The Power of Joining Maps: A Comprehensive Exploration of Map Test Joins
Related Articles: The Power of Joining Maps: A Comprehensive Exploration of Map Test Joins
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Power of Joining Maps: A Comprehensive Exploration of Map Test Joins. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Power of Joining Maps: A Comprehensive Exploration of Map Test Joins
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Power of Joining Maps: A Comprehensive Exploration of Map Test Joins
- 3.1 Understanding the Essence of Map Test Joins
- 3.2 Delving Deeper: Types of Map Test Joins
- 3.3 Unlocking the Potential: Benefits of Map Test Joins
- 3.4 Practical Applications: Real-World Examples
- 3.5 FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
- 3.6 Tips for Effective Map Test Join Implementation
- 3.7 Conclusion: The Significance of Map Test Joins
- 4 Closure
The Power of Joining Maps: A Comprehensive Exploration of Map Test Joins

In the realm of data analysis, the ability to combine information from multiple sources is paramount. This is where the concept of a "map test join" comes into play. This powerful technique, often employed in spatial analysis and database management, enables users to merge data sets based on their spatial relationships, effectively weaving together geographically referenced information to generate insightful conclusions.
Understanding the Essence of Map Test Joins
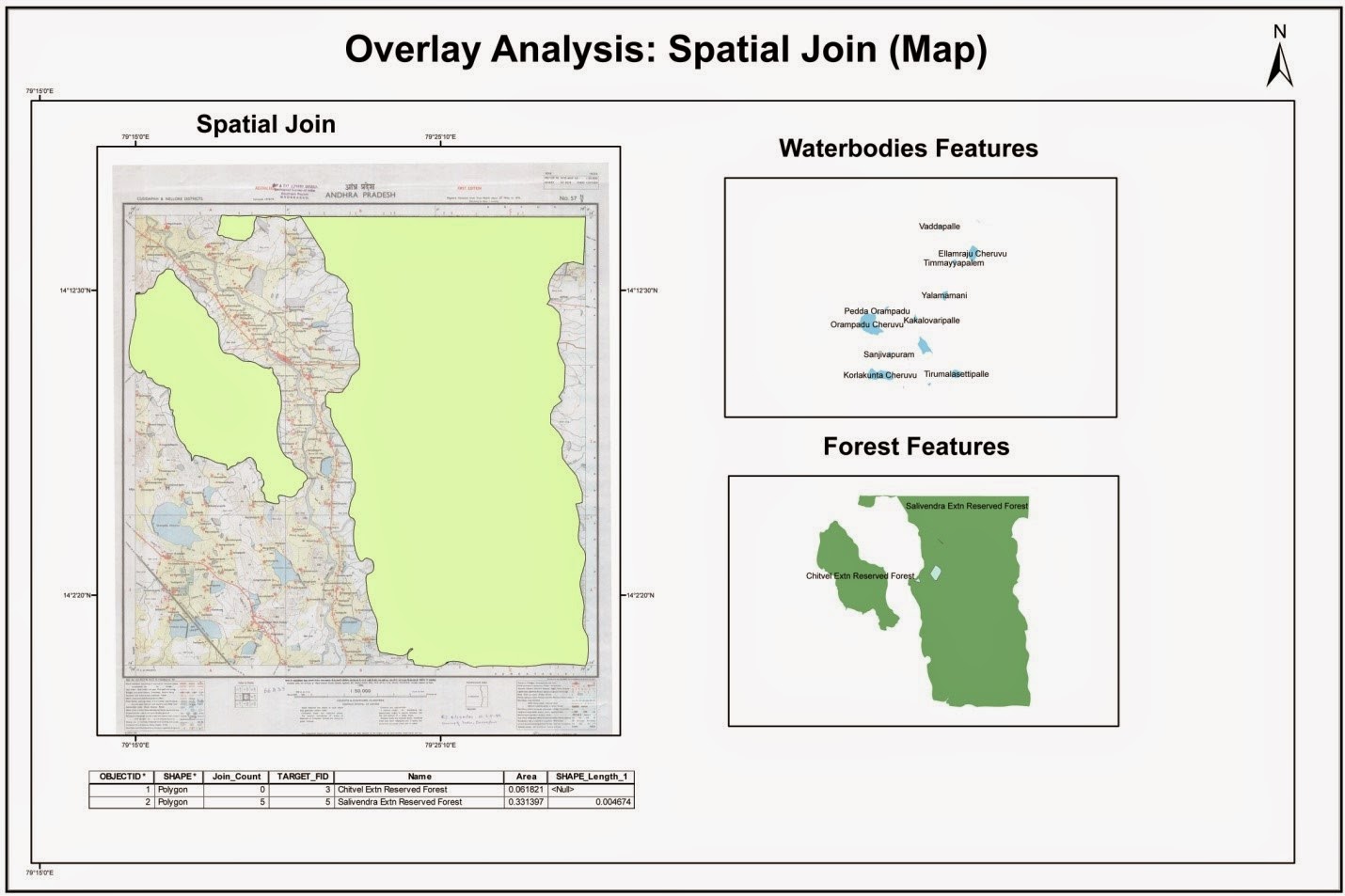
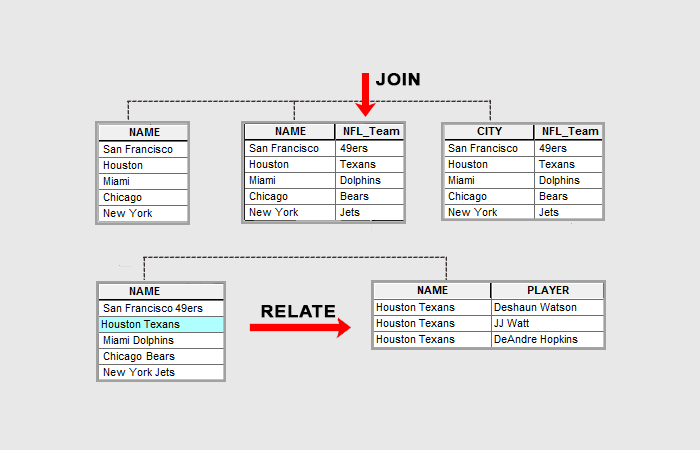
At its core, a map test join utilizes spatial relationships as the primary criterion for merging data. Unlike traditional joins, which rely on matching values in specific columns, map test joins leverage the spatial proximity or overlap between geographic features. This allows analysts to combine datasets that might not share common identifiers but are intrinsically linked by their location.
