The Taiwanese Election Map: A Visual Representation of Political Power and Identity
Related Articles: The Taiwanese Election Map: A Visual Representation of Political Power and Identity
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Taiwanese Election Map: A Visual Representation of Political Power and Identity. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Taiwanese Election Map: A Visual Representation of Political Power and Identity

The Taiwanese election map, a vibrant tapestry of colors representing different political parties and their electoral successes, serves as a powerful tool for understanding the political landscape of the island nation. It goes beyond a simple visual representation, offering insights into the complex interplay of political ideologies, social demographics, and historical context that shape Taiwanese politics.
A Historical Perspective:
Understanding the Taiwanese election map necessitates a brief look into the island’s history. Taiwan’s political landscape has been shaped by decades of political turmoil, beginning with the Kuomintang (KMT) government’s retreat to the island after losing the Chinese Civil War in 1949. The KMT, representing mainland China, initially held absolute control over Taiwan, implementing a one-party system that suppressed local identities and dissent.
However, the seeds of democratic change were sown in the 1980s, culminating in the lifting of martial law in 1987 and the democratization of the political system. The first multi-party elections in 1996 marked a significant turning point, ushering in an era of competitive politics and a gradual shift in power from the KMT to the Democratic Progressive Party (DPP), which advocated for Taiwanese independence.
Mapping the Political Divide:
The Taiwanese election map reflects this historical evolution and the ongoing political divide between the two major parties:
- Kuomintang (KMT): The KMT, historically representing mainland China, has traditionally held strong support in rural areas and among older generations who experienced the post-war period. They generally favor maintaining the status quo with China, advocating for closer economic and cultural ties while maintaining Taiwan’s de facto independence.
- Democratic Progressive Party (DPP): The DPP, advocating for Taiwanese independence, has gained significant support in urban areas and among younger generations who identify more strongly with a Taiwanese identity. They generally favor a more assertive stance towards China, seeking greater international recognition for Taiwan.
The election map also reveals the presence of smaller political parties, including the Taiwan People’s Party (TPP) and the New Power Party (NPP), which often represent specific political ideologies or appeal to particular demographics.
Interpreting the Map:
The Taiwanese election map offers valuable insights into the political dynamics of the island:
- Regional Differences: The map often highlights distinct regional differences in political preferences. For example, traditionally, the KMT has held strong support in southern and eastern Taiwan, while the DPP has enjoyed greater support in northern and western Taiwan. This regional divide can be attributed to factors such as historical ties to the mainland, economic development, and cultural identities.
- Generational Divide: The map also reveals a generational divide, with younger generations generally leaning towards the DPP and its pro-independence stance, while older generations tend to favor the KMT and its stance on maintaining the status quo. This reflects the evolving understanding of Taiwan’s identity and its relationship with China among different age groups.
- Electoral Trends: The election map provides a snapshot of electoral trends, allowing analysts to identify areas where specific parties have gained or lost support over time. This can be valuable in understanding the factors influencing electoral outcomes and predicting future trends.
The Importance of the Election Map:
The Taiwanese election map serves as a vital tool for:
- Political Analysis: It provides a visual representation of political power and distribution, enabling analysts to understand the underlying dynamics of Taiwanese politics.
- Electoral Strategy: Political parties can use the map to identify key areas of support and target their campaigns accordingly.
- Public Engagement: The map can help citizens visualize the political landscape and understand the distribution of political power in their communities.
- International Relations: The map provides insights into the political climate in Taiwan, which is of significant interest to international observers given its complex relationship with China.
FAQs:
Q: How often is the Taiwanese election map updated?
A: The Taiwanese election map is typically updated after every major election, including presidential, legislative, and local elections.
Q: Are there any limitations to interpreting the Taiwanese election map?
A: While the election map provides valuable insights, it is important to note that it does not capture the full complexity of Taiwanese politics. Other factors, such as voter turnout, campaign strategies, and external events, can also influence election results.
Q: How does the Taiwanese election map compare to election maps in other democracies?
A: The Taiwanese election map shares similarities with election maps in other democracies, such as the United States and the United Kingdom, in terms of its use of colors to represent different political parties and its ability to highlight regional and demographic differences. However, the specific political context and historical background of Taiwan make its election map unique.
Tips:
- Pay attention to the colors and symbols used on the map. Each color typically represents a specific political party, and symbols can indicate the winner of a particular election.
- Compare the map to previous elections. This can help identify shifts in political power and trends in voter preferences.
- Consider the demographic and geographic factors that may influence electoral outcomes. This can provide a deeper understanding of the political landscape.
