The Unsung Hero of the Engine: Understanding the 2002 Tahoe’s Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
Related Articles: The Unsung Hero of the Engine: Understanding the 2002 Tahoe’s Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Unsung Hero of the Engine: Understanding the 2002 Tahoe’s Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Unsung Hero of the Engine: Understanding the 2002 Tahoe’s Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor

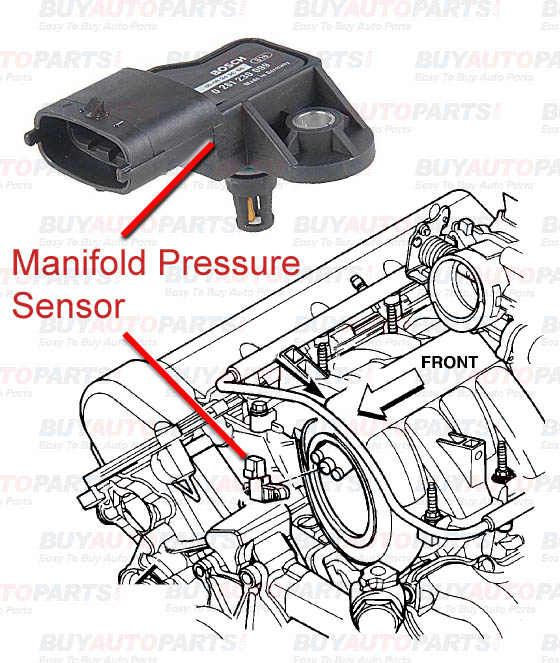
The 2002 Chevrolet Tahoe, a popular SUV known for its ruggedness and spaciousness, relies on a complex network of sensors and actuators to ensure smooth and efficient operation. Among these crucial components, the Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor plays a vital role in regulating engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions.
The MAP Sensor: A Vital Link in the Engine Control System
The MAP sensor, a small, cylindrical device typically located in the intake manifold, measures the absolute pressure within the intake manifold. This pressure, which reflects the amount of air entering the engine, is a critical parameter for the engine control unit (ECU). The ECU utilizes this information to calculate the optimal air-fuel ratio, ignition timing, and other crucial engine parameters.
How the MAP Sensor Works
The MAP sensor operates on the principle of piezoresistive technology. A diaphragm within the sensor is sensitive to pressure changes. When the pressure within the intake manifold increases, the diaphragm deflects, altering the electrical resistance within the sensor. This change in resistance is then translated into a voltage signal that is sent to the ECU.
The MAP Sensor’s Role in Engine Performance
The MAP sensor’s influence extends across various aspects of engine performance:
- Fuel Efficiency: The ECU uses the MAP sensor readings to determine the optimal amount of fuel to inject into the cylinders. By ensuring an accurate air-fuel mixture, the sensor contributes to efficient fuel consumption.
- Emissions Control: The MAP sensor plays a critical role in minimizing harmful emissions by providing the ECU with precise information for optimizing the combustion process.
- Engine Power and Responsiveness: The MAP sensor data enables the ECU to fine-tune ignition timing, ensuring optimal engine performance and responsiveness across various driving conditions.
- Boost Pressure Control (Turbocharged Engines): In turbocharged engines, the MAP sensor is also used to monitor boost pressure, ensuring proper operation of the turbocharger system.
Signs of a Failing MAP Sensor
A malfunctioning MAP sensor can lead to a range of symptoms, including:
- Engine Stalling or Hesitation: An inaccurate MAP sensor reading can cause the ECU to miscalculate the air-fuel mixture, leading to engine stalling or hesitation.
- Poor Fuel Economy: A faulty sensor can lead to an overly rich or lean air-fuel mixture, resulting in increased fuel consumption.
- Rough Idling: An inaccurate MAP sensor reading can disrupt the engine’s idle speed, causing rough idling.
- Check Engine Light Illumination: A malfunctioning MAP sensor will typically trigger the check engine light, indicating a fault within the engine control system.
- Reduced Engine Power: A faulty MAP sensor can hinder the ECU’s ability to optimize engine performance, leading to a noticeable decrease in power.
Diagnosing a MAP Sensor Fault
Diagnosing a faulty MAP sensor typically involves a combination of:
- Visual Inspection: Check the sensor for any visible damage, loose connections, or signs of corrosion.
- Diagnostic Scan Tool: Using a scan tool, check for any error codes related to the MAP sensor.
- Pressure Testing: Utilize a pressure gauge to verify the sensor’s output against known pressure values.
- Voltage Testing: Use a multimeter to measure the voltage signal output by the sensor under various conditions.
Replacing a Faulty MAP Sensor
Replacing a faulty MAP sensor is a relatively straightforward process that can be accomplished by a qualified mechanic. The process typically involves:
- Locating the MAP Sensor: The MAP sensor is typically located in the intake manifold, easily identifiable by its cylindrical shape and electrical connector.
- Disconnecting the Electrical Connector: Disconnect the electrical connector leading to the sensor.
- Removing the Sensor: Depending on the vehicle model, the sensor may be secured with a bolt or clip.
- Installing the New Sensor: Install the new sensor in the same location, ensuring a secure connection.
- Reconnecting the Electrical Connector: Reconnect the electrical connector to the new sensor.
FAQs Regarding the MAP Sensor
Q: Can I clean a dirty MAP sensor?
A: While cleaning a dirty MAP sensor may seem appealing, it is generally not recommended. The sensor’s internal components are delicate and easily damaged. A thorough cleaning may not always be effective, and attempting to clean the sensor can potentially worsen the problem.
Q: How often should I replace the MAP sensor?
A: MAP sensors are generally quite durable and can last for many years. However, they are subject to wear and tear, and their lifespan can be affected by factors such as environmental conditions and driving habits. If you notice any symptoms of a failing sensor, it’s advisable to have it inspected and replaced as needed.
Q: Can I drive with a faulty MAP sensor?
A: While it may be possible to drive with a faulty MAP sensor for a short period, it’s not recommended. A malfunctioning sensor can lead to reduced engine performance, increased fuel consumption, and potentially damage the engine over time.
Q: What is the cost of replacing a MAP sensor?
A: The cost of replacing a MAP sensor varies depending on the vehicle make and model, as well as the labor costs in your area. However, the sensor itself is typically inexpensive, while the labor cost may be more significant.
Tips for Maintaining a Healthy MAP Sensor
- Regularly Inspect the Sensor: Visually inspect the sensor for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections during routine maintenance checks.
- Keep the Intake Manifold Clean: A clean intake manifold helps to prevent dirt and debris from accumulating on the MAP sensor.
- Avoid Using Low-Quality Fuel: Using low-quality fuel can lead to deposits forming on the sensor, potentially affecting its performance.
- Address Engine Problems Promptly: Ignoring engine problems can lead to issues that may affect the MAP sensor’s functionality.
Conclusion
The MAP sensor plays a vital role in ensuring optimal engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions control in the 2002 Chevrolet Tahoe. Understanding its function, recognizing potential signs of failure, and taking proactive measures for maintenance can help to prolong the sensor’s lifespan and ensure the vehicle operates at its best.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Unsung Hero of the Engine: Understanding the 2002 Tahoe’s Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