For instance, imagine a scenario where one dataset contains information about air quality readings across a city, while another dataset holds details about the locations of schools. Using a map test join, analysts could seamlessly merge these datasets based on the proximity of air quality monitoring stations to schools. This would enable them to analyze the potential impact of air pollution on school environments, revealing valuable insights that wouldn’t be accessible through traditional join methods.
Delving Deeper: Types of Map Test Joins
The execution of a map test join can vary depending on the specific spatial relationship being explored. Common types of map test joins include:
- Spatial Containment: This join identifies features that are entirely contained within another feature. For example, finding all houses located within a specific neighborhood boundary.
- Spatial Intersection: This join identifies features that share a common area. For example, identifying all roads that intersect with a particular park.
- Spatial Proximity: This join identifies features that are within a specified distance from each other. For example, identifying all restaurants within a 5-kilometer radius of a shopping mall.
Unlocking the Potential: Benefits of Map Test Joins
The application of map test joins brings numerous benefits to data analysis, empowering users to:
- Gain Comprehensive Insights: By combining geographically related datasets, map test joins provide a holistic view of the data, allowing analysts to understand complex spatial patterns and relationships.
- Enhance Decision-Making: The insights derived from map test joins can inform strategic decision-making in various fields, from urban planning and environmental management to public health and resource allocation.
- Improve Efficiency: Map test joins streamline the data analysis process by eliminating the need for manual spatial matching, saving time and effort while ensuring accuracy.
- Facilitate Data Visualization: The merged datasets resulting from map test joins can be effectively visualized using geographic information system (GIS) software, providing a clear and intuitive representation of spatial patterns and trends.
Practical Applications: Real-World Examples
The power of map test joins extends across diverse domains, impacting our daily lives in numerous ways:
- Urban Planning: Map test joins can be used to analyze the impact of new development projects on existing infrastructure, optimize public transportation routes, and identify areas requiring improved access to essential services.
- Environmental Management: Map test joins can aid in identifying pollution hotspots, monitoring deforestation patterns, and predicting the impact of climate change on various ecosystems.
- Public Health: Map test joins can be used to analyze the spread of diseases, identify areas with high risk factors, and develop targeted interventions to improve public health outcomes.
- Resource Management: Map test joins can be used to optimize the allocation of resources, such as water, energy, and agricultural land, ensuring efficient and sustainable utilization.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
Q: What are the key differences between traditional joins and map test joins?
A: Traditional joins operate on matching values in specific columns, while map test joins utilize spatial relationships between geographic features as the primary criterion for merging data.
Q: What are the prerequisites for performing a map test join?
A: Both datasets must have geographic attributes, such as coordinates or spatial geometries, that can be used to determine their spatial relationships.
Q: What software tools are available for performing map test joins?
A: Various GIS software packages, such as ArcGIS, QGIS, and PostGIS, offer robust tools for performing map test joins.
Q: How can I ensure the accuracy of map test joins?
A: It is essential to ensure that the spatial data used in the join is accurate and up-to-date. Verification and validation of the data can help mitigate potential errors.
Q: What are the limitations of map test joins?
A: Map test joins are primarily suited for data with spatial attributes. They may not be suitable for datasets lacking geographic information.
Tips for Effective Map Test Join Implementation
- Data Quality: Prioritize accurate and well-defined spatial data for optimal join results.
- Spatial Relationships: Clearly define the spatial relationship to be used for the join, ensuring it aligns with the analytical objective.
- Data Visualization: Utilize GIS software to visualize the merged datasets, facilitating a deeper understanding of spatial patterns.
- Performance Optimization: Employ techniques to optimize join performance, especially when dealing with large datasets.
Conclusion: The Significance of Map Test Joins
The map test join stands as a powerful tool in the arsenal of data analysis, offering a unique and effective approach to merging geographically referenced information. Its ability to integrate spatial relationships into the data analysis process unlocks profound insights, driving informed decision-making and fostering a deeper understanding of the world around us. By leveraging the power of map test joins, analysts can unlock the hidden potential within spatially related data, paving the way for groundbreaking discoveries and impactful solutions across diverse fields.
![]()





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Joining Maps: A Comprehensive Exploration of Map Test Joins. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
