The MAP Sensor: A Vital Component in Modern Engines
Related Articles: The MAP Sensor: A Vital Component in Modern Engines
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The MAP Sensor: A Vital Component in Modern Engines. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The MAP Sensor: A Vital Component in Modern Engines

The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor, a crucial component in modern internal combustion engines, plays a pivotal role in determining the engine’s air intake and, subsequently, fuel delivery. By accurately measuring the pressure within the engine’s intake manifold, the MAP sensor provides the engine control unit (ECU) with critical data for optimizing engine performance and fuel efficiency.
Understanding the MAP Sensor’s Function
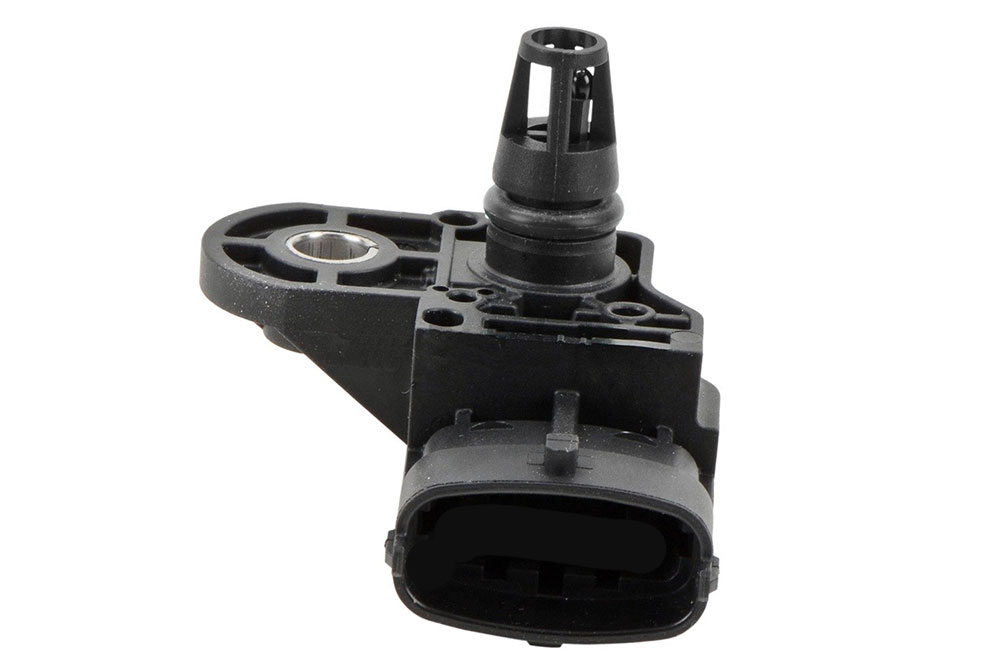
The MAP sensor, a small, robust device, is essentially a pressure transducer. It converts the pressure within the intake manifold into an electrical signal that the ECU can interpret. This signal, representing the absolute pressure in the intake manifold, is used to calculate the engine load, a crucial parameter for determining the optimal air-fuel ratio.
