The Southwest United States: A Geographic and Cultural Tapestry Revealed through Mapping
Related Articles: The Southwest United States: A Geographic and Cultural Tapestry Revealed through Mapping
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Southwest United States: A Geographic and Cultural Tapestry Revealed through Mapping. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Southwest United States: A Geographic and Cultural Tapestry Revealed through Mapping
The Southwest United States, a region encompassing a diverse array of landscapes, cultures, and histories, presents a fascinating study in geography and human interaction. Its distinct characteristics, from arid deserts to towering mountains, from vibrant Native American traditions to bustling urban centers, are best understood through the lens of mapping.
Mapping the Southwest: Unveiling a Complex Landscape
The Southwest’s unique geography is characterized by dramatic contrasts. The towering peaks of the Rocky Mountains, the vast expanse of the Colorado Plateau, the scorching deserts of the Mojave and Sonoran, and the fertile valleys of the Rio Grande all contribute to the region’s diverse topography.
Physical Geography:
- The Colorado Plateau: This high-elevation plateau, covering much of northern Arizona, Utah, and parts of Colorado and New Mexico, is renowned for its dramatic canyons, mesas, and buttes. The Grand Canyon, a natural wonder carved by the Colorado River, stands as a testament to the region’s geological history.
- The Rocky Mountains: The Southern Rockies, traversing Colorado and New Mexico, are a defining feature of the Southwest, providing a dramatic backdrop to the region’s diverse ecosystems. Their high peaks and rugged terrain influence weather patterns and contribute to the region’s rich biodiversity.
- The Basin and Range Province: This region, stretching across Nevada, Utah, Arizona, and parts of California, is characterized by alternating mountain ranges and valleys. These valleys, often filled with dry lakebeds, contribute to the region’s arid climate.
- The Mojave and Sonoran Deserts: These vast desert regions, covering parts of Arizona, California, Nevada, and Mexico, are home to unique plant and animal life adapted to extreme heat and aridity.
Human Geography:
The Southwest is not only defined by its physical features but also by the diverse human communities that have shaped its history and culture.
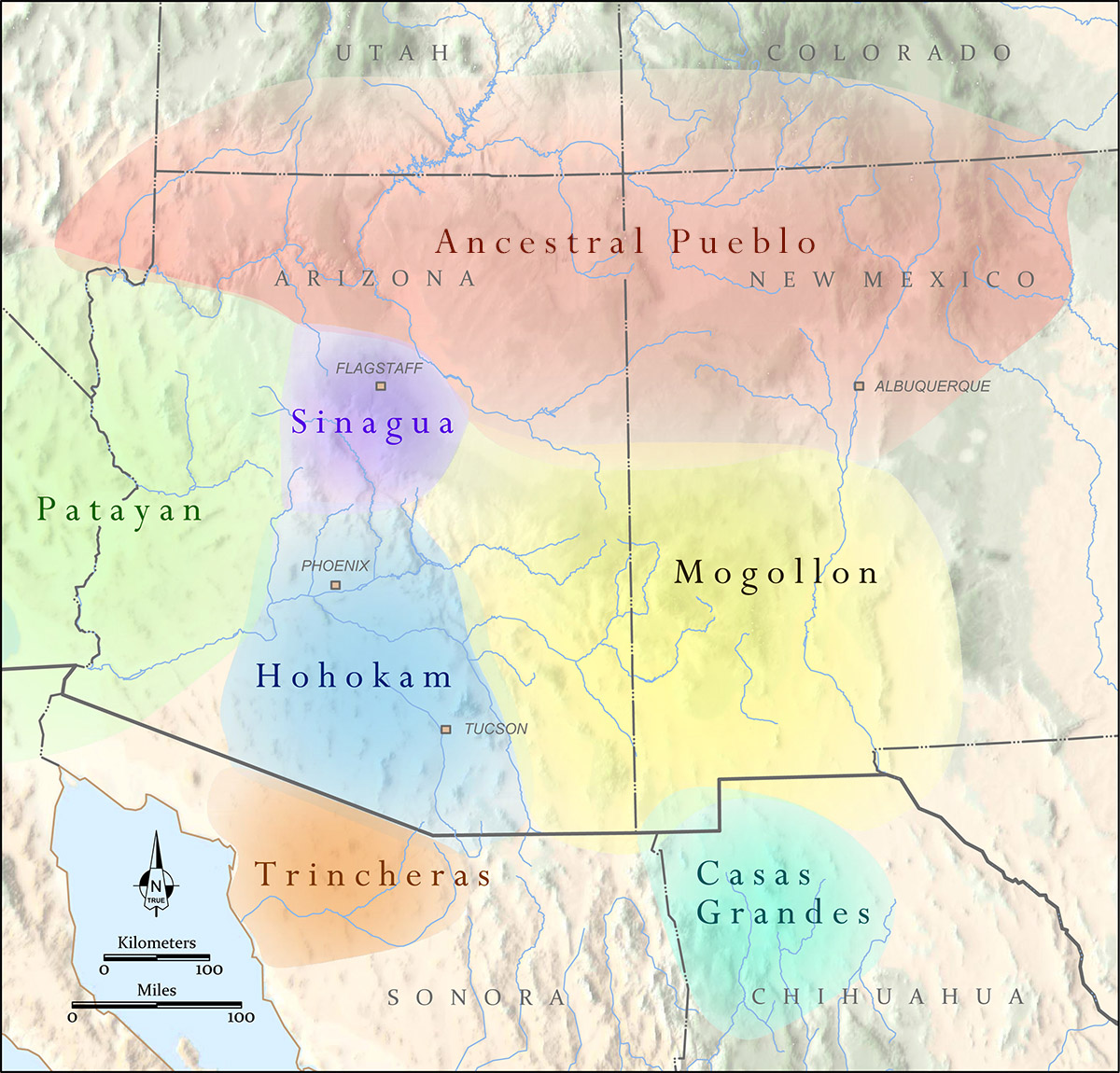
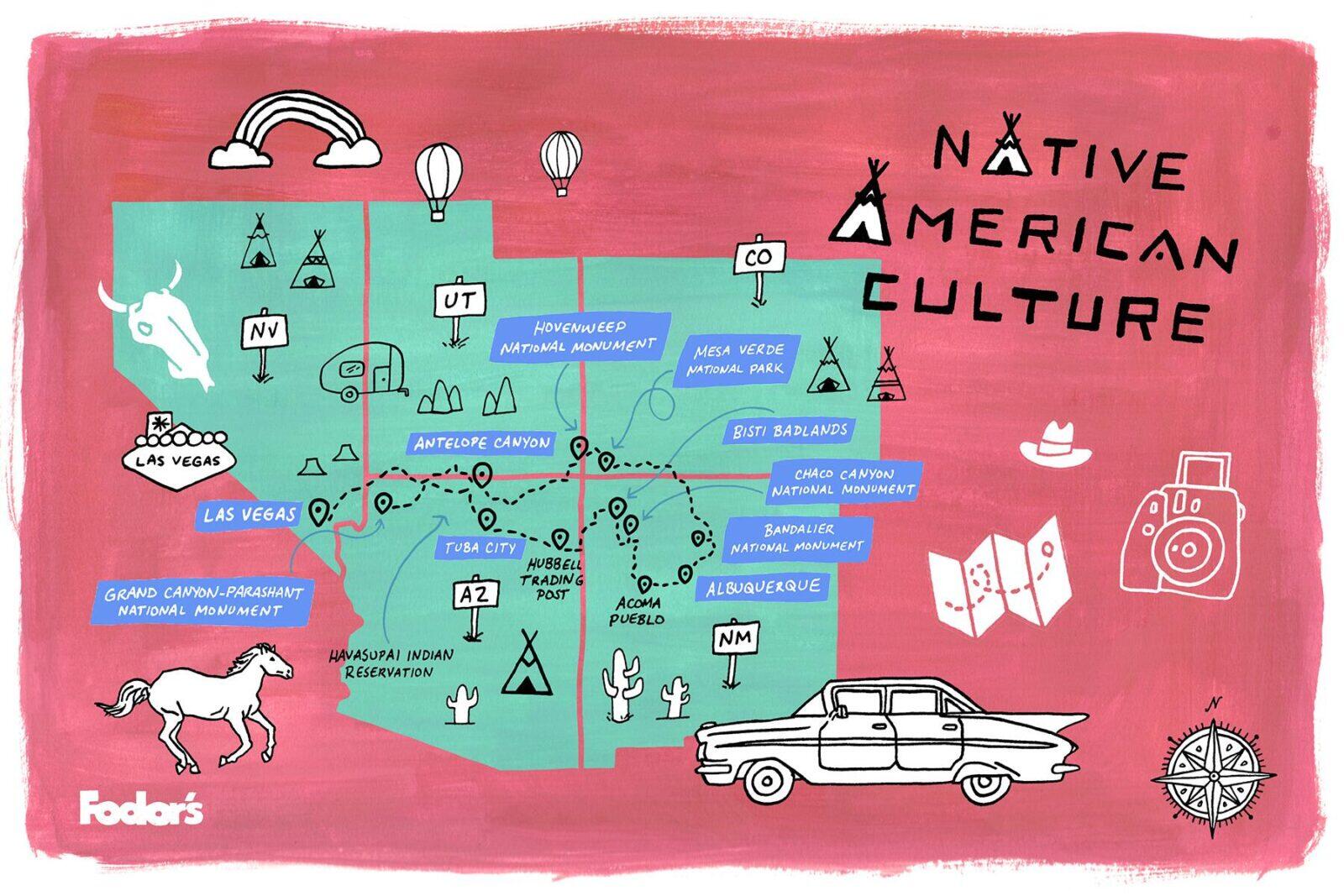
- Native American Heritage: The region has been home to indigenous peoples for millennia, with tribes like the Navajo, Hopi, Apache, and Pueblo maintaining rich cultural traditions and ancestral lands.
