Taiwan is dominated by a central mountain range, the Central Mountain Range, which runs the length of the island and boasts several peaks exceeding 3,000 meters. This mountainous terrain has significantly impacted Taiwan’s development, influencing its transportation infrastructure and agricultural practices.
- Coastal Plains and Plateaus: Despite the mountainous core, Taiwan features coastal plains and plateaus that provide fertile land for agriculture. The western plains are particularly important for rice cultivation, while the eastern coastal areas are renowned for their fishing industry.
- Diverse Ecosystems: Taiwan’s varied topography supports a wide range of ecosystems. From subtropical forests and grasslands to coastal wetlands and coral reefs, the island exhibits a remarkable biodiversity.
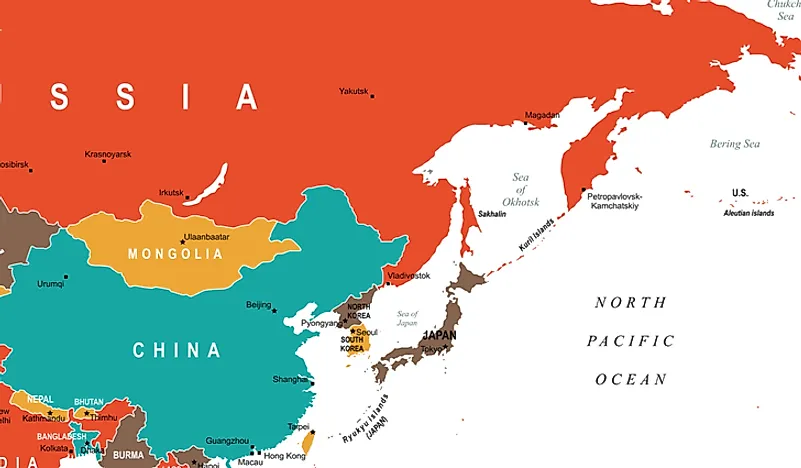
Japan: A Volcanic Archipelago with Varied Topography
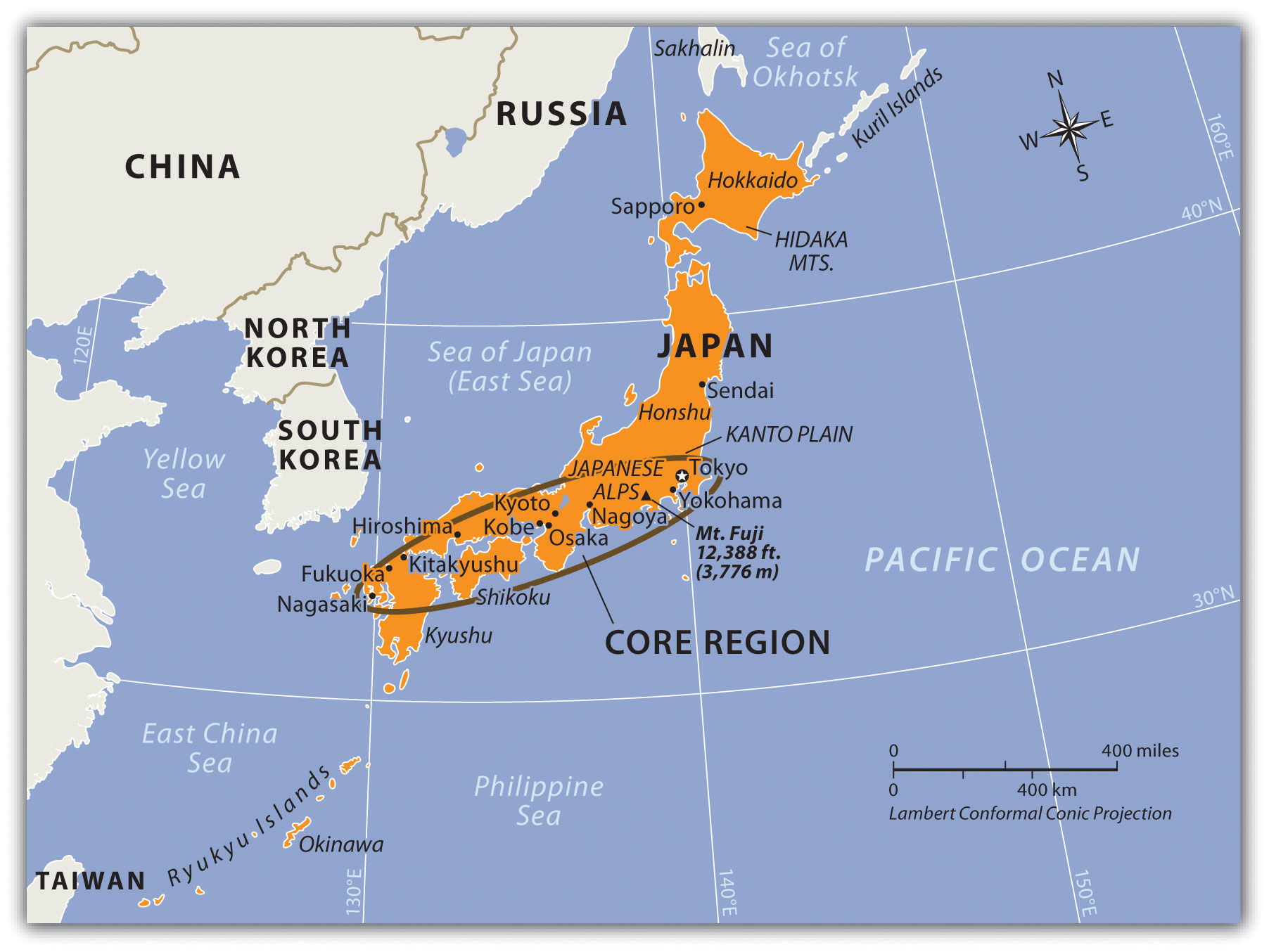
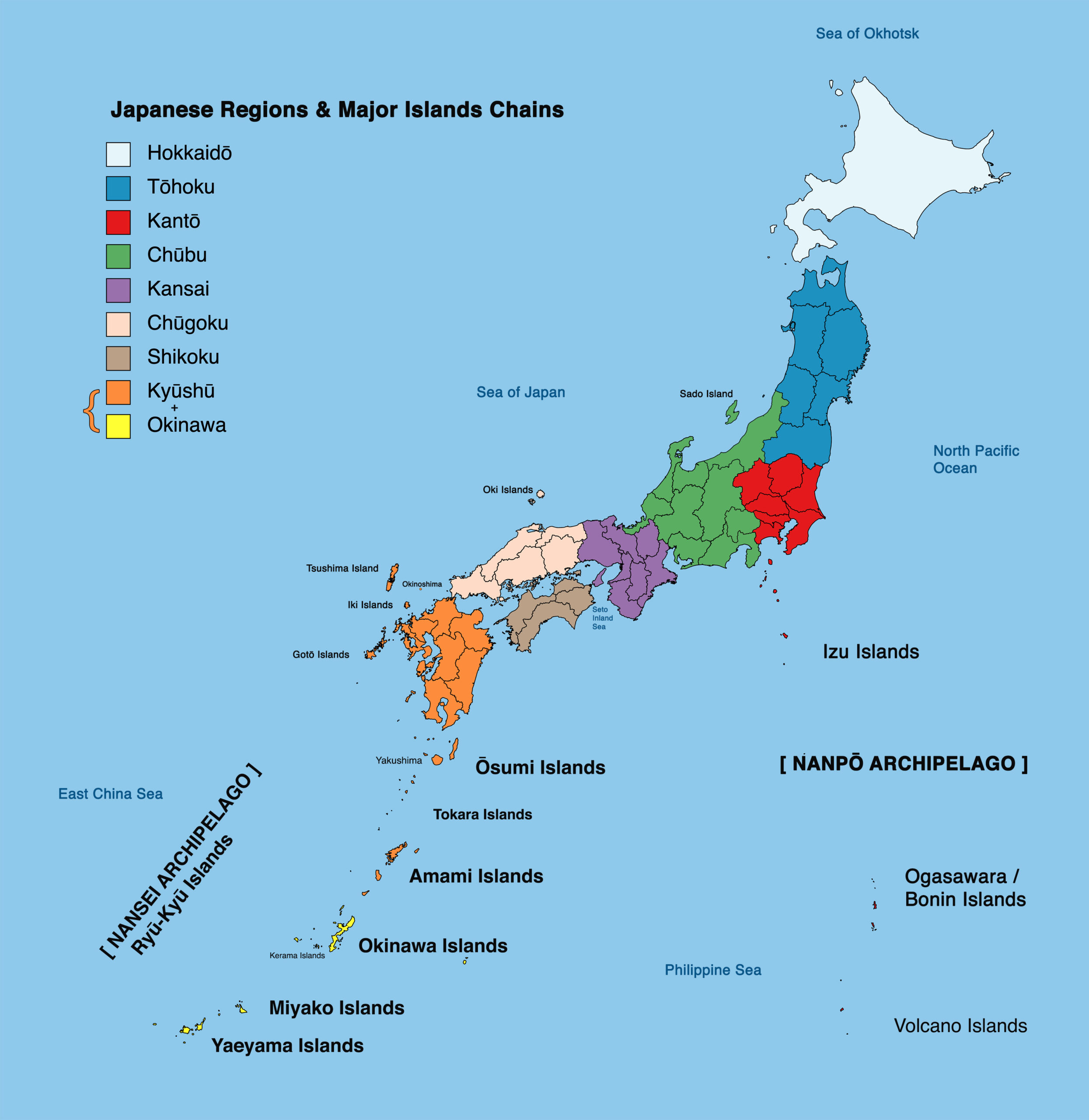
Japan, a nation of four main islands (Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu) and over 6,800 smaller islands, is an archipelago located in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. Its volcanic origins and tectonic activity have shaped its unique and dramatic landscape.
