The Significance of Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor Readings at Idle: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: The Significance of Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor Readings at Idle: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Significance of Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor Readings at Idle: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Significance of Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor Readings at Idle: A Comprehensive Guide

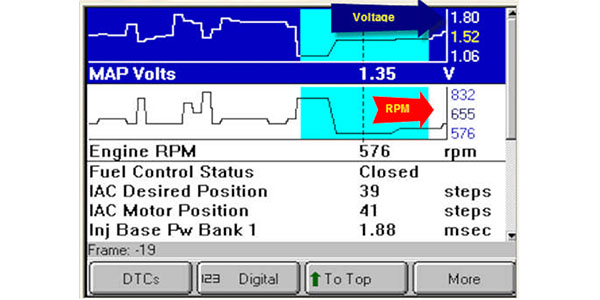
The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor plays a crucial role in modern internal combustion engines, providing the engine control unit (ECU) with vital information about the pressure within the intake manifold. This information is essential for optimizing fuel delivery, ignition timing, and other critical engine functions. Understanding the MAP sensor reading at idle, specifically its value in inches of mercury (inHg), is crucial for diagnosing engine performance issues and ensuring efficient operation.
Understanding the MAP Sensor and its Role in Engine Control
The MAP sensor is a small, electronically controlled device typically located in the intake manifold. It measures the absolute pressure inside the manifold, which is the pressure relative to a perfect vacuum. This pressure reading is directly proportional to the amount of air entering the engine cylinders.
The ECU utilizes the MAP sensor reading to:
- Calculate Air Mass: By correlating the MAP reading with engine speed and temperature, the ECU can determine the mass of air entering the engine. This information is essential for calculating the optimal amount of fuel to inject.
- Adjust Fuel-Air Ratio: The ECU uses the MAP reading to adjust the fuel-air ratio, ensuring a proper mixture for combustion. A lean mixture (too much air) can lead to engine knocking, while a rich mixture (too much fuel) can result in poor fuel economy and increased emissions.
- Control Ignition Timing: The MAP sensor reading also helps the ECU adjust ignition timing. The ECU can advance or retard ignition timing based on the pressure reading, optimizing combustion efficiency and performance.
- Monitor Engine Vacuum: The MAP sensor reading provides a measure of the vacuum created by the engine during operation. This information can be used to diagnose issues such as intake manifold leaks or faulty valves.
MAP Sensor Readings at Idle: A Key Indicator of Engine Health
At idle, the engine is operating at its lowest speed, and the intake manifold pressure is typically at its lowest point. The MAP sensor reading at idle provides valuable insights into the engine’s overall health and performance.
Typical Idle MAP Sensor Readings:
- Naturally Aspirated Engines: The typical MAP sensor reading at idle for naturally aspirated engines ranges from 18 to 22 inHg. This reading can vary slightly depending on factors such as engine size, temperature, and altitude.
- Turbocharged Engines: Turbocharged engines operate at higher boost pressures, resulting in significantly higher MAP sensor readings at idle, often exceeding 25 inHg.
Analyzing Deviations from Normal Readings:
Any significant deviation from the expected MAP sensor reading at idle can indicate a potential issue with the engine or its associated systems. Here are some common scenarios:
-
High MAP Reading: A high MAP reading at idle could indicate:
- Intake Manifold Leak: A leak in the intake manifold can allow unmetered air to enter the engine, increasing the pressure inside the manifold.
- Faulty Vacuum Line: A cracked or disconnected vacuum line can also lead to a higher MAP reading.
- Faulty MAP Sensor: A malfunctioning MAP sensor could provide inaccurate readings, leading to a high MAP reading at idle.
-
Low MAP Reading: A low MAP reading at idle could indicate:
- Restricted Airflow: An obstruction in the intake system, such as a clogged air filter or a partially closed throttle plate, can restrict airflow and reduce the pressure inside the manifold.
- Vacuum Leak: A vacuum leak can cause a drop in manifold pressure, resulting in a low MAP reading.
- Faulty MAP Sensor: A malfunctioning MAP sensor could provide inaccurate readings, leading to a low MAP reading at idle.
Troubleshooting MAP Sensor Issues at Idle:
Diagnosing MAP sensor issues at idle requires a systematic approach involving visual inspection, diagnostic tools, and careful analysis of the engine’s behavior.
1. Visual Inspection:
- Inspect the MAP Sensor: Examine the MAP sensor for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Check Vacuum Lines: Inspect all vacuum lines connected to the MAP sensor for cracks, leaks, or disconnections.
- Inspect Intake Manifold: Visually inspect the intake manifold for any signs of leaks or cracks.
2. Diagnostic Tools:
- OBD-II Scanner: Use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve any diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to the MAP sensor.
- Digital Multimeter: A digital multimeter can be used to test the MAP sensor’s electrical resistance and voltage output.
- Vacuum Gauge: A vacuum gauge can be used to measure the actual vacuum pressure in the intake manifold and compare it to the MAP sensor reading.
3. Engine Behavior Analysis:
- Engine Idle Quality: Observe the engine’s idle quality. A rough idle or stalling could indicate a problem with the MAP sensor or its associated systems.
- Engine Performance: Check for any noticeable changes in engine performance, such as reduced power or hesitation.
- Fuel Consumption: Monitor fuel consumption for any significant increases, which could be a sign of a rich fuel mixture caused by a faulty MAP sensor.
FAQs about MAP Sensor Readings at Idle:
Q: What is the normal MAP sensor reading at idle for a specific engine model?
A: The normal MAP sensor reading at idle can vary depending on the specific engine model. Refer to the vehicle’s repair manual or consult a trusted mechanic for the expected reading for your particular engine.
Q: How can I test the MAP sensor myself?
A: Testing the MAP sensor requires specialized tools and technical knowledge. It is recommended to consult a professional mechanic for accurate testing and diagnosis.
Q: What are the consequences of a faulty MAP sensor?
A: A faulty MAP sensor can lead to a variety of engine issues, including poor fuel economy, reduced power, rough idle, increased emissions, and even engine damage in severe cases.
Q: How often should the MAP sensor be replaced?
A: The MAP sensor typically has a long lifespan and rarely needs replacement unless it is damaged or malfunctions. However, regular maintenance and inspection can help identify potential issues early on.
Tips for Maintaining Optimal MAP Sensor Performance:
- Regularly Inspect Vacuum Lines: Inspect vacuum lines for cracks, leaks, or disconnections during routine maintenance.
- Replace Air Filter: Regularly replace the air filter to ensure optimal airflow and prevent restriction.
- Use Quality Fuel: Use high-quality fuel to minimize the risk of fuel system issues that can impact the MAP sensor’s performance.
Conclusion:
The MAP sensor plays a vital role in ensuring optimal engine performance and efficiency. Understanding the significance of its readings at idle, particularly in inches of mercury, is essential for identifying potential engine issues and maintaining proper operation. By carefully analyzing the MAP sensor reading at idle and performing regular maintenance, you can ensure your engine runs smoothly and efficiently for years to come. Remember, if you suspect a problem with your MAP sensor or any other engine system, it’s always best to consult a qualified mechanic for diagnosis and repair.
/MAP_analog.png)






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Significance of Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor Readings at Idle: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