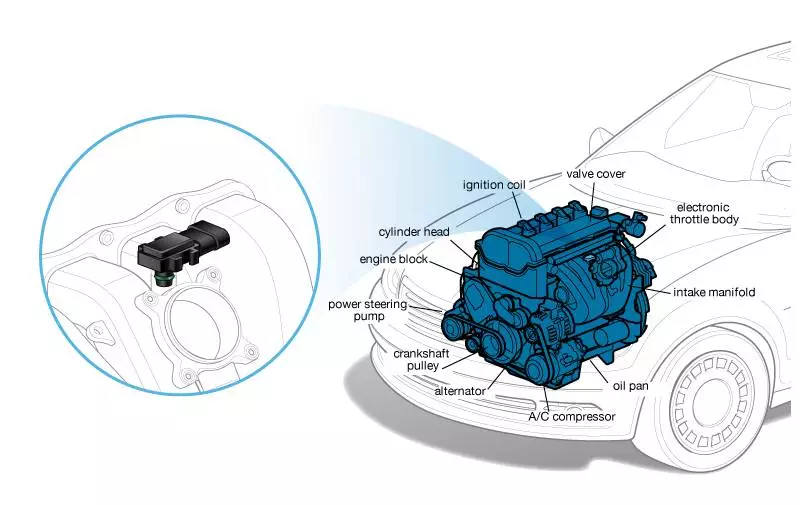
Location of the MAP Sensor
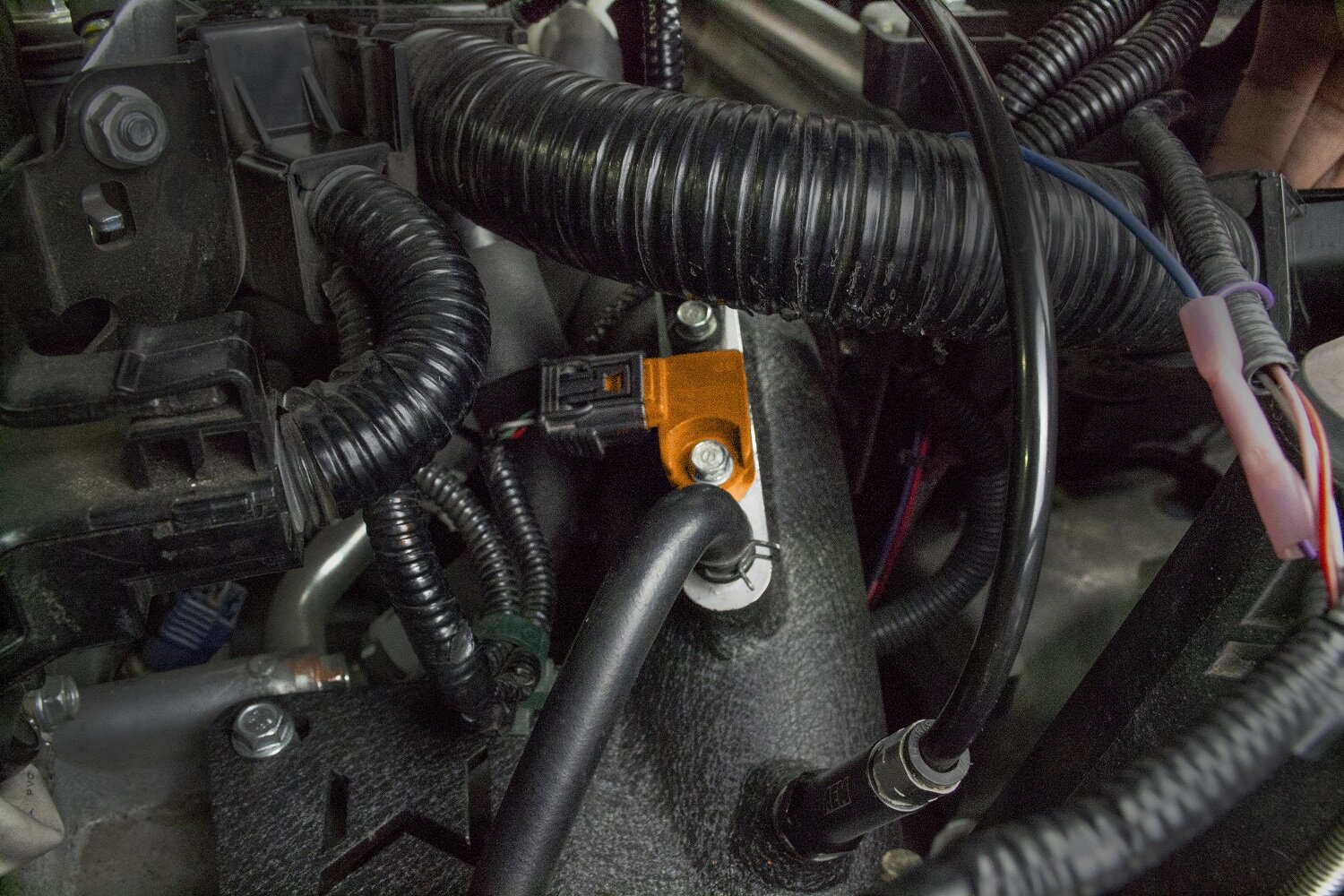
The location of the MAP sensor varies depending on the vehicle’s make, model, and engine configuration. However, it is generally found in one of the following locations:
- Intake Manifold: The MAP sensor is often directly mounted on the intake manifold itself, usually in a readily accessible location. This placement allows for accurate pressure measurement directly within the manifold.
- Vacuum Line: In some vehicles, the MAP sensor is attached to a vacuum line connected to the intake manifold. This setup allows for a more flexible installation and routing of the sensor.
- Air Intake System: In certain cases, the MAP sensor may be located within the air intake system, typically near the throttle body. This placement facilitates the measurement of pressure before it enters the intake manifold.
Identifying the MAP Sensor
Identifying the MAP sensor can be straightforward. It is usually a small, cylindrical device with a single electrical connector and a vacuum port or a threaded fitting. The sensor may be labeled with "MAP," "Manifold Absolute Pressure," or "Barometric Pressure" markings.