- Volcanic Activity: Japan is situated on the Pacific Ring of Fire, an area of intense seismic and volcanic activity. This geological characteristic has shaped the Japanese landscape, creating towering mountains, active volcanoes, and hot springs. The iconic Mount Fuji, Japan’s highest peak, is a prime example of this volcanic influence.
- Mountain Ranges: Japan is characterized by numerous mountain ranges, including the Japanese Alps, which dominate the central part of Honshu. These mountains have played a crucial role in Japan’s history and culture, shaping its settlements, transportation routes, and spiritual beliefs.
- Coastal Features: Japan boasts a long and intricate coastline, with numerous bays, inlets, and peninsulas. This coastline has been vital for Japan’s development, providing access to resources and fostering a strong maritime culture.
Shared Features and Differences:
While Taiwan and Japan share some geographical similarities, such as their island nature and mountainous terrain, they also exhibit distinct characteristics.
- Size and Shape: Taiwan is a relatively small island, with a total land area of approximately 36,000 square kilometers. Japan, in contrast, is a much larger archipelago, covering over 377,000 square kilometers.
- Climate: Both Taiwan and Japan experience a subtropical climate, with warm, humid summers and mild winters. However, Taiwan’s climate is generally more tropical, while Japan’s climate is more temperate.
- Natural Resources: Taiwan is relatively resource-poor, relying heavily on imports for energy and raw materials. Japan, on the other hand, possesses more diverse natural resources, including forests, fisheries, and mineral deposits.
The Importance of Geography in Shaping Societies:
The geographical features of Taiwan and Japan have played a profound role in shaping their societies, economies, and cultures.
- Impact on Infrastructure and Development: The mountainous terrain of both islands has posed challenges for transportation and infrastructure development. However, it has also fostered unique agricultural practices and cultural traditions.
- Influence on Settlement Patterns: The distribution of fertile land and coastal areas has influenced settlement patterns in both Taiwan and Japan. Coastal cities and agricultural communities have flourished, while mountainous areas have remained less populated.
- Cultural and Spiritual Influences: The natural landscapes of Taiwan and Japan have deeply influenced their cultures and spiritual beliefs. Mountains have been revered as sacred sites, while the sea has played a central role in their folklore and mythology.
FAQs on Taiwan and Japan’s Geography:
Q: What are the highest mountains in Taiwan and Japan?
A: The highest mountain in Taiwan is Yushan, also known as Mount Jade, with an elevation of 3,952 meters. The highest mountain in Japan is Mount Fuji, with an elevation of 3,776 meters.
Q: What are the major rivers in Taiwan and Japan?
A: The major rivers in Taiwan include the Tamsui River, the Danshui River, and the Zhuoshui River. The major rivers in Japan include the Tone River, the Shinano River, and the Ishikari River.
Q: What are the major cities in Taiwan and Japan?
A: The major cities in Taiwan include Taipei, Taichung, and Tainan. The major cities in Japan include Tokyo, Osaka, and Nagoya.
Q: What are the major natural disasters that affect Taiwan and Japan?
A: Taiwan is prone to earthquakes, typhoons, and landslides. Japan is also prone to earthquakes, tsunamis, and volcanic eruptions.
Tips for Understanding Taiwan and Japan’s Geography:
- Use maps and satellite imagery: Visualizing the landscapes of Taiwan and Japan through maps and satellite imagery can provide a deeper understanding of their geographical features.
- Explore online resources: Websites and databases from government agencies, research institutions, and geographical societies offer detailed information about the geography of Taiwan and Japan.
- Travel to the islands: Experiencing the landscapes of Taiwan and Japan firsthand can provide invaluable insights into their geographical diversity and cultural significance.
Conclusion:
The geography of Taiwan and Japan, two island nations in East Asia, plays a critical role in shaping their societies, economies, and cultures. Their diverse landscapes, from towering mountains and volcanic peaks to fertile plains and coastal areas, have shaped their historical development, influenced their settlement patterns, and inspired their cultural expressions. Understanding the geography of these island nations is essential for appreciating their unique characteristics and the challenges and opportunities they face in the modern world.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Geography of Taiwan and Japan: Island Nations in East Asia. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
