The LT1 Engine’s Unsung Hero: Decoding the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
Related Articles: The LT1 Engine’s Unsung Hero: Decoding the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The LT1 Engine’s Unsung Hero: Decoding the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The LT1 Engine’s Unsung Hero: Decoding the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor

The LT1 engine, a cornerstone of General Motors’ performance lineage, boasts a robust and sophisticated design. Within this intricate system, a seemingly unassuming component plays a critical role in ensuring optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency: the Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor. This article delves into the workings of the MAP sensor within the LT1 engine, exploring its function, importance, and potential issues, ultimately revealing its vital contribution to the overall engine’s performance.
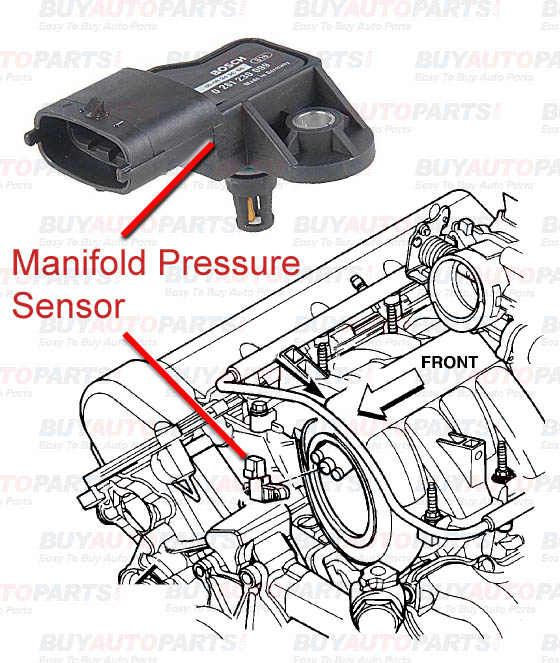
Understanding the MAP Sensor’s Role
The MAP sensor acts as a critical link between the engine’s intake manifold and the engine control unit (ECU). Its primary function is to measure the absolute pressure within the intake manifold, providing the ECU with a crucial piece of information for calculating the amount of air entering the engine. This data is then used to determine the appropriate fuel injection timing and duration, ultimately affecting engine power output, fuel consumption, and emissions.
The Inner Workings of the MAP Sensor
The MAP sensor, a simple yet sophisticated device, utilizes a diaphragm that is sensitive to pressure changes. When air enters the intake manifold, it pushes against the diaphragm, causing it to flex. This flexing movement is measured by a variable resistor, which transforms the physical displacement into an electrical signal. The ECU interprets this signal, converting it into a reading of absolute pressure within the intake manifold.
Why the MAP Sensor is Crucial
The MAP sensor’s importance lies in its ability to provide the ECU with real-time information about the engine’s operating conditions. This information is essential for:
- Optimizing Fuel Injection: The ECU uses the MAP sensor reading to determine the precise amount of fuel needed for each combustion cycle. This ensures optimal fuel efficiency and reduces emissions.
- Fine-Tuning Ignition Timing: The MAP sensor reading allows the ECU to adjust ignition timing, maximizing combustion efficiency and power output.
- Boost Pressure Control (Turbocharged Engines): In turbocharged LT1 engines, the MAP sensor plays a crucial role in monitoring and controlling boost pressure, ensuring optimal performance and preventing damage to the engine.
- Diagnostic Functions: The MAP sensor’s data is also used by the ECU for diagnostic purposes, allowing it to detect potential issues within the engine’s intake system.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Like any mechanical component, the MAP sensor can be prone to failure. Common issues include:
- Contamination: Dust, dirt, or oil buildup can affect the sensor’s diaphragm, causing inaccurate pressure readings.
- Electrical Malfunctions: Worn or damaged wiring can interrupt the signal transmission between the sensor and the ECU.
- Sensor Failure: The sensor itself can fail, resulting in inaccurate pressure readings and impacting engine performance.
Troubleshooting a Faulty MAP Sensor
Identifying a faulty MAP sensor can be achieved through a combination of diagnostic tools and observation:
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): The ECU will often register error codes related to a faulty MAP sensor. These codes can be retrieved using an OBD-II scanner.
-
Engine Performance Symptoms: A faulty MAP sensor can manifest in various symptoms, including:
- Rough Idle: The engine may struggle to maintain a smooth idle.
- Reduced Power: The engine may lack power, especially during acceleration.
- Stalling: The engine may stall unexpectedly.
- Increased Fuel Consumption: The engine may consume more fuel than usual.
- Vacuum Leak Check: A vacuum leak in the intake manifold can mimic a faulty MAP sensor reading. Inspecting the intake manifold for leaks is crucial.
- Visual Inspection: Inspect the MAP sensor for signs of damage, contamination, or corrosion.
FAQs about the MAP Sensor
Q: Can I clean a dirty MAP sensor?
A: Cleaning a contaminated MAP sensor may be possible using a specialized sensor cleaner. However, it’s crucial to use the correct cleaning solution and avoid damaging the sensor’s delicate components. In some cases, replacement may be the best option.
Q: How do I test a MAP sensor?
A: Testing a MAP sensor requires a specialized tool that applies a vacuum to the sensor and measures the resulting voltage output. This test can be performed by a qualified mechanic or using a DIY kit.
Q: What are the symptoms of a faulty MAP sensor?
A: Symptoms of a faulty MAP sensor include rough idle, reduced power, stalling, and increased fuel consumption.
Q: How often should I replace my MAP sensor?
A: The lifespan of a MAP sensor varies depending on driving conditions and maintenance practices. However, regular inspections and maintenance can help extend its lifespan.
Tips for Maintaining a Healthy MAP Sensor
- Regular Maintenance: Ensure regular inspections and cleaning of the MAP sensor as part of routine engine maintenance.
- Proper Air Filter Maintenance: A clogged air filter can restrict airflow to the intake manifold, potentially affecting the MAP sensor’s readings.
- Avoid Excessive Engine Modifications: Significant engine modifications can alter the airflow dynamics, potentially leading to sensor issues.
Conclusion
The MAP sensor, while seemingly inconspicuous, plays a vital role in the LT1 engine’s performance, fuel efficiency, and overall health. Understanding its function, potential issues, and troubleshooting techniques is crucial for maintaining a smooth-running and reliable engine. By addressing any potential issues promptly and adhering to regular maintenance practices, owners can ensure that their LT1 engine continues to perform at its peak, maximizing power, fuel efficiency, and longevity.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The LT1 Engine’s Unsung Hero: Decoding the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
