The Unsung Hero of Your Engine: Unveiling the Importance of the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
Related Articles: The Unsung Hero of Your Engine: Unveiling the Importance of the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Unsung Hero of Your Engine: Unveiling the Importance of the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Unsung Hero of Your Engine: Unveiling the Importance of the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Unsung Hero of Your Engine: Unveiling the Importance of the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
- 3.1 Understanding the MAP Sensor: A Window into the Engine’s Breathing
- 3.2 The MAP Sensor’s Impact on Engine Performance: Beyond Simple Measurement
- 3.3 Recognizing the Signs of a Faulty MAP Sensor: A Delicate Balancing Act
- 3.4 Troubleshooting and Replacing a Faulty MAP Sensor: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 3.5 FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about the MAP Sensor
- 3.6 Tips for Maintaining Your MAP Sensor: Ensuring Optimal Performance
- 3.7 Conclusion: The Unsung Hero of Engine Performance
- 4 Closure
The Unsung Hero of Your Engine: Unveiling the Importance of the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor

In the intricate symphony of a modern car engine, numerous components work in harmony to ensure smooth and efficient operation. While the spark plugs ignite the fuel, the injectors deliver the precise amount, and the crankshaft transforms the combustion into motion, a lesser-known but equally crucial component silently monitors the engine’s breathing – the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor (MAP sensor).
This small, often overlooked device plays a vital role in determining the engine’s air intake, influencing the fuel-air mixture and ultimately affecting the power output, fuel efficiency, and emissions. Its function, however, goes far beyond simply measuring pressure.
Understanding the MAP Sensor: A Window into the Engine’s Breathing
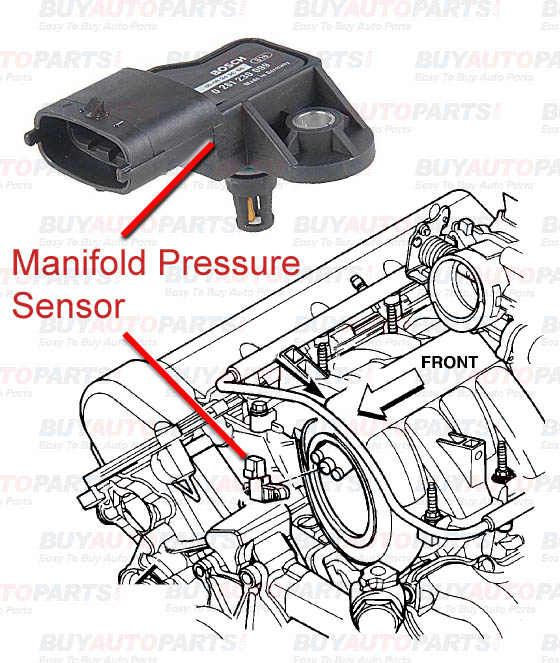
The MAP sensor, typically located within the intake manifold, acts as a pressure transducer, converting the absolute pressure inside the manifold into an electrical signal. This signal is then sent to the engine control unit (ECU), which uses it to calculate critical parameters for engine operation.
Here’s a simplified breakdown of how the MAP sensor works:
- Air Intake: As the engine draws in air through the intake manifold, the pressure inside the manifold changes based on the throttle position and engine speed.
- Pressure Measurement: The MAP sensor, utilizing a diaphragm and a pressure-sensitive element, detects this pressure change.
- Signal Conversion: The sensor translates the pressure variation into an electrical signal, typically a voltage, proportional to the pressure.
- ECU Interpretation: The ECU receives this signal and uses it to determine the amount of air entering the engine.
The MAP Sensor’s Impact on Engine Performance: Beyond Simple Measurement
The MAP sensor’s role transcends merely measuring air intake; it serves as a vital input for the ECU to make critical adjustments, impacting various aspects of engine performance:
1. Fuel-Air Ratio Optimization: The ECU uses the MAP sensor data to calculate the optimal fuel-air ratio for combustion. This ensures efficient burning of the fuel, maximizing power output and minimizing emissions. A faulty MAP sensor can lead to a rich or lean fuel mixture, resulting in poor performance, rough idling, and increased fuel consumption.
2. Ignition Timing Adjustment: The MAP sensor also provides data for precise ignition timing. By understanding the air intake, the ECU can adjust the ignition timing to ensure optimal combustion and power delivery. A malfunctioning MAP sensor can lead to improper ignition timing, resulting in engine knocking, misfires, and potential damage.
3. Throttle Response Enhancement: The MAP sensor plays a crucial role in providing smooth and responsive throttle control. By sensing the pressure changes during acceleration, the ECU can adjust fuel delivery and ignition timing accordingly, ensuring a seamless power delivery.