- Consult with political analysts and experts. They can provide valuable insights into the interpretation of the map and the factors influencing Taiwanese politics.
Conclusion:
The Taiwanese election map serves as a powerful tool for understanding the complex political landscape of the island nation. It reflects the historical evolution of Taiwanese politics, the ongoing divide between the KMT and DPP, and the various factors influencing electoral outcomes. By analyzing the map and considering the broader political context, individuals can gain valuable insights into the dynamics of Taiwanese politics and its implications for the future of the island.



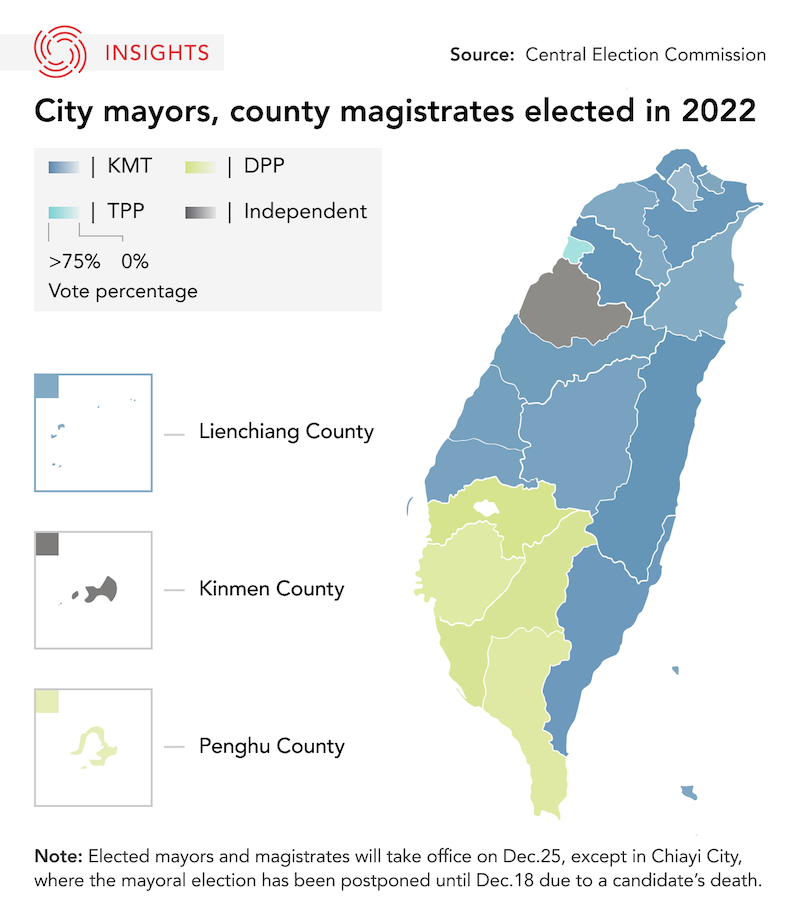


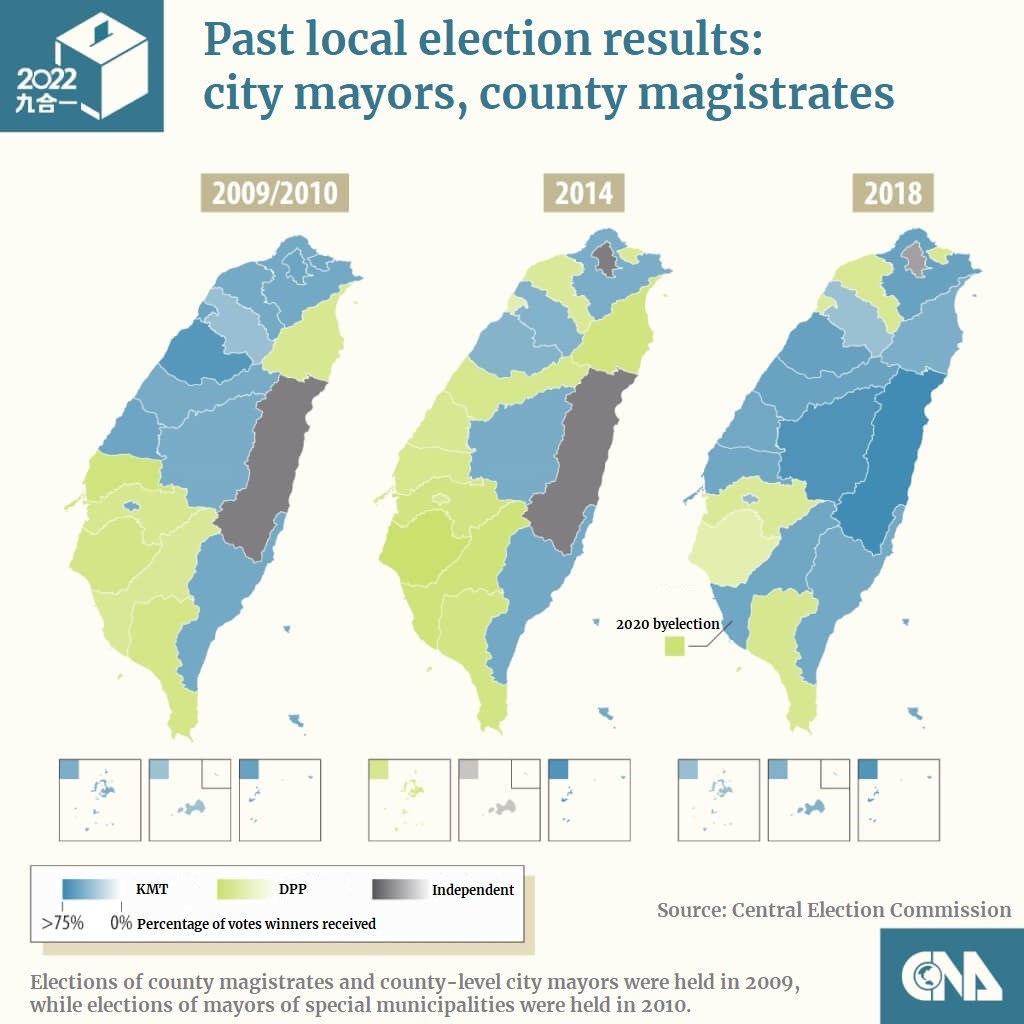
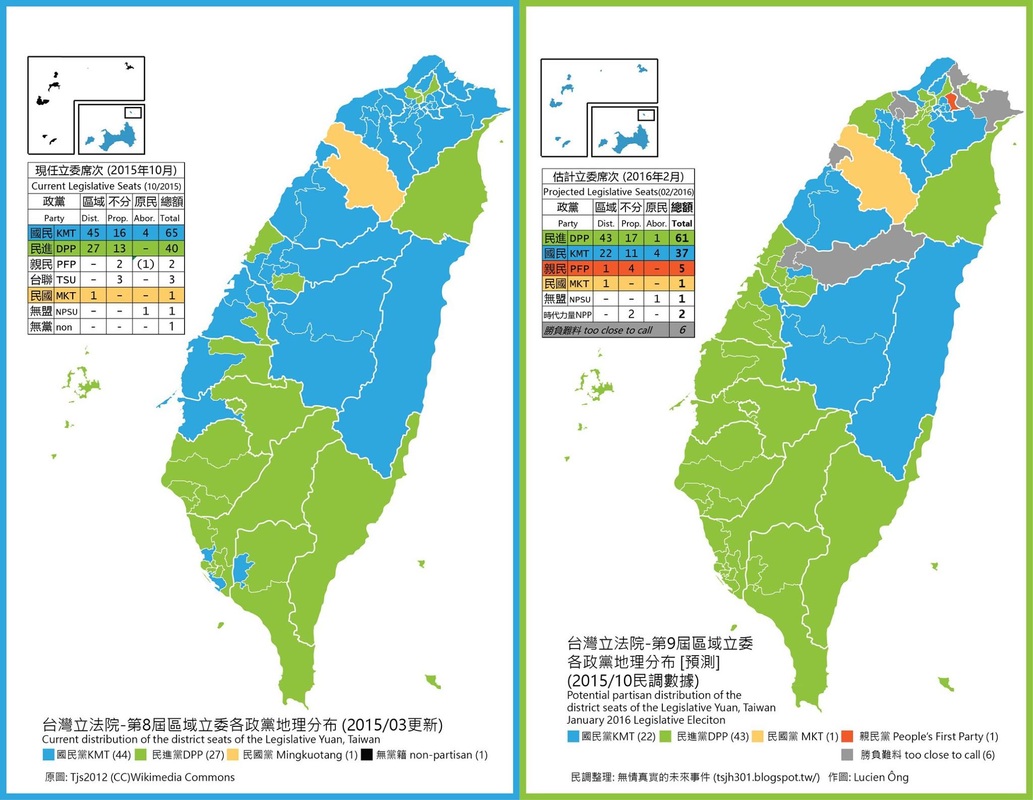
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Taiwanese Election Map: A Visual Representation of Political Power and Identity. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