- Spanish Colonization: The arrival of Spanish conquistadors in the 16th century brought significant changes, including the introduction of cattle ranching, agriculture, and the Spanish language. Spanish influence is still evident in place names, architecture, and cultural traditions.
- American Expansion: The 19th century saw the arrival of American settlers, drawn by the promise of land and opportunity. This led to conflicts with indigenous populations and the development of new industries, including mining and agriculture.
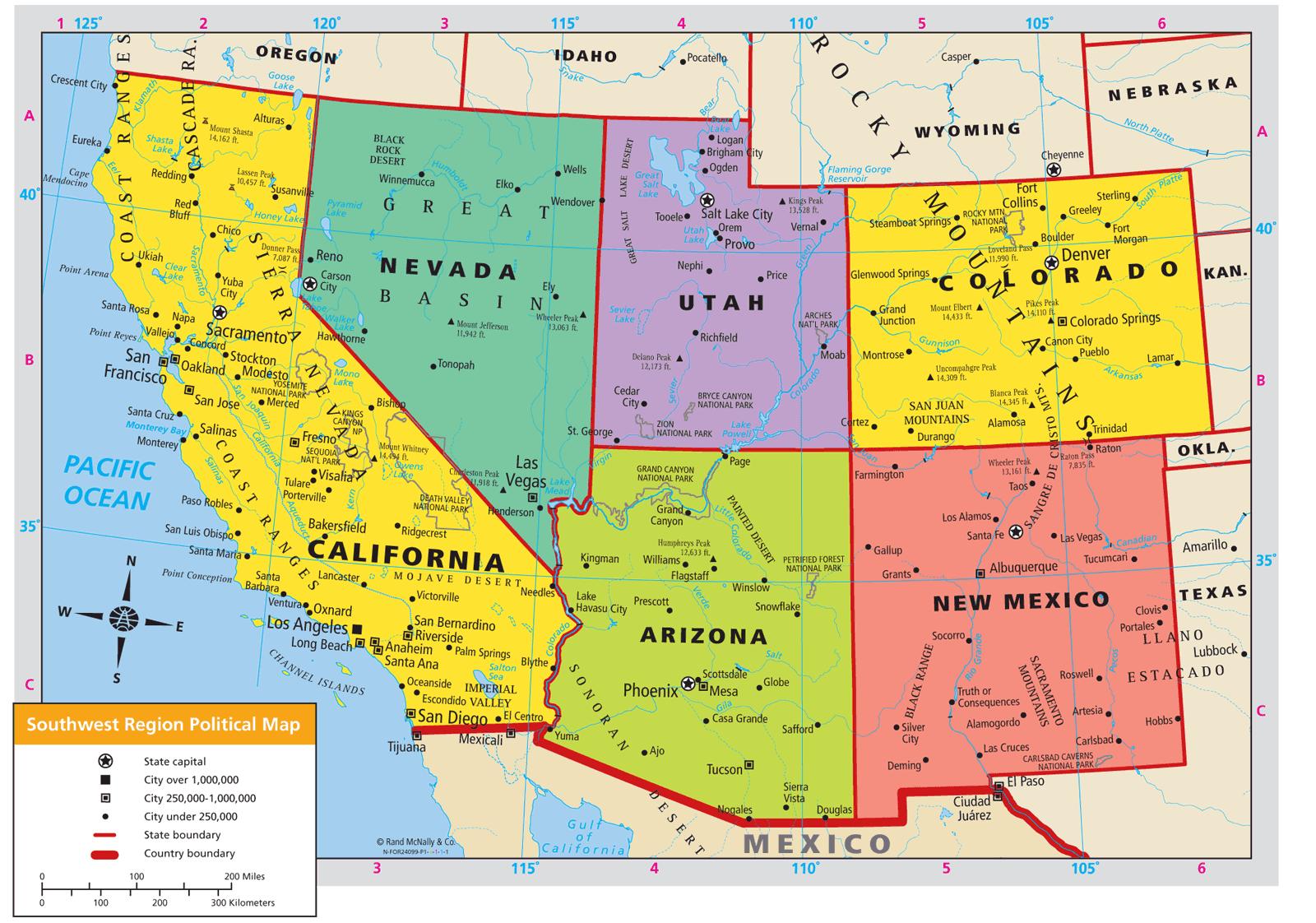
- Modern Southwest: The 20th and 21st centuries have seen rapid urbanization and population growth in the Southwest, with cities like Phoenix, Las Vegas, and Albuquerque becoming major centers of commerce and culture.