4. Emissions Control: The MAP sensor contributes significantly to reducing harmful emissions. By providing accurate air intake information, the ECU can fine-tune the fuel-air mixture, minimizing the production of pollutants like carbon monoxide and unburnt hydrocarbons.
Recognizing the Signs of a Faulty MAP Sensor: A Delicate Balancing Act
While the MAP sensor silently performs its crucial role, it can also develop issues over time. Recognizing these issues early can prevent further damage and ensure optimal engine performance.
Here are some common signs of a malfunctioning MAP sensor:
- Rough Idling: A faulty MAP sensor can lead to erratic idle speeds, stalling, or a rough running engine.
- Poor Acceleration: The engine might struggle to accelerate, feeling sluggish or lacking power.
- Increased Fuel Consumption: An inaccurate air intake reading can lead to a rich fuel mixture, increasing fuel consumption.
- Engine Misfires: A faulty sensor can cause misfires, resulting in a rough engine operation and potential damage.
- Check Engine Light: A malfunctioning MAP sensor will often trigger the check engine light, accompanied by a diagnostic code related to the sensor.
Troubleshooting and Replacing a Faulty MAP Sensor: A Step-by-Step Guide
If you suspect a faulty MAP sensor, it’s essential to diagnose the problem accurately before replacing the sensor.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to troubleshooting and replacing a MAP sensor:
- Check the Diagnostic Codes: Using an OBD-II scanner, check for any diagnostic codes related to the MAP sensor. These codes can pinpoint the specific issue with the sensor.
- Visual Inspection: Inspect the MAP sensor for any visible damage, such as cracks, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Vacuum Leak Test: Check for vacuum leaks in the intake manifold, as these can affect the MAP sensor readings.
- Pressure Test: If the sensor is suspected to be faulty, use a pressure gauge to check the actual pressure reading against the sensor’s output.
- Replacement: If the sensor is confirmed to be faulty, disconnect the electrical connector and replace the sensor with a new one. Ensure you purchase a compatible sensor for your specific vehicle model.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about the MAP Sensor
1. Can I clean a MAP sensor?
While cleaning a MAP sensor might seem tempting, it’s generally not recommended. The sensor’s delicate internal components can be easily damaged during cleaning. If the sensor is dirty, replacing it is usually the best course of action.
2. What is the difference between a MAP sensor and a MAF sensor?
Both MAP and MAF sensors measure air intake, but they operate differently. The MAP sensor measures the pressure inside the intake manifold, while the MAF sensor measures the mass airflow entering the engine. Some vehicles use both sensors for more accurate air intake measurement.
3. How often should I replace my MAP sensor?
The lifespan of a MAP sensor varies depending on the vehicle and driving conditions. However, it’s typically recommended to replace it every 100,000 miles or if it starts showing signs of malfunction.
4. Can a faulty MAP sensor cause a car to stall?
Yes, a faulty MAP sensor can cause a car to stall, especially at idle. An inaccurate air intake reading can lead to an incorrect fuel-air mixture, causing the engine to stall.
5. What are the consequences of ignoring a faulty MAP sensor?
Ignoring a faulty MAP sensor can lead to various problems, including poor fuel economy, reduced engine performance, increased emissions, and potential engine damage.
Tips for Maintaining Your MAP Sensor: Ensuring Optimal Performance
While the MAP sensor is a relatively robust component, following these tips can help ensure its longevity and optimal performance:
- Regular Maintenance: As part of routine maintenance, inspect the MAP sensor for any visible damage or dirt buildup.
- Clean Intake System: Regularly clean the air filter and intake manifold to prevent dirt and debris from reaching the sensor.
- Avoid Harsh Chemicals: Avoid using harsh chemicals or cleaners near the MAP sensor, as they can damage the sensor’s delicate components.
- Professional Inspection: If you notice any signs of a malfunctioning MAP sensor, have it inspected by a qualified mechanic.
Conclusion: The Unsung Hero of Engine Performance
The MAP sensor, despite its inconspicuous nature, plays a vital role in maintaining optimal engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions. Its accurate measurement of air intake provides the ECU with essential information to fine-tune fuel delivery, ignition timing, and other critical engine functions.
By understanding the importance of the MAP sensor and recognizing the signs of a malfunction, car owners can ensure their vehicles run smoothly and efficiently, minimizing fuel consumption and environmental impact. Regular maintenance and timely replacement of a faulty sensor can prevent potential engine damage and ensure a long and healthy life for your vehicle.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Unsung Hero of Your Engine: Unveiling the Importance of the Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