Importance of the MAP Sensor
The MAP sensor plays a crucial role in optimizing engine performance and fuel economy. Its accurate pressure readings allow the ECU to:
- Determine Engine Load: The MAP sensor provides the ECU with information about the engine’s load, enabling it to adjust fuel delivery accordingly.
- Control Air-Fuel Ratio: Based on the engine load and other sensor inputs, the ECU adjusts the air-fuel ratio to maintain optimal combustion.
- Regulate Ignition Timing: The MAP sensor data contributes to the ECU’s calculation of the ideal ignition timing for efficient combustion.
- Enhance Fuel Efficiency: By optimizing the air-fuel ratio and ignition timing, the MAP sensor contributes to improved fuel efficiency.
- Reduce Emissions: Accurate fuel delivery and combustion timing minimize harmful emissions.
Consequences of a Faulty MAP Sensor
A malfunctioning MAP sensor can lead to a range of engine problems, including:
- Poor Engine Performance: A faulty MAP sensor can result in inconsistent fuel delivery, leading to rough idling, hesitation, and reduced power.
- Increased Fuel Consumption: Erratic fuel delivery due to a faulty MAP sensor can lead to increased fuel consumption.
- Engine Misfires: Incorrect air-fuel ratios can cause engine misfires, leading to rough running and potential damage.
- Check Engine Light: A faulty MAP sensor will likely trigger the check engine light, indicating a problem with the engine’s control system.
Diagnosing a Faulty MAP Sensor
Diagnosing a faulty MAP sensor often involves a combination of diagnostic procedures:
- Visual Inspection: Inspect the MAP sensor for signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Check Engine Light: A check engine light may indicate a problem with the MAP sensor.
- Diagnostic Scan Tool: Using a scan tool, check for any diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to the MAP sensor.
- Pressure Testing: Perform a pressure test on the MAP sensor to verify its accuracy.
- Voltage Testing: Measure the voltage output of the MAP sensor to ensure it is within the specified range.
Replacing a Faulty MAP Sensor
Replacing a faulty MAP sensor is a relatively straightforward procedure, often requiring basic tools.
- Locate the MAP Sensor: Identify the MAP sensor’s location as described earlier.
- Disconnect the Electrical Connector: Disconnect the electrical connector from the MAP sensor.
- Remove the Sensor: Depending on the sensor’s mounting method, either unscrew it from the manifold or disconnect it from the vacuum line.
- Install the New Sensor: Install the new MAP sensor in the same location as the old one, ensuring it is securely fastened.
- Reconnect the Electrical Connector: Reconnect the electrical connector to the new MAP sensor.
- Clear Diagnostic Codes: Use a scan tool to clear any stored diagnostic codes.
FAQs
Q: How often should I replace my MAP sensor?
A: The lifespan of a MAP sensor can vary depending on factors such as environmental conditions and driving habits. However, most MAP sensors are designed to last for the life of the vehicle.
Q: Can I clean my MAP sensor?
A: While cleaning a MAP sensor may seem like a viable option, it is generally not recommended. Attempting to clean the sensor can potentially damage its delicate internal components.
Q: What are the symptoms of a faulty MAP sensor?
A: Common symptoms of a faulty MAP sensor include rough idling, hesitation, reduced power, increased fuel consumption, engine misfires, and the check engine light illuminating.
Q: Can I drive my car with a faulty MAP sensor?
A: While it may be possible to drive a car with a faulty MAP sensor for a short period, it is not recommended. A faulty MAP sensor can lead to poor engine performance, increased fuel consumption, and potential damage to the engine.
Tips
- Regular Maintenance: Routine maintenance, including inspecting and cleaning the intake system, can help prevent premature failure of the MAP sensor.
- Avoid Harsh Environments: Exposure to extreme temperatures, dust, and moisture can shorten the lifespan of the MAP sensor.
- Use Quality Parts: When replacing a faulty MAP sensor, always use genuine or high-quality aftermarket parts to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
Conclusion
The MAP sensor, a crucial component in modern engines, plays a vital role in optimizing engine performance and fuel efficiency. By accurately measuring the pressure within the intake manifold, the MAP sensor provides the ECU with critical data for adjusting fuel delivery, controlling air-fuel ratios, and regulating ignition timing. Understanding the MAP sensor’s function, location, and importance is crucial for maintaining optimal engine performance and avoiding potential problems. Regular maintenance, careful inspection, and timely replacement are essential for ensuring the reliable operation of this vital component.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The MAP Sensor: A Vital Component in Modern Engines. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