Mapping the Southwest: Tools for Understanding and Planning
Mapping plays a critical role in understanding the Southwest’s complex landscape and its human history. Various types of maps offer insights into different aspects of the region:
- Topographic Maps: These maps depict the elevation and landforms of the region, providing crucial information for hikers, climbers, and researchers.
- Geological Maps: These maps illustrate the rock formations, faults, and other geological features of the Southwest, helping us understand its past and predict future geological events.
- Climate Maps: These maps show the average temperature, precipitation, and other climate data, highlighting the region’s diverse climate zones and the challenges they pose.
- Vegetation Maps: These maps illustrate the distribution of different plant communities, providing insights into the Southwest’s unique biodiversity and the impacts of climate change.
- Cultural Maps: These maps depict the distribution of different cultural groups, languages, and traditions, highlighting the rich tapestry of the Southwest’s human history.
Beyond Static Maps: Using Technology to Explore the Southwest
Modern technology has revolutionized the way we map and interact with the Southwest. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and online mapping platforms allow us to visualize and analyze data in new ways:
- GIS Analysis: GIS software allows researchers to overlay various datasets, such as population density, climate data, and land use, to identify patterns and trends. This can help us understand the impact of urbanization, climate change, and other factors on the Southwest’s environment and communities.
- Interactive Mapping: Online platforms like Google Maps and OpenStreetMap provide interactive maps that allow users to explore the Southwest in detail, zooming in on specific locations, finding points of interest, and even contributing to the map itself.
- 3D Modeling: Advances in 3D modeling and visualization allow us to create realistic representations of the Southwest’s landscape, offering immersive experiences for education and tourism.
Understanding the Southwest: A Multifaceted Approach
Mapping the Southwest is not just about creating static representations; it is about understanding the complex interplay between the region’s physical geography, human history, and cultural diversity. By combining traditional cartography with modern technology, we can gain a deeper understanding of the Southwest and its challenges:
- Water Resources Management: Mapping water sources, groundwater levels, and water usage patterns is crucial for managing the Southwest’s limited water resources in a sustainable way.
- Climate Change Impacts: Mapping climate data and its effects on vegetation, wildlife, and human communities can help us anticipate and mitigate the impacts of climate change on the Southwest.
- Conservation and Preservation: Mapping biodiversity hotspots, endangered species habitats, and cultural sites is essential for protecting the Southwest’s natural and cultural heritage.
- Urban Planning: Mapping population density, transportation infrastructure, and environmental factors can inform urban planning decisions and promote sustainable development.
FAQs about Mapping the Southwest:
1. Why is mapping important for understanding the Southwest?
Mapping provides a visual representation of the Southwest’s complex geography, history, and culture, helping us understand its unique characteristics and the challenges it faces.
2. What are some of the different types of maps used to study the Southwest?
Topographic, geological, climate, vegetation, and cultural maps offer insights into different aspects of the region.
3. How does technology play a role in mapping the Southwest?
GIS analysis, interactive mapping platforms, and 3D modeling allow us to visualize and analyze data in new ways, providing a deeper understanding of the region.
4. What are some of the challenges facing the Southwest that mapping can help address?
Mapping can help address challenges related to water resources management, climate change impacts, conservation and preservation, and urban planning.
5. What are some resources for learning more about mapping the Southwest?
There are numerous online resources, including websites of government agencies, universities, and non-profit organizations, that provide maps, data, and information about the Southwest.
Tips for Mapping the Southwest:
- Use a variety of map resources: Explore different types of maps, including topographic, geological, climate, vegetation, and cultural maps, to gain a comprehensive understanding of the region.
- Consider the scale of your map: Choose a map scale appropriate for your research or exploration needs.
- Use online mapping tools: Utilize interactive mapping platforms and GIS software to analyze data and create custom maps.
- Collaborate with experts: Consult with geographers, historians, and other experts to enhance your understanding of the Southwest.
Conclusion:
Mapping the Southwest is a vital tool for understanding its complex landscape, diverse cultures, and the challenges it faces. By combining traditional cartography with modern technology, we can gain a deeper understanding of the region and develop effective solutions for managing its resources, mitigating climate change impacts, and preserving its rich heritage. Through mapping, we can reveal the Southwest’s unique character and contribute to its sustainable future.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Southwest United States: A Geographic and Cultural Tapestry Revealed through Mapping. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
