The Role of Standardized Testing in Public Schools: A Comprehensive Overview
Related Articles: The Role of Standardized Testing in Public Schools: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Role of Standardized Testing in Public Schools: A Comprehensive Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Role of Standardized Testing in Public Schools: A Comprehensive Overview
Standardized testing has become an integral part of the educational landscape in public schools, often sparking passionate debates about its impact on students, teachers, and the overall learning environment. While the practice is not without its critics, it serves a crucial role in providing valuable data for educators, policymakers, and researchers, enabling them to assess student progress, identify areas needing improvement, and inform educational decisions. This article will delve into the multifaceted world of standardized testing in public schools, exploring its purpose, methodologies, benefits, limitations, and the ongoing discourse surrounding its implementation.
Understanding the Purpose of Standardized Testing
Standardized tests are designed to measure student achievement against a common set of standards, providing a consistent framework for evaluating educational progress. These assessments typically cover core subjects like reading, writing, math, and science, and are administered to students at various grade levels. The primary objectives of standardized testing in public schools can be summarized as follows:
- Assessing Student Achievement: Standardized tests provide a snapshot of student learning, allowing educators to gauge how well students are mastering essential skills and knowledge. This data can inform instruction and guide individualized learning plans.
- Monitoring School and District Performance: By comparing student scores across different schools and districts, standardized tests offer insights into the effectiveness of educational programs and the overall quality of education within a region. This information is crucial for policymakers and administrators in making informed decisions about resource allocation and program development.
- Identifying Areas for Improvement: Standardized test results can highlight areas where students are struggling, allowing educators to focus on specific skill development and address learning gaps.
- Ensuring Accountability and Transparency: Standardized tests promote accountability by providing objective measures of student achievement, enabling parents, educators, and the public to assess the effectiveness of schools and the quality of education being provided.
Types of Standardized Tests and their Administration
Standardized tests can be broadly categorized into two types:
- Achievement Tests: These tests measure students’ mastery of specific subject matter and skills acquired through instruction. Examples include the Stanford Achievement Test (SAT), the Iowa Tests of Basic Skills (ITBS), and the Metropolitan Achievement Test (MAT).
- Aptitude Tests: These tests assess students’ general cognitive abilities and potential for future academic success. The Scholastic Aptitude Test (SAT) and the American College Testing (ACT) are prominent examples of aptitude tests used for college admissions.
The administration of standardized tests varies depending on the specific assessment and the grade level. Tests can be administered in a variety of formats, including paper-based tests, computer-based tests, and online tests. Some tests are administered individually, while others are administered in a group setting.
The Advantages of Standardized Testing
Standardized testing offers several potential advantages, contributing to a more effective and equitable educational system:
- Objective Measurement: Standardized tests provide an objective measure of student achievement, minimizing subjectivity and bias in assessment. This allows for a more consistent and reliable evaluation of student progress.
- Common Standards: Standardized tests establish common standards across schools and districts, ensuring that students are assessed against the same benchmarks. This promotes consistency and fairness in the evaluation process.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: Standardized test data provides valuable insights into student performance, enabling educators to tailor instruction to meet individual needs and identify areas requiring additional support. This data-driven approach helps to optimize the learning process.
- Accountability and Transparency: Standardized tests promote accountability by providing objective measures of student achievement, making schools and districts more transparent in their performance. This can incentivize continuous improvement and ensure that students are receiving a high-quality education.
- Monitoring Progress and Identifying Trends: Standardized tests can be used to track student progress over time and identify emerging trends in student performance. This data can inform educational policies and program development, ensuring that the education system remains responsive to evolving student needs.
The Limitations and Criticisms of Standardized Testing
While standardized testing offers valuable benefits, it is not without its limitations and critics. The following are some of the key concerns raised regarding standardized testing:
- Narrow Focus on Specific Skills: Standardized tests often focus on a limited range of skills and knowledge, neglecting other important aspects of learning such as creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving. This narrow focus can create an overly simplistic view of student achievement and may not adequately reflect the full range of student abilities.
- Teaching to the Test: The emphasis on standardized tests can lead to "teaching to the test," where educators focus on preparing students for specific test questions rather than developing a broader understanding of the subject matter. This practice can undermine the overall quality of education and limit students’ intellectual growth.
- Stress and Anxiety: Standardized tests can create significant stress and anxiety for students, particularly those who are test-anxious or struggling with certain subjects. This can negatively impact student performance and create an unhealthy learning environment.
- Cultural and Socioeconomic Bias: Standardized tests may inadvertently favor students from certain socioeconomic backgrounds or cultural groups, potentially leading to unfair assessments and perpetuating existing educational inequalities.
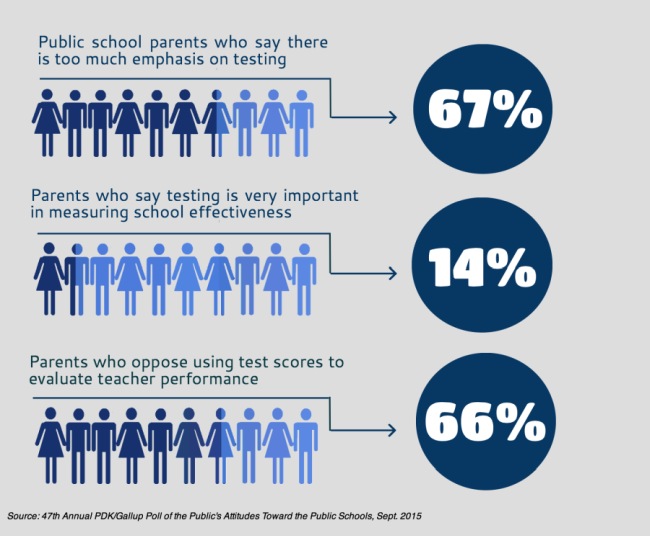
- Overemphasis on Testing: The excessive reliance on standardized testing can create a high-stakes environment, where students and teachers feel pressured to perform well on tests. This can lead to a narrow focus on test scores and a decline in the overall quality of education.
The Ongoing Debate: Balancing Benefits and Concerns
The debate surrounding standardized testing is complex and multifaceted, with valid arguments on both sides. While standardized tests offer valuable data for assessing student achievement and informing educational decisions, concerns about their potential limitations and negative consequences cannot be ignored.
Advocates for standardized testing emphasize the importance of objective measurement, accountability, and data-driven decision-making. They argue that standardized tests provide a common framework for evaluating student progress and ensuring that all students have access to a high-quality education. Critics, however, argue that standardized tests are too narrow in scope, create undue stress for students, and can perpetuate existing educational inequalities. They advocate for a more holistic approach to assessment that considers a broader range of student abilities and learning styles.
Moving Forward: Finding a Balanced Approach
To address the concerns surrounding standardized testing, educators, policymakers, and researchers are continually exploring ways to improve the design and implementation of these assessments. Some key strategies include:
- Expanding the Scope of Assessment: Moving beyond a narrow focus on specific skills and knowledge, assessments should incorporate a broader range of learning outcomes, including creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving.
- Reducing Test Anxiety: Educators can implement strategies to reduce test anxiety, such as providing students with adequate preparation and support, creating a positive testing environment, and fostering a growth mindset.
- Addressing Cultural and Socioeconomic Bias: Researchers are working to develop tests that are culturally and socioeconomically sensitive, ensuring that all students have an equal opportunity to succeed.
- Using Data Responsibly: Standardized test data should be used responsibly and ethically, focusing on identifying areas for improvement rather than simply ranking schools or students.
Conclusion
Standardized testing remains a complex and controversial topic in public education. While it offers valuable data for assessing student achievement and informing educational decisions, concerns about its potential limitations and negative consequences cannot be ignored. The key to achieving a balanced approach lies in ensuring that standardized tests are used responsibly and ethically, complementing rather than replacing other forms of assessment. By embracing a broader view of student success and prioritizing a holistic approach to education, we can strive to create a learning environment that fosters both academic achievement and the development of well-rounded individuals.
FAQs: Standardized Testing in Public Schools
1. What are the most common standardized tests used in public schools?
Some of the most widely used standardized tests in public schools include:
- Achievement Tests: Stanford Achievement Test (SAT), Iowa Tests of Basic Skills (ITBS), Metropolitan Achievement Test (MAT), TerraNova, and the National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP).
- Aptitude Tests: Scholastic Aptitude Test (SAT), American College Testing (ACT), and the Graduate Record Examinations (GRE).
2. How often are standardized tests administered in public schools?
The frequency of standardized testing varies depending on the specific tests and the grade levels. Generally, students in elementary, middle, and high school take standardized tests annually, with some states requiring additional assessments at specific grade levels.
3. Are standardized test scores the only factor considered in evaluating student performance?
No, standardized test scores are not the only factor considered in evaluating student performance. Educators also take into account other factors such as classroom participation, homework assignments, projects, and portfolios.
4. How are standardized test scores used to make decisions about students?
Standardized test scores can be used to inform a variety of decisions about students, including:
- Placement in classes or programs: Scores may be used to determine student placement in advanced or remedial classes.
- Individualized learning plans: Scores can help educators identify areas where students need additional support or enrichment.
- Graduation requirements: Some states use standardized test scores as part of their graduation requirements.
5. What can parents do to help their children prepare for standardized tests?
Parents can play an important role in helping their children prepare for standardized tests by:
- Encouraging regular reading and studying: Encourage children to read regularly and review their schoolwork.
- Providing a supportive and positive learning environment: Create a calm and supportive environment at home where children can focus on their studies.
- Familiarizing children with the test format: Provide children with practice tests and materials that mimic the actual test format.
- Talking to their children about the importance of the tests: Help children understand the purpose of the tests and why it is important to do their best.
Tips for Success in Standardized Testing
- Preparation is Key: Encourage students to study regularly and familiarize themselves with the test format.
- Practice Makes Perfect: Provide students with ample opportunities to practice test-taking strategies and time management skills.
- Foster a Positive Mindset: Help students approach the tests with confidence and a belief in their abilities.
- Address Test Anxiety: Provide support and strategies for managing test anxiety, such as relaxation techniques and deep breathing exercises.
- Focus on the Process, Not Just the Score: Emphasize the importance of learning and growth, rather than solely focusing on achieving a high score.
Conclusion
Standardized testing remains a complex and evolving aspect of public education. By understanding its purpose, benefits, and limitations, educators, policymakers, and parents can work together to ensure that these assessments are used responsibly and ethically, ultimately contributing to a more effective and equitable education system.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Role of Standardized Testing in Public Schools: A Comprehensive Overview. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
